Phase shift grating of asymmetric structure and DFB semiconductor laser
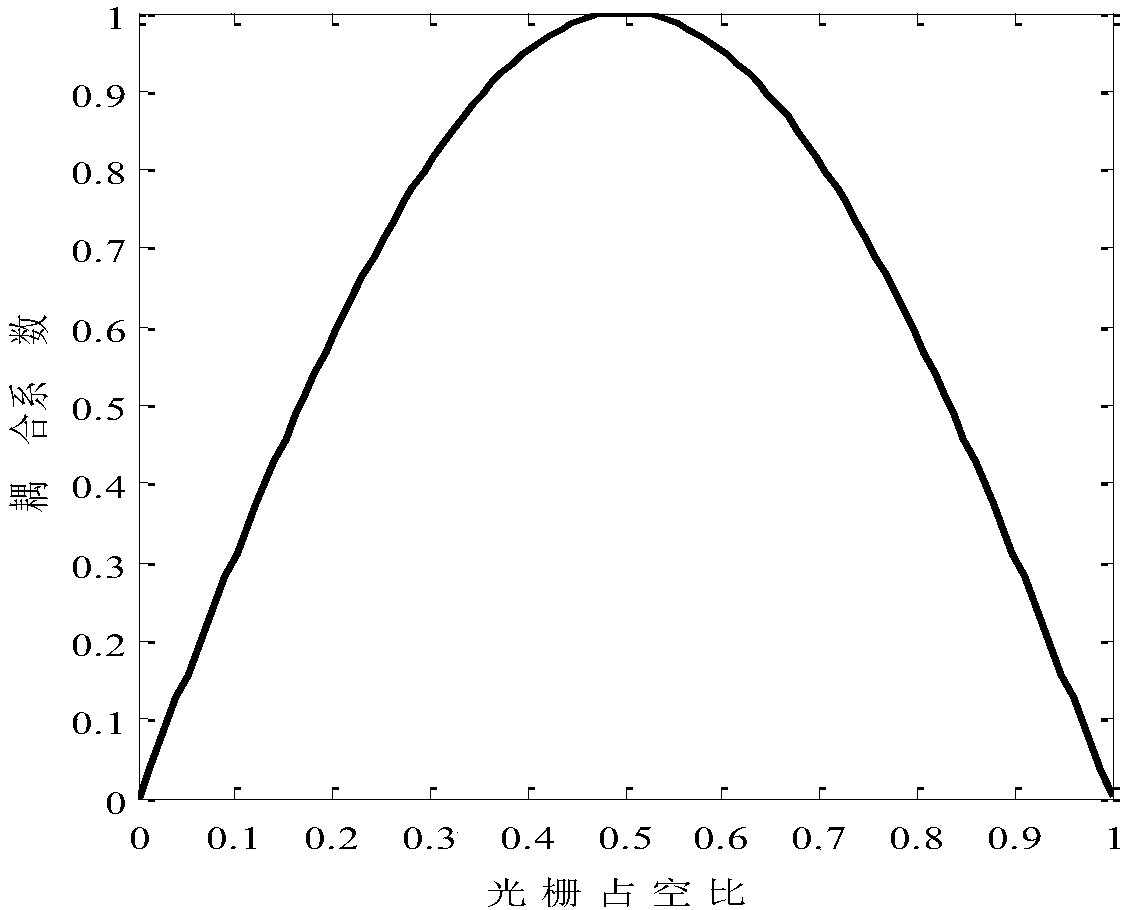
An asymmetric structure, phase-shift grating technology, used in semiconductor lasers, lasers, phonon exciters, etc., can solve the problems of uncontrollable negative effects of lasers, reduced single-mode stability and yield, and aggravated space hole burning effect. , to reduce the influence of the spatial hole burning effect, improve the single-mode stability, and increase the output optical power.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
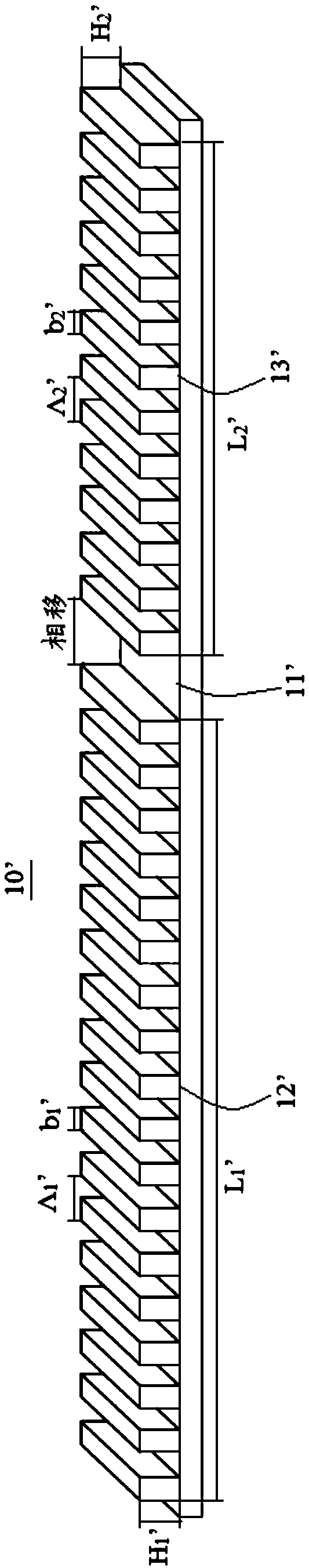
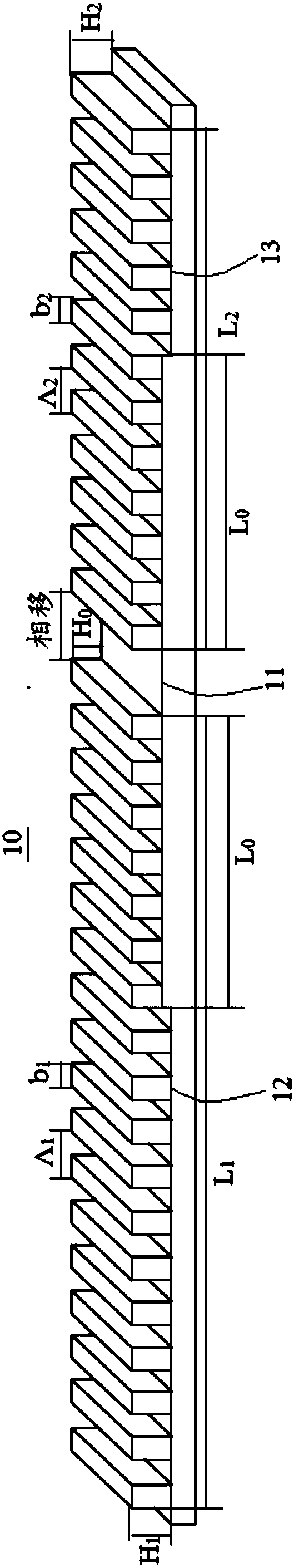
[0026] The application will be described in detail below in conjunction with specific implementations shown in the accompanying drawings. However, these implementations do not limit the present application, and any structural, method, or functional changes made by those skilled in the art based on these implementations are included in the protection scope of the present application.
[0027] In each drawing of the present application, some dimensions of structures or parts are exaggerated relative to other structures or parts for the convenience of illustration, and therefore, are only used to illustrate the basic structure of the subject matter of the present application.
[0028] Terms used herein, such as "left", "right", "left side", "right side", etc. to express relative positions in space are for the purpose of description to describe a unit or feature as shown in the drawings relative to A relationship to another cell or feature. The terms of spatial relative position ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com