Catalyst and its preparation method and application
A technology of catalyst and hydrogenation reaction, applied in the direction of catalyst activation/preparation, catalyst, carbon compound catalyst, etc., can solve the problem of low ethylene selectivity and achieve high acetylene conversion rate and ethylene selectivity effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
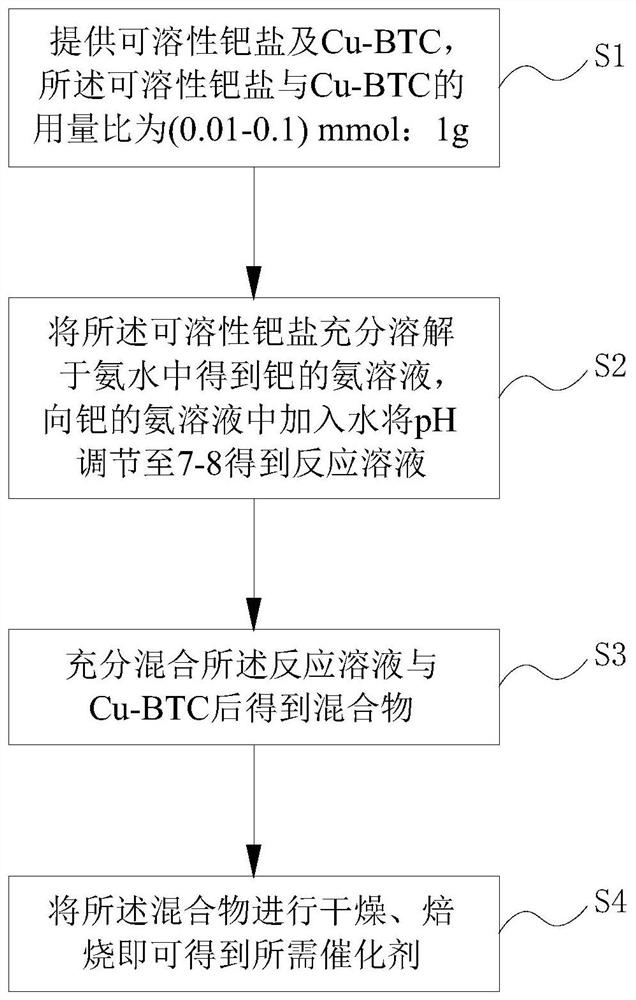
[0029] Such as figure 1 Shown, a kind of preparation method of catalyst comprises:
[0030] Step S1: providing soluble palladium salt and Cu-BTC, the dosage ratio of the soluble palladium salt and Cu-BTC is (0.01-0.1) mmol: 1g;
[0031] Step S2: fully dissolving the soluble palladium salt in ammonia water to obtain an ammonia solution of palladium, adding water to the ammonia solution of palladium to adjust the pH to 7-8 to obtain a reaction solution;
[0032] Step S3: fully mixing the reaction solution and Cu-BTC to obtain a mixture;
[0033] Step S4: drying and calcining the mixture to obtain the desired catalyst. The catalyst can be recorded as Pd-Cu / C catalyst.
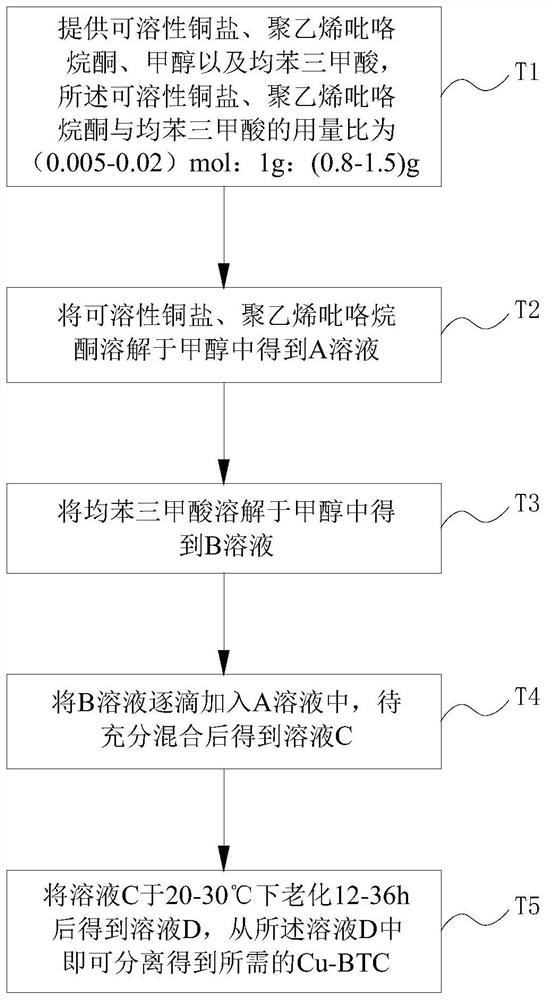
[0034] In the preparation method of the catalyst, the soluble palladium salt referred to in step S1 may be palladium chloride, palladium nitrate and the like. Cu-BTC can be purchased directly or prepared by yourself. Preferably, the preparation method of the catalyst further includes the preparation of Cu-BTC...
Embodiment 2
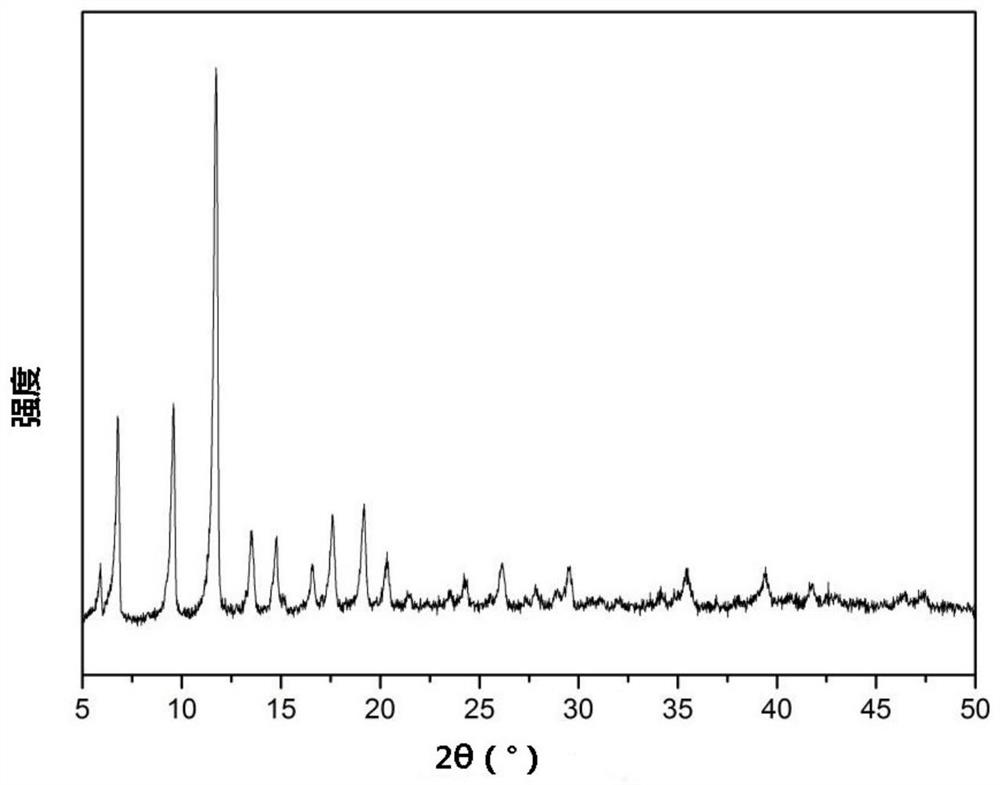
[0068] A catalyst, prepared by the preparation method of the catalyst in Example 1. as mentioned above and Figure 6-8 It can be seen that the catalyst has a quasi-octahedral structure, and the distribution is uniform and the size is uniform and regular. In addition, the surface of the catalyst is covered with pores and small round particles. The BET specific surface area of the catalyst is 100-150m2 / g. The average pore diameter of the catalyst is 10-25nm.
Embodiment 3
[0070] An application of the catalyst, the catalyst in the second embodiment is applied to remove acetylene from ethylene, and the hydrogenation reaction of the acetylene is catalyzed to remove it. It can be understood that the content of acetylene is less, and the purpose of this catalyst is, one, to remove acetylene as much as possible, that is, hope to obtain a higher conversion rate of acetylene; second, to obtain more ethylene, that is, to use unnecessary Acetylene is converted to ethylene, that is, a higher ethylene selectivity is expected.
[0071] Using this catalyst to remove acetylene from ethylene, the results are shown in the table below:
[0072] temperature(℃) Acetylene conversion rate (%) Ethylene selectivity (%) 75 45 96 100 70 92 125 86 84 150 90 80
[0073] The reaction condition is 2.91vol% H 2 ,0.97vol%C 2 h 2 and 96.11vol%C 2 h 4
[0074] It can be seen from the above table that the catalyst has better acety...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com