Simultaneous estimation of respiratory mechanics and patient effort via parametric optimization
A parametric, respiratory muscle technology, applied in the respiratory field, can solve problems such as interference with the mechanical ventilation mode of treatment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
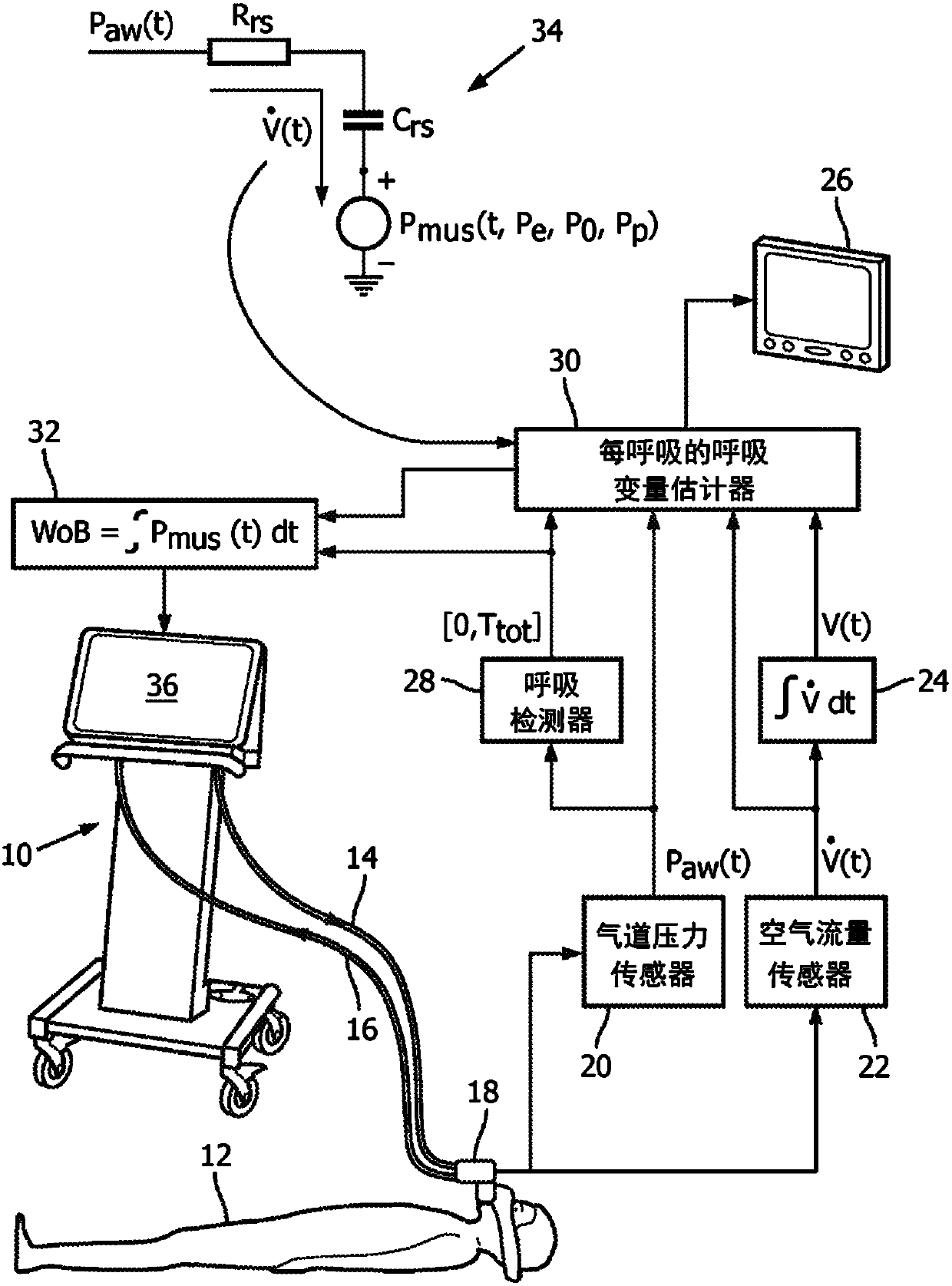
[0021] In the methods disclosed herein, the respiratory muscle pressure P mus (t), respiratory system resistance R rs and respiratory compliance C rs or Elastic E rs =1 / C rs Simultaneously estimated on a breath-by-breath basis by the formula for evaluating lung motion:
[0022]
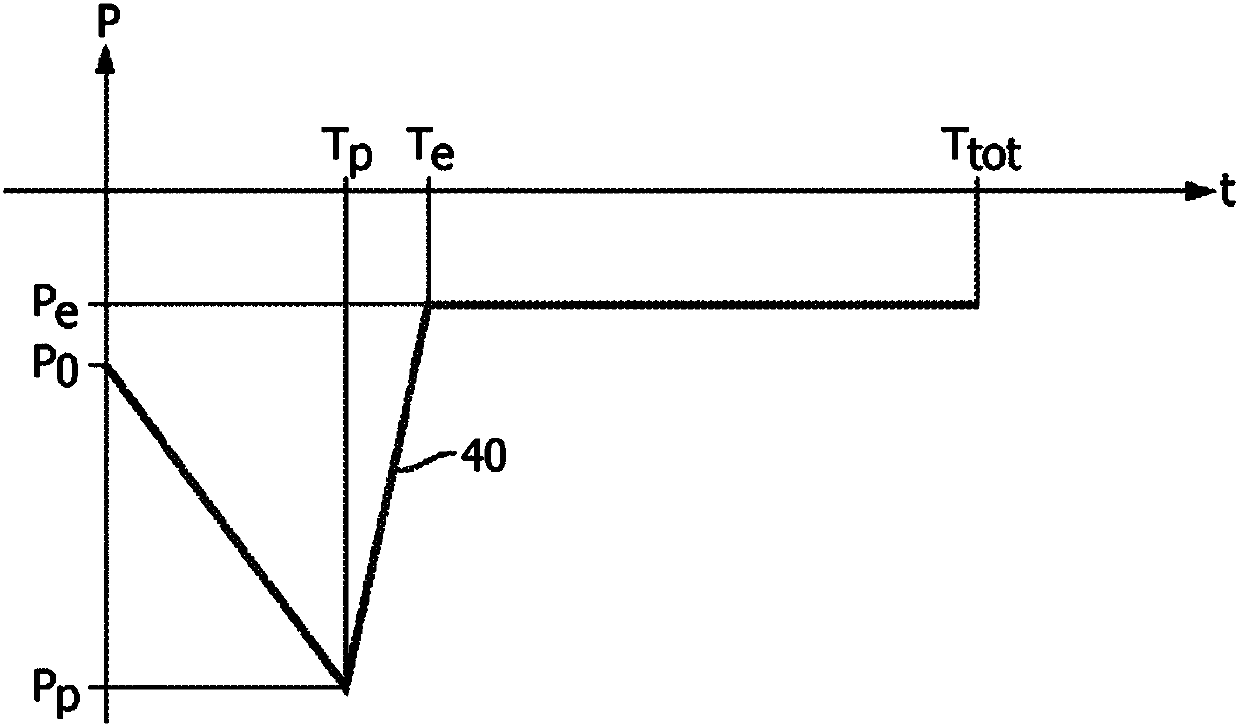
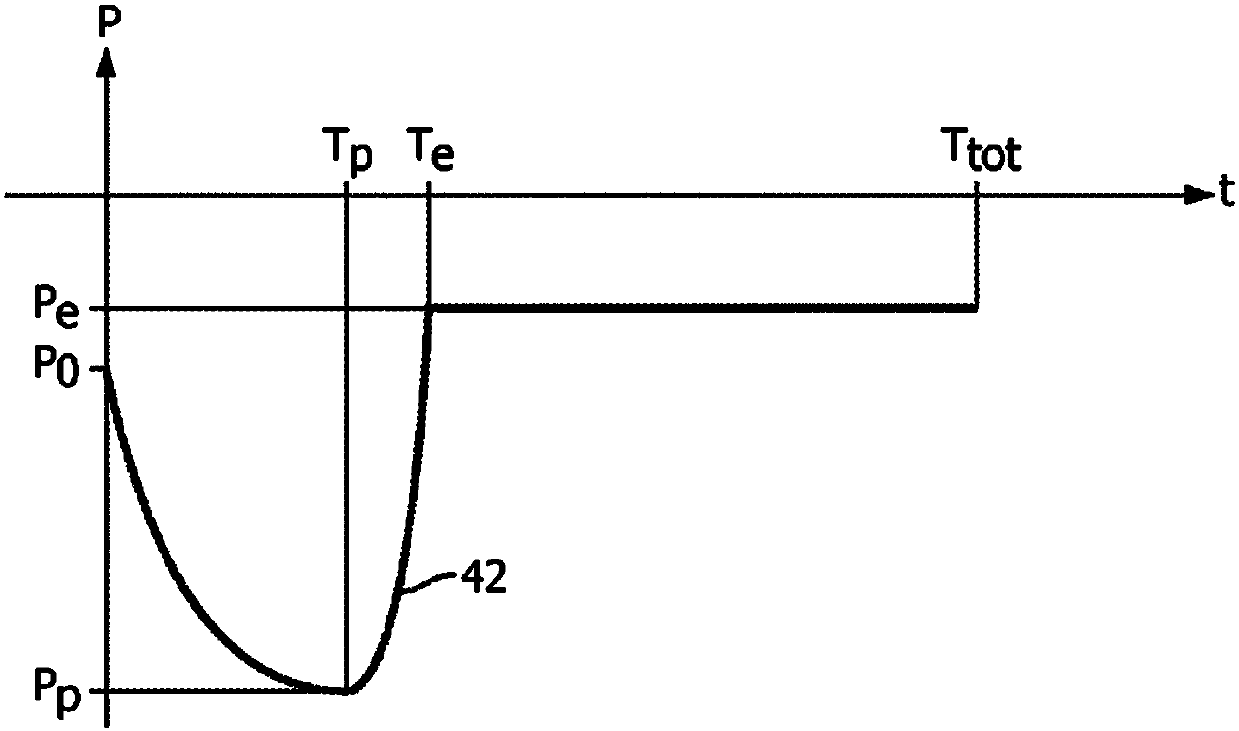
[0023] Among them, P aw (t) is the measured airway pressure, is the measured airway flow, V(t) is the volume of air breathed, that is and P 基线 is a constant. In performing this simultaneous estimation, the airway pressure P aw (t) and airway flow is sampled. Evaluating N samples requires N+2 unknowns (including N P mus The value of (t) and R rs and C rs value) to solve. This is an underdetermined problem because the number of data points (N) is less than the number of unknowns (N+2).
[0024] In addition to the fact that the problem is underdetermined, another challenge recognized in this paper is that the measured airway pressure P aw (t) and airway flow Can be noisy, especial...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com