Battery pack welding execution device, robot and battery pack welding production workstation
A welding robot and actuator technology, applied in welding equipment, resistance welding equipment, resistance electrode holders, etc., can solve the problems of unfavorable batch automatic welding of battery packs and reduce the efficiency of battery pack welding, so as to reduce labor burden and improve automation Degree, mobile and flexible effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
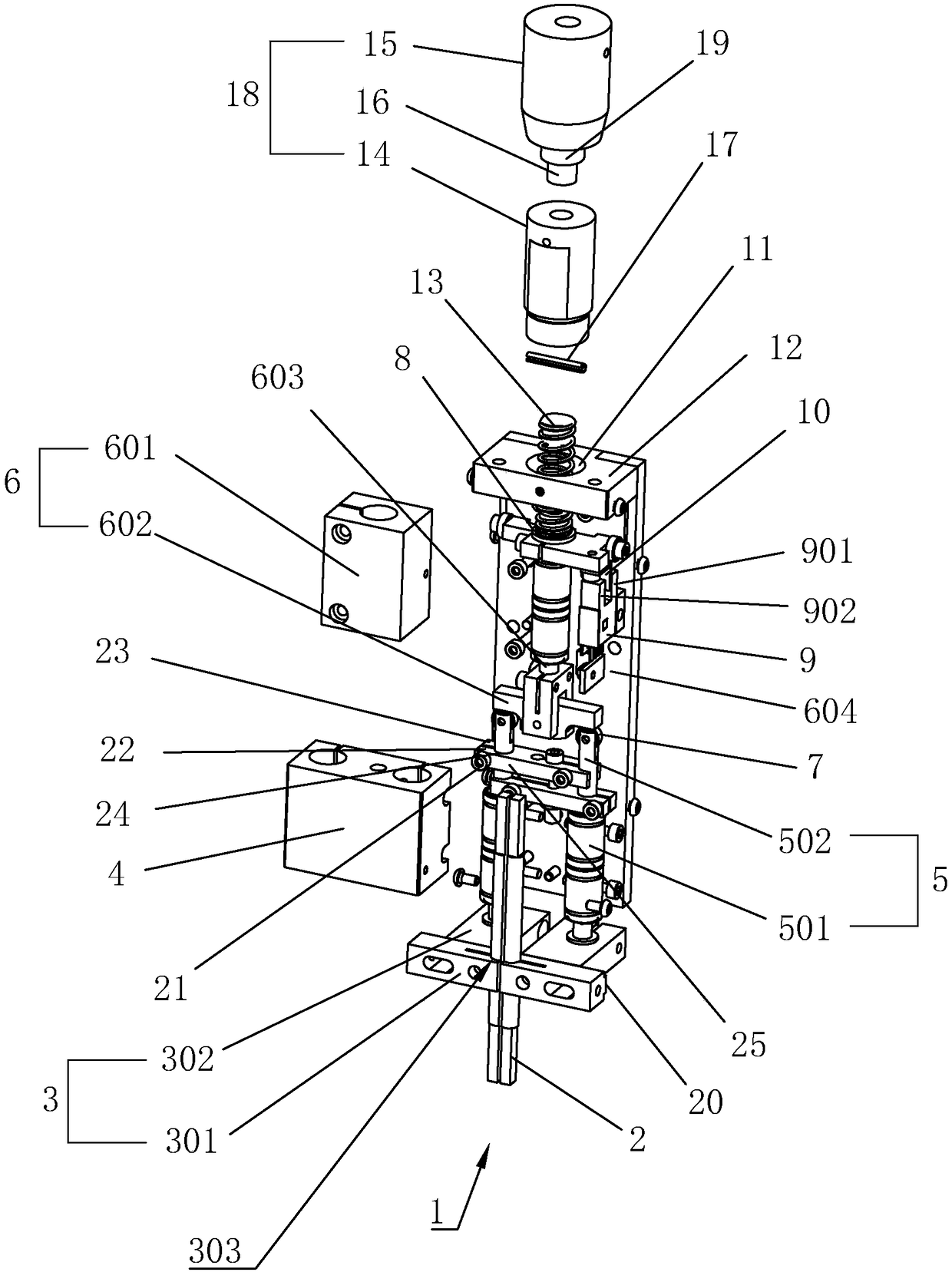
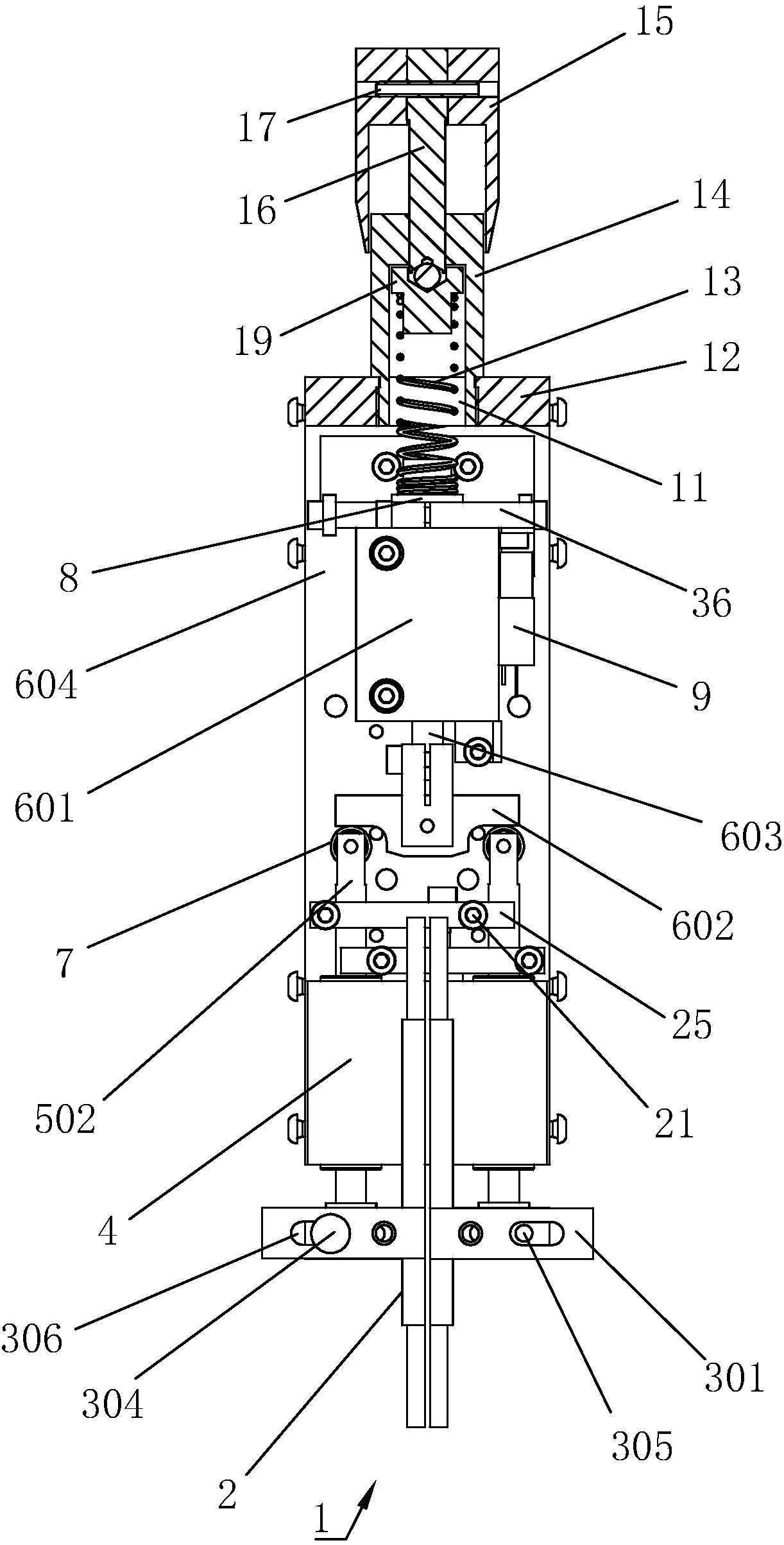
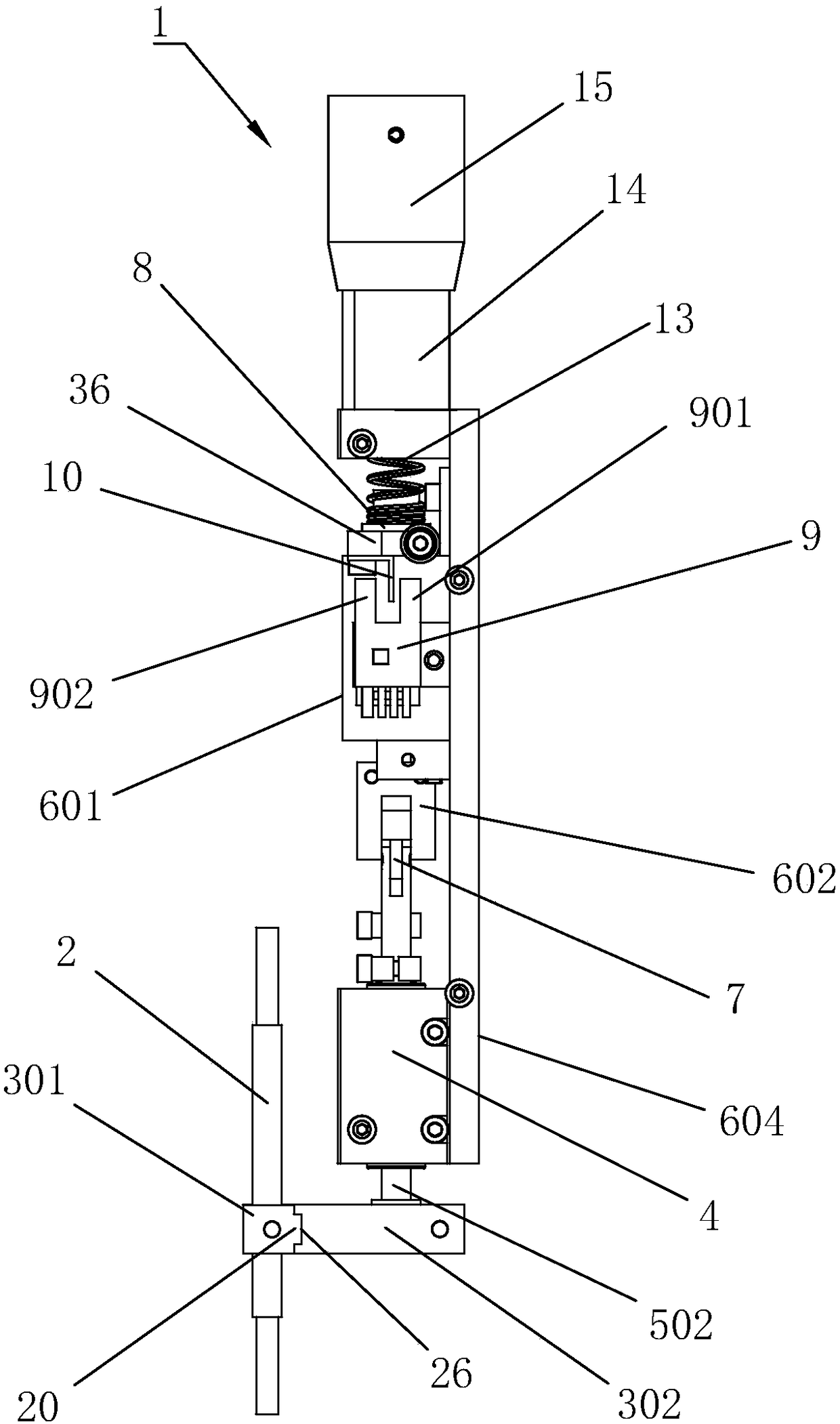
[0038] Embodiment 1: A battery pack welding execution device 1, such as Figure 1 to Figure 3 As shown, it includes an electrode rod 2, a clamp 3 for clamping the electrode rod 2, and a push-down driving mechanism 6 that drives the clamp 3 to move so that the lower end of the electrode rod 2 is pressed on the battery pack. The shape of the electrode rod 2 is a cuboid , the four vertices of its lower end face are welding points that can be contact-welded with the nickel sheet, and the number of clamps 3 can be one or multiple, and each clamp 3 holds at least one electrode rod 2. In this implementation In the example, the number of clamps 3 is preferably two, and each clamp 3 includes an elastic clamping block 301 and a clamping block 302, and each elastic clamping block 301 clamps an electrode rod 2, elastic clamping The block 301 is made of elastic metal material, and there is a clamping groove 303 vertically penetrating through the elastic clamping block 301 on the top, inser...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Embodiment 2: a battery pack welding robot, such as Figure 4 As shown, including the above-mentioned embodiment 1, the battery welding robot includes a six-axis robot 27. The lower end of the willow-axis robot is placed on the ground, and the upper end is a free end. The free end is fixedly connected to the battery pack welding actuator 1. The six-axis robot 27 For the existing six-axis robot 27, the battery pack welding actuator 1 is installed on the six-axis robot 27, and the six-axis robot 27 can drive the battery pack welding actuator 1 to move in multiple directions, so that the six-axis robot 27 can accurately Position it to the position where the battery pack is to be welded.
[0046] The working process of this embodiment is as follows: the six-axis robot 27 is placed in the workshop, and the battery pack welding actuator 1 is controlled by the six-axis robot 27 to move, so that the electrode rod 2 on the battery pack welding actuator 1 can be vertically downwa...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Embodiment 3: A battery pack welding production workstation, such as Figure 5 and Figure 6 As shown, it includes the above-mentioned embodiment 2. In addition, it also includes a frame 30. The frame 30 is provided with a feed delivery mechanism 28 for transferring the battery pack to the six-axis robot 27. The feed delivery mechanism 28 includes a feed delivery mechanism 28. The material conveyor belt 2801 and the feed drive motor (not shown in the figure) driving the feed conveyor belt 2801 drive, the feed drive motor works, and drives the feed conveyor belt 2801 to transmit. The number of battery pack welding robots is two, respectively located in the feed On the left and right sides of the conveyor belt 2801, the battery pack is conveyed between the two battery pack welding robots through the feed conveyor belt 2801, and the two battery pack welding robots can weld the battery pack at the same time, which greatly improves the welding efficiency; rack 30 The output...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com