Feature extraction method for facial expression recognition based on Weber multi-directional descriptor
A facial expression recognition and feature extraction technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve the problems of high time complexity of the feature extraction algorithm, asymmetry of the algorithm, and reduced recognition rate, so as to improve the recognition rate of facial expression and improve the recognition rate. Effects of stability and generalizability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0037] Embodiments of the present invention are described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings:
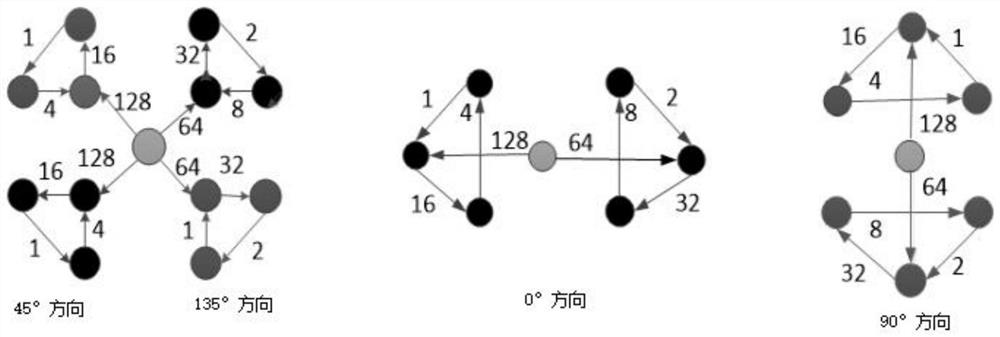
[0038] A feature extraction method for facial expression recognition based on Weber's multi-directional descriptor, comprising the following steps:
[0039] Step 1: Transform the facial expression image into a Gabor feature map of 5 scales and 8 directions through Gabor wavelet transform, and fuse the Gabor features of the same scale and 8 directions to obtain a fusion map of facial expressions at different scales, and The facial expression fusion map at each scale is divided into non-overlapping sub-blocks.
[0040] In this step, the Gabor wavelet transform uses a Gabor filter, and the calculation formula of the kernel function G(k, x, y, θ) of the Gabor filter is as follows:
[0041]
[0042]Among them, (x, y) represents the central pixel point, θ represents the direction of the Gabor kernel function, k u,v Is the center frequency of the fil...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com