A process for warm forming an age hardenable aluminum alloy in t4 temper
An age-hardening, aluminum alloy technology, applied in the field of aluminum alloys, can solve problems such as adverse effects on the ability of hardened parts, reduced formability, etc., to achieve the effect of improving fuel efficiency and reducing vehicle weight
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0078] High temperature tensile test
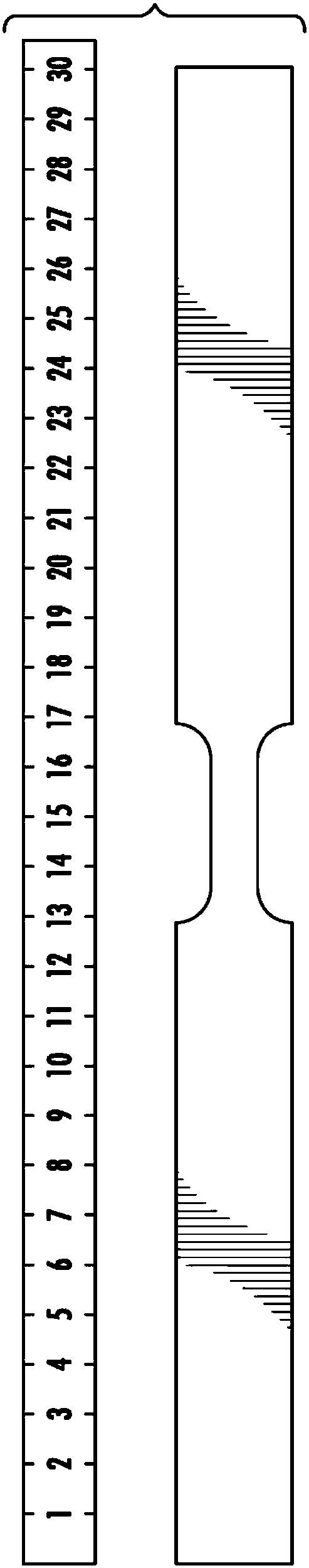
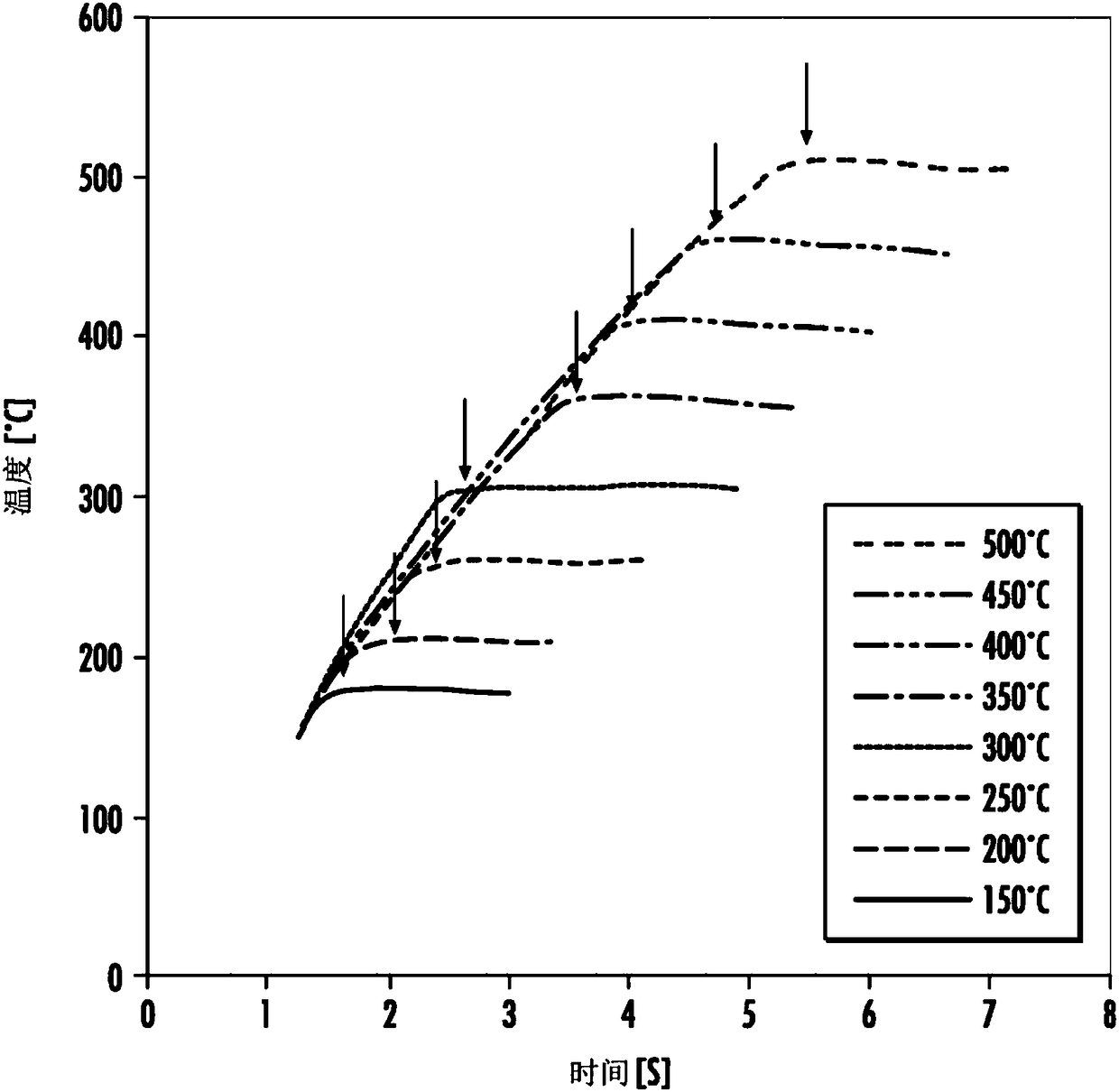
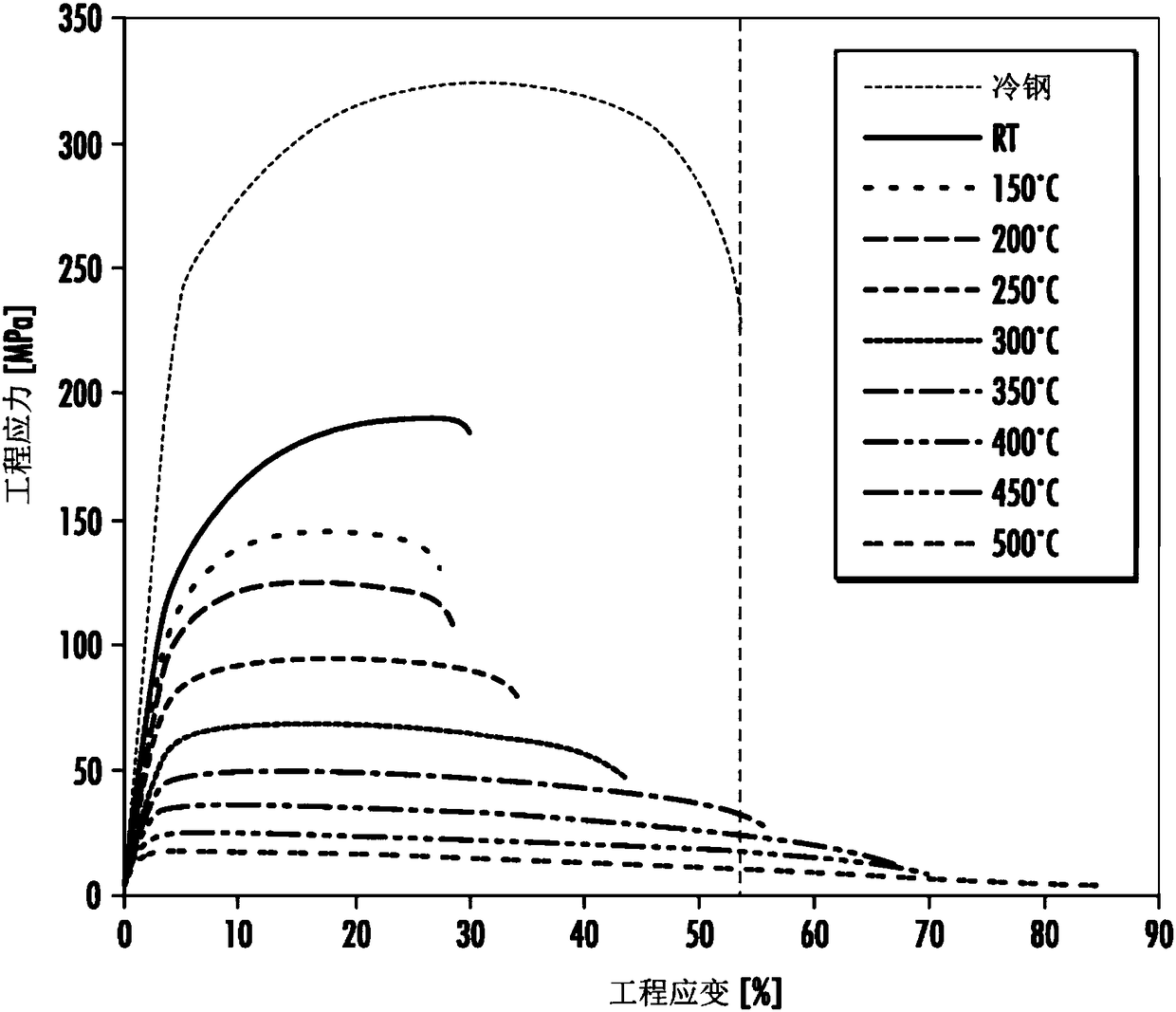
[0079] High temperature tensile tests of AA6016 alloy samples were carried out. The test sample is a sample of formed AA6016 alloy, such as figure 1 shown in . These test pieces had a thickness of 1.2 mm. For the high temperature test, the samples were heated to various temperatures by induction heating at a heating rate of 90 °C / s. A pyrometer was used to measure the temperature of each sample. During the tensile test, maintain the specified test temperature for each specimen. figure 2 The heating curves of the AA6016 samples before and during the tensile test are shown, where the arrows indicate that the tensile test was started once these samples reached the target temperature. AA6016 coupons and steel coupons (DX56D (low carbon steel) from Voestalpine, Linz, Austria) were also tested at room temperature. Steel samples tested at room temperature were image 3 is referred to as "cold steel", while AA6016 specimens tested at roo...
example 2
[0082] Tensile test after heat treatment
[0083] Tensile tests of AA6016 alloy samples after heat treatment were carried out. The test sample is a sample of formed AA6016 alloy, such as figure 1 shown in . These test pieces had a thickness of 1.2 mm. For post-heat treatment tests, the samples were heated to various temperatures by induction heating at a heating rate of 90°C / s, cooled in water ("water quenching"), then quenched and aged at room temperature for one week. Samples of AA6016 maintained at room temperature ("room temperature samples") were also tested for comparison. Figure 4 The stress-strain curves of the AA6016 specimens after heat treatment are shown. Figure 4 The stress-strain curves after heat treatment shown in have roughly similar shape and magnitude and are also similar to the stress-strain curves of the room temperature specimen (ref T4). Figure 4 The stress-strain curves shown in show that the heat treatment employed in the tests did not alter t...
example 3
[0086] Tensile test after heat treatment of samples heated at different heating rates
[0087] Tensile tests after heat treatment of AA6016 alloy samples heated at different heating rates were carried out. The test sample is a sample of AA6016 alloy, such as figure 1 shown in . These test pieces had a thickness of 1.2 mm. As far as the test after heat treatment is concerned, by induction heating at a heating rate of 90 °C / s ( Figure 7 The upper set of curves in , and Figure 8 left histogram in each group) or a heating rate of 3°C / s ( Figure 7 The lower set of curves in , and Figure 8 Right histograms in each group in ) These samples were heated to (at Figure 7 and Figure 8 referred to as "HT") various temperatures, cooled in water (i.e., referred to as "WQ" for water quenching), naturally aged at room temperature for up to a week, heat treated at 180°C for up to 10 hours, then cooled to room temperature. Also for AA6016 kept at room temperature (in Figure 7 a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| ultimate tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| ultimate tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com