Microstrip antenna RFID label-based array strain sensor
An RFID tag and strain sensor technology, which is applied to antennas, antenna parts, antenna grounding devices, etc., can solve the problems of complex monitoring structure, inability to guarantee accuracy, time-consuming and labor-intensive, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
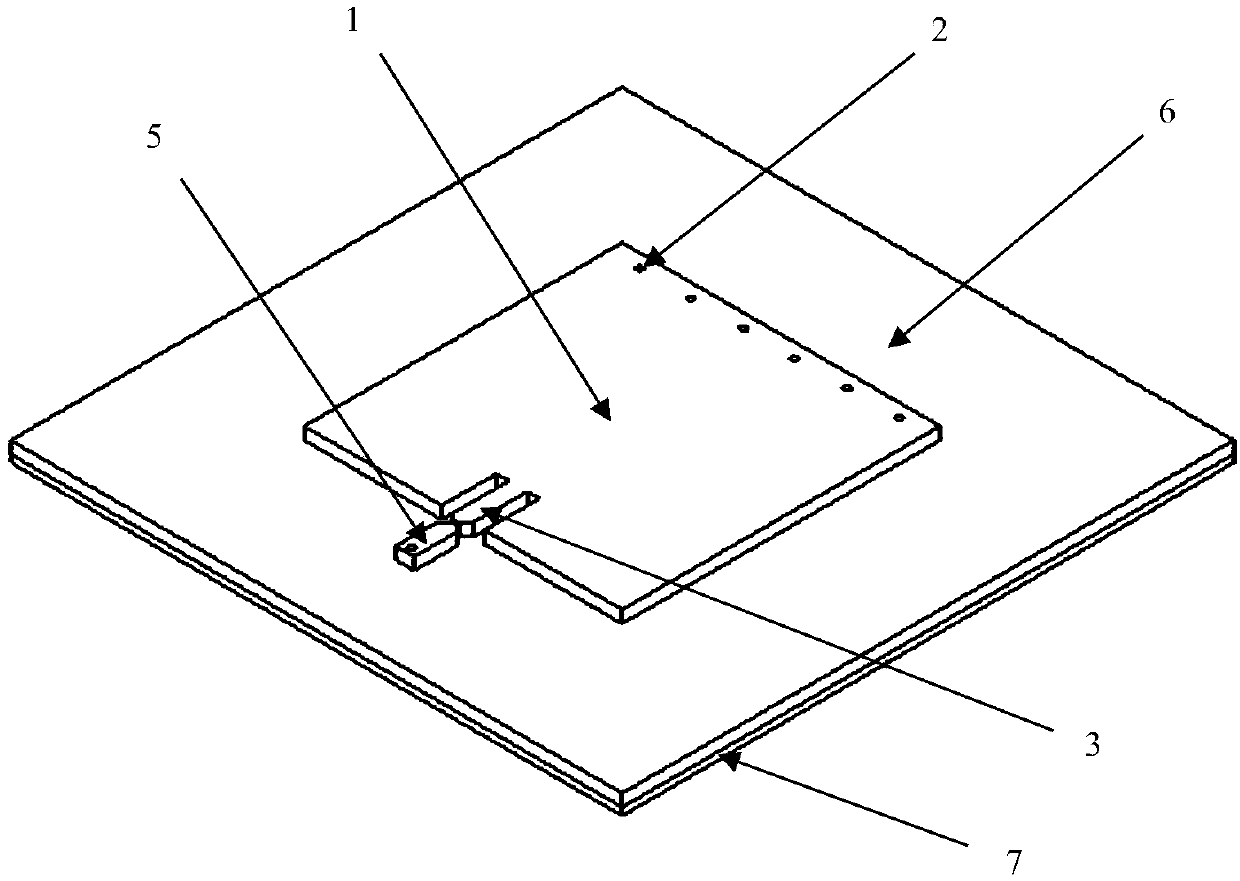
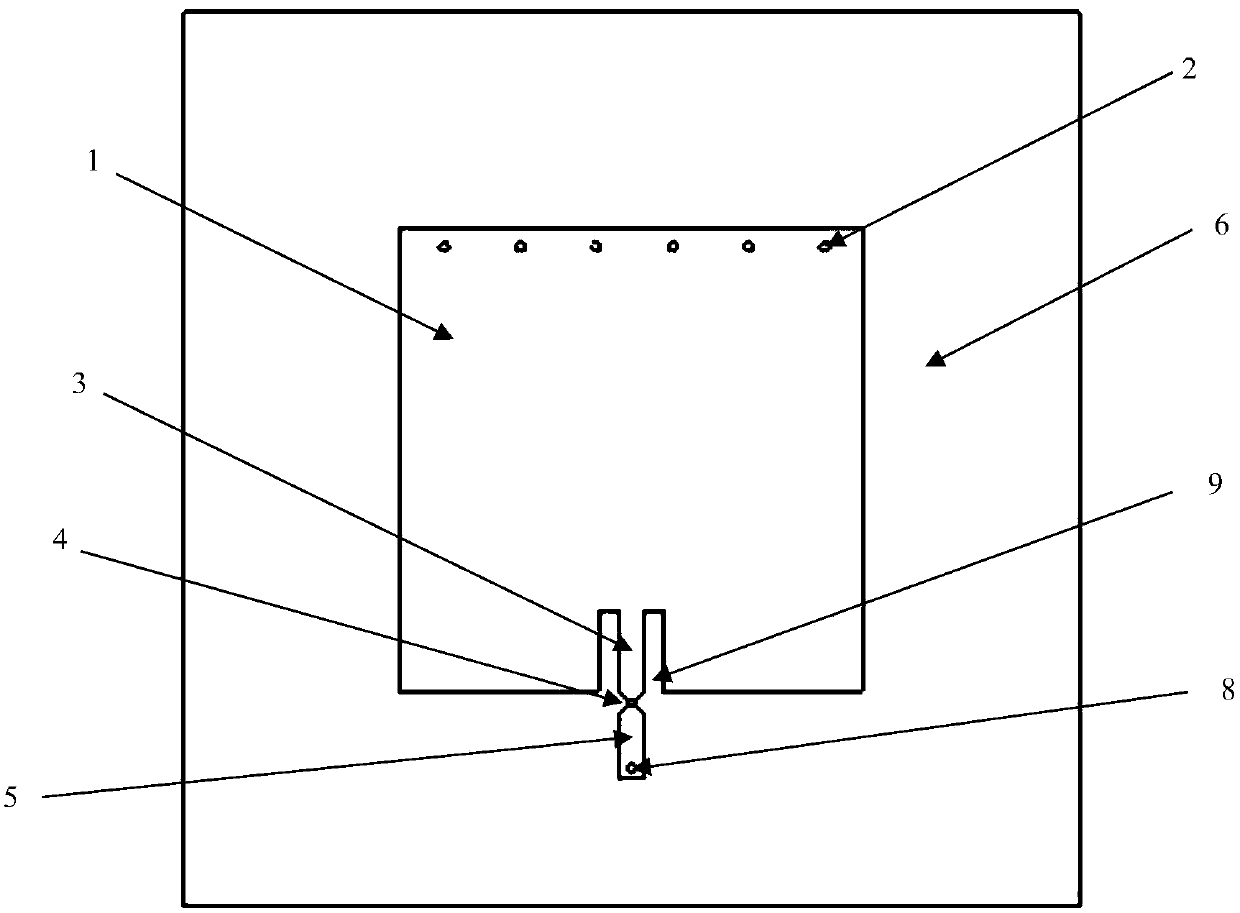
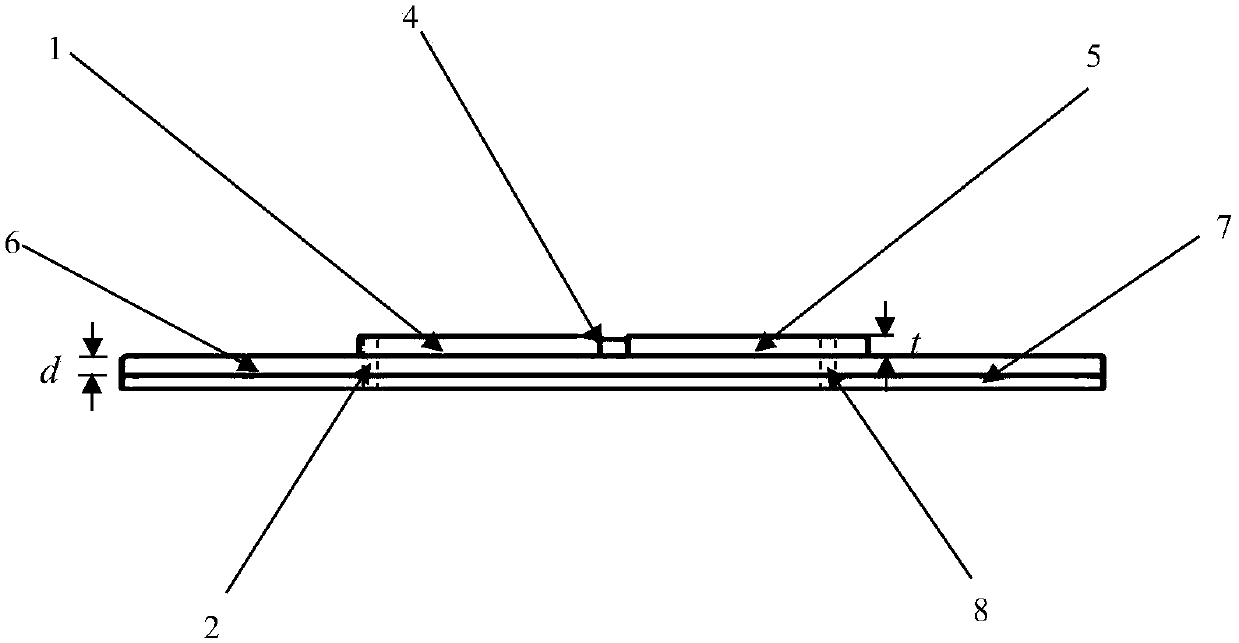
[0017] Such as Figure 1-5 As shown, the material of the dielectric base layer (6) is Rogers high-frequency board, the dielectric constant is 2.2, and the two conductor layers on the sensor include the metal radiation surface (1), the short-circuit wall (2), the first feeder (3), and the chip (4), the second feeder (5), the dielectric base layer (6), the metal base plate (7), and the short-circuit hole (8) all use copper foil as the material, and the main parameter dimensions of the sensor are shown in Table 1 below:
[0018] Table 1 sensor size parameter table
[0019]
[0020]
[0021] The tag antenna is designed in the form of a microstrip antenna to receive the energy from the reader, the energy is transmitted to the tag chip and activates the sensor (the minimum energy to activate the sensor is called the activation threshold of the tag sensor), when the tag antenna is at the resonant frequency , the sensor has the highest energy receiving efficiency, so the activa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com