Patents
Literature
72results about How to "Increase output optical power" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
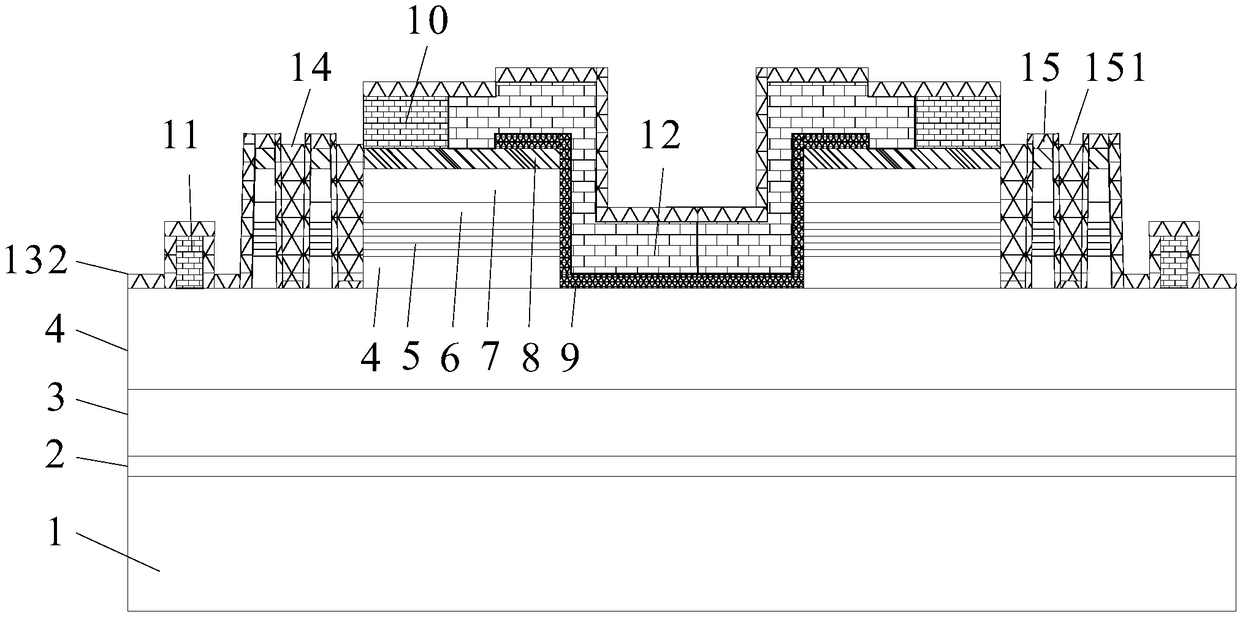
III-V group compound semiconductor light-emitting diode
InactiveUS20070200135A1Easy to getHigh outputSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesIn planeCompound (substance)
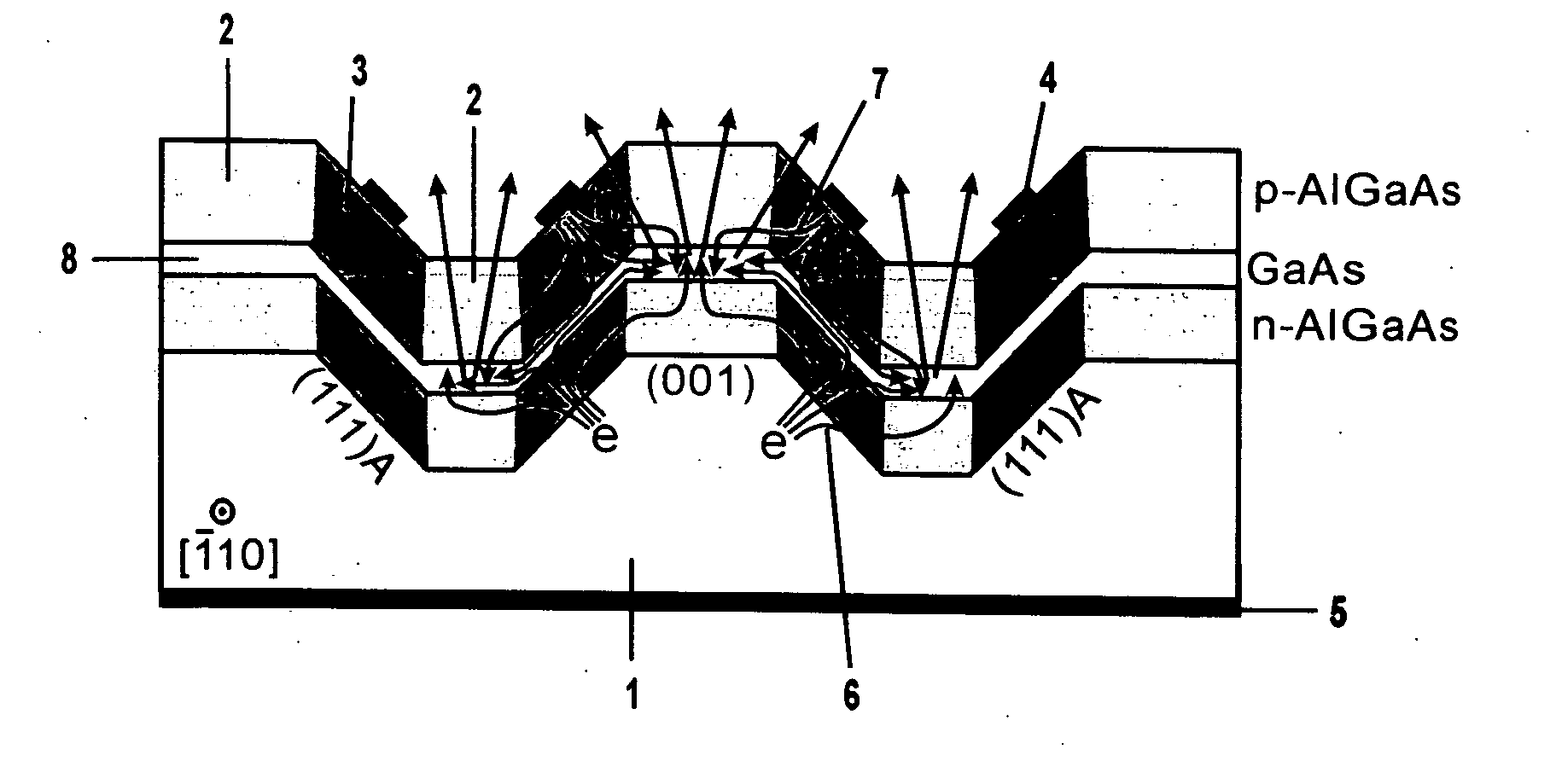
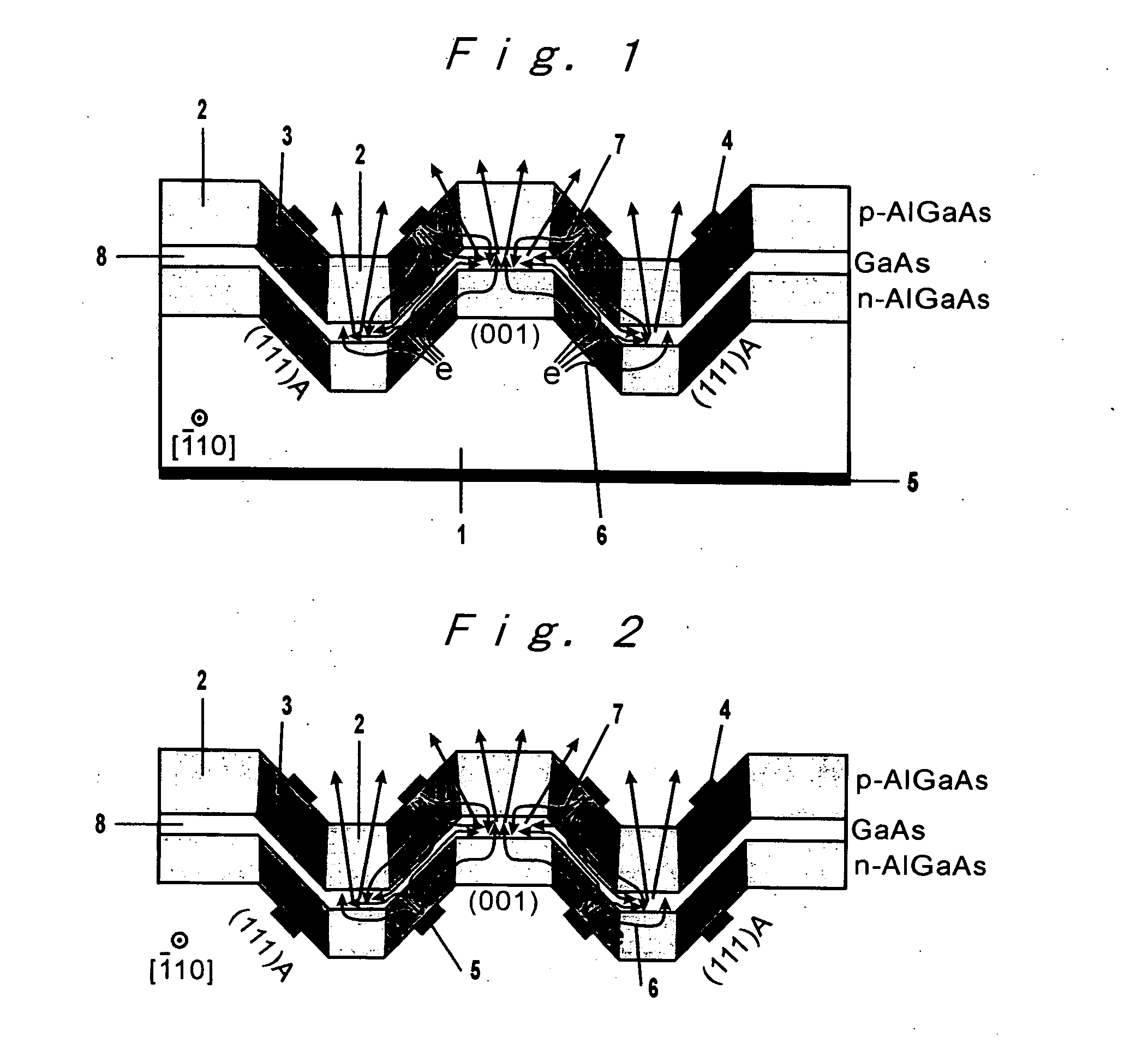
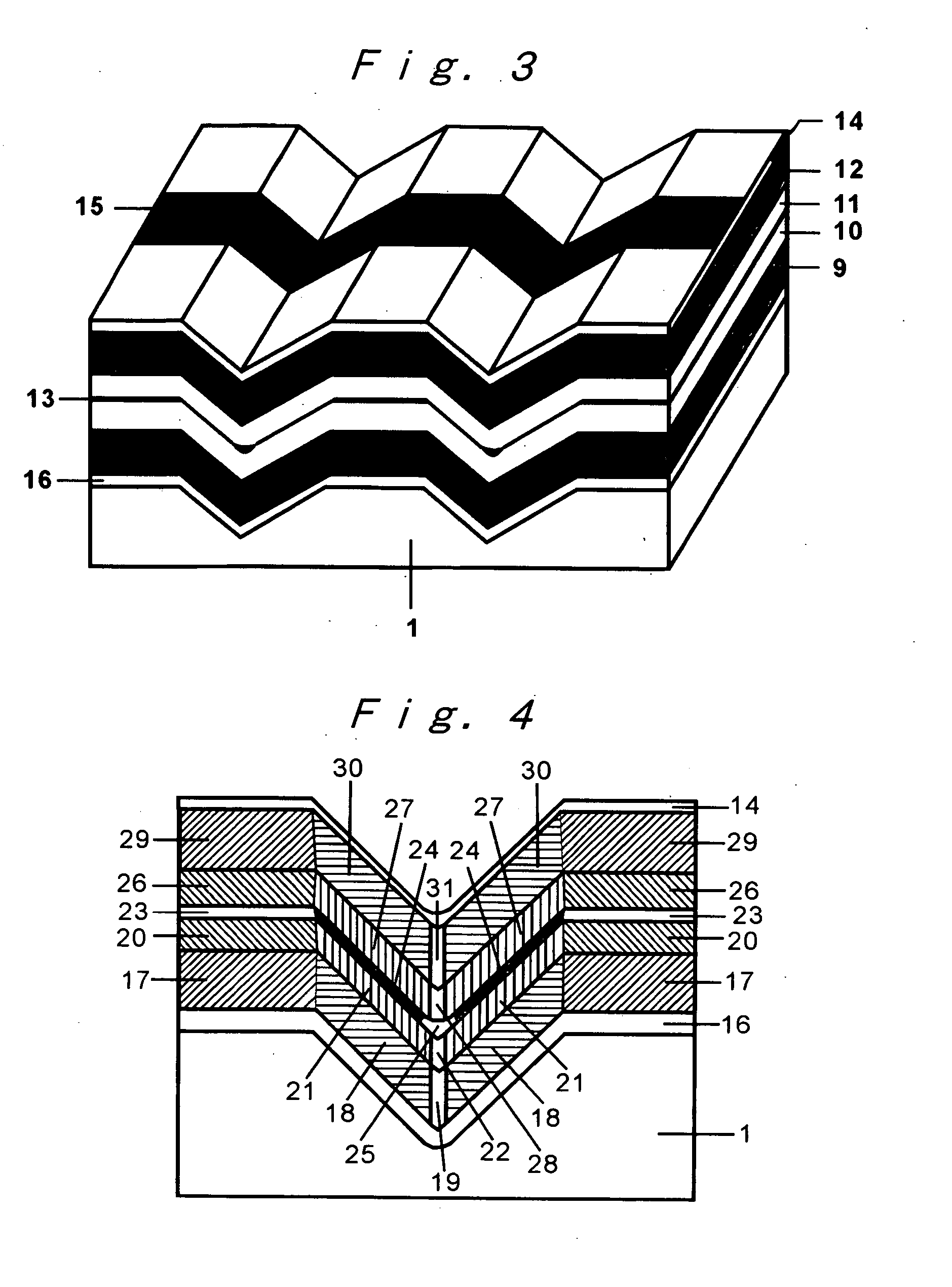
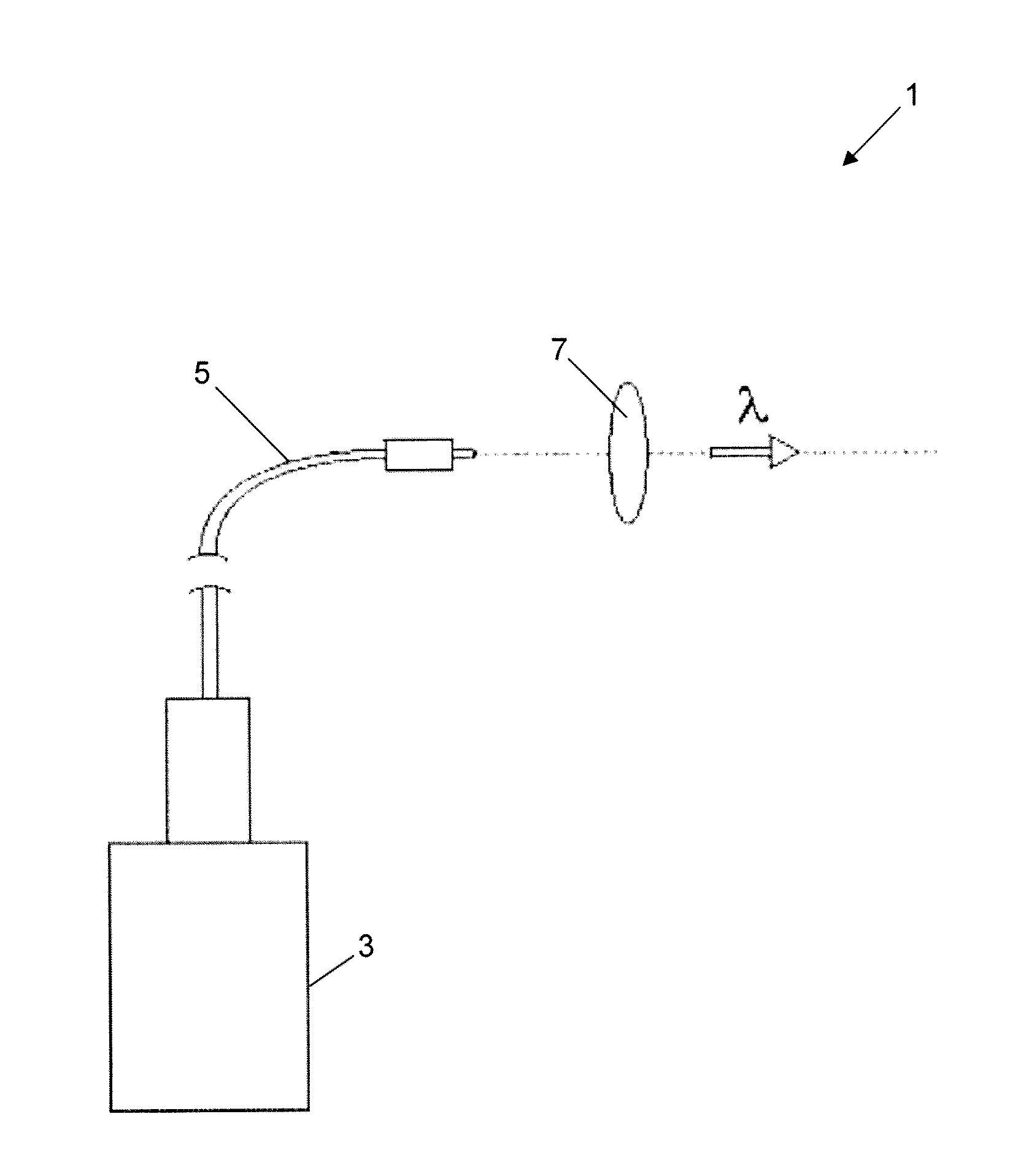
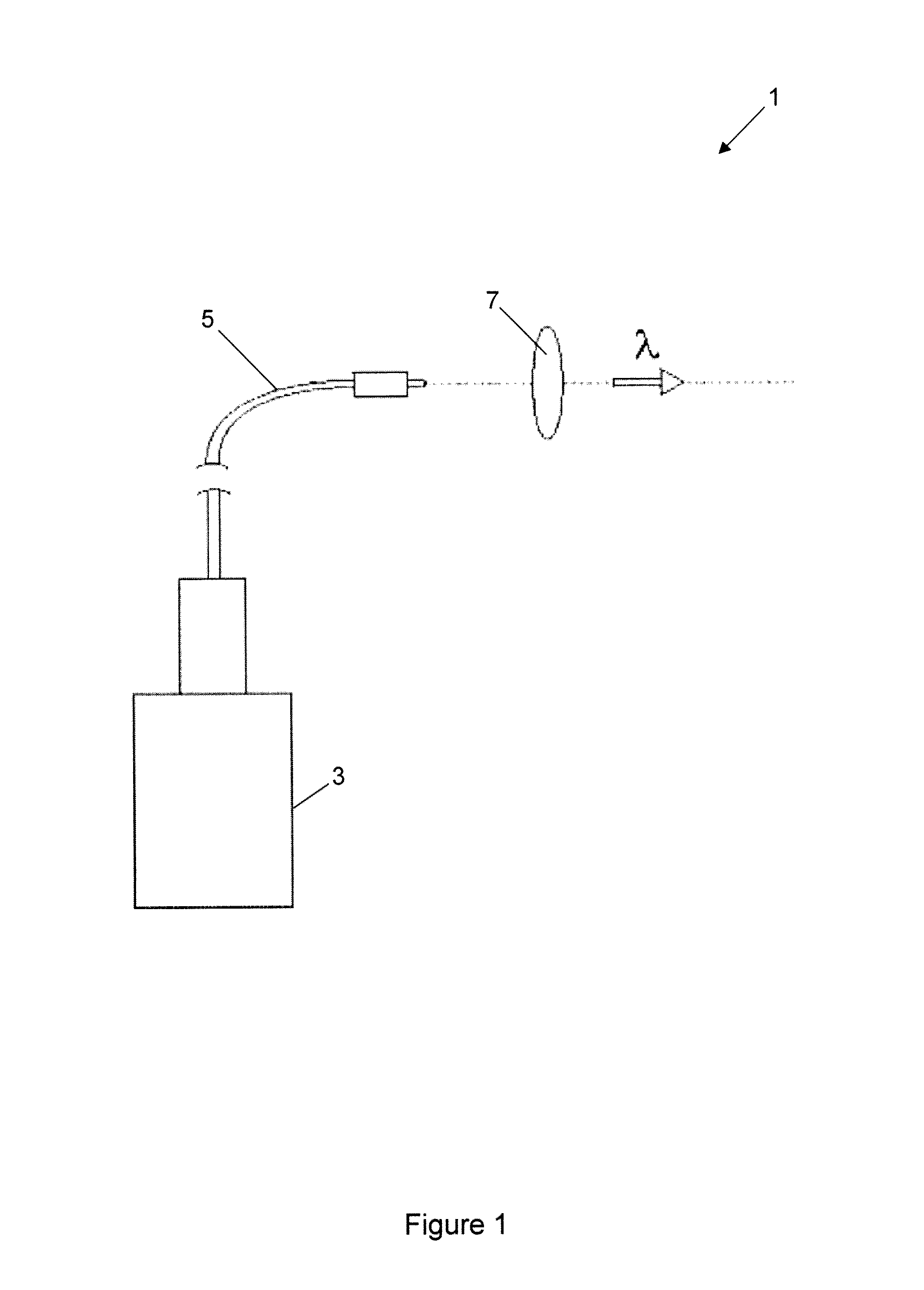
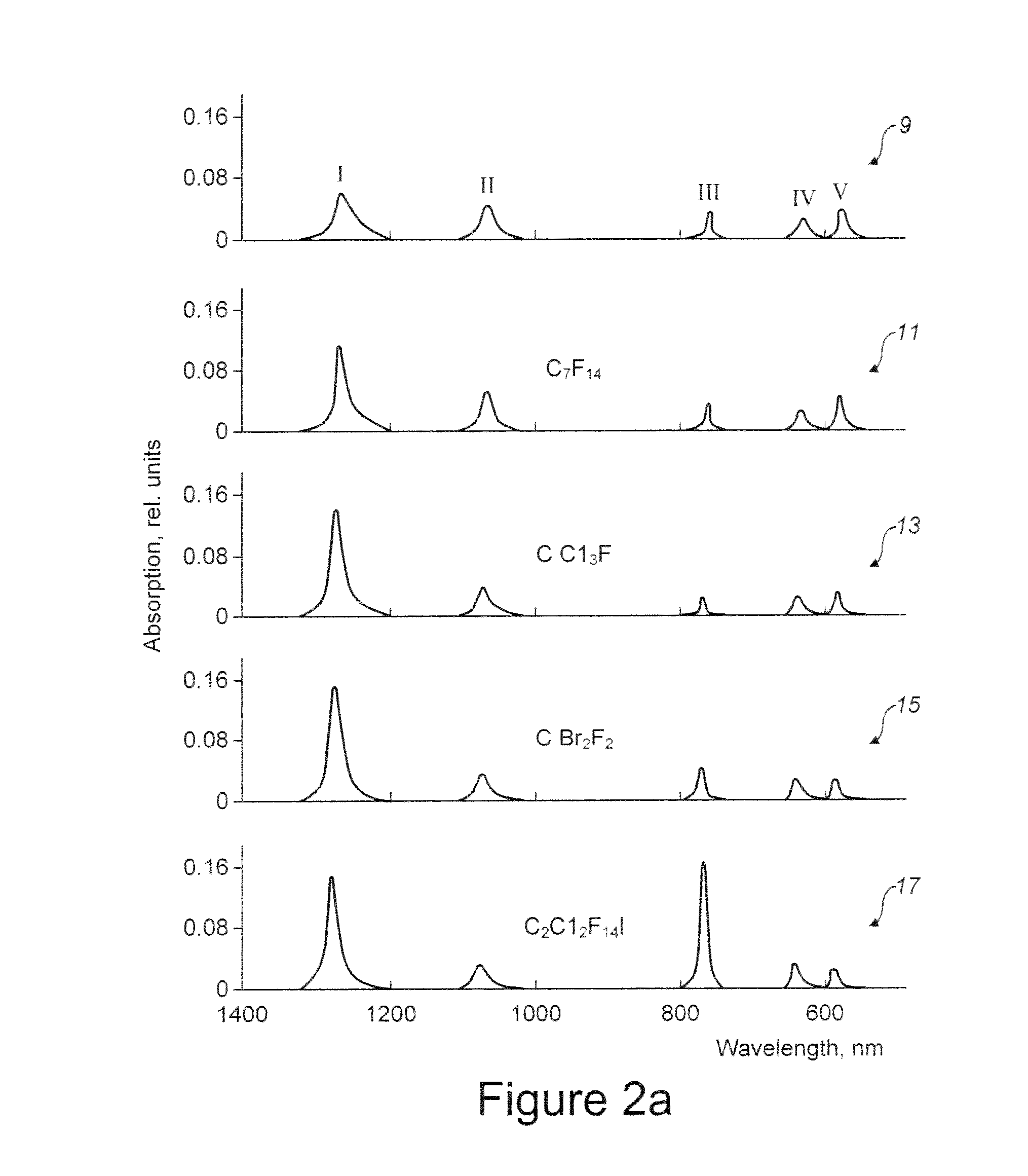
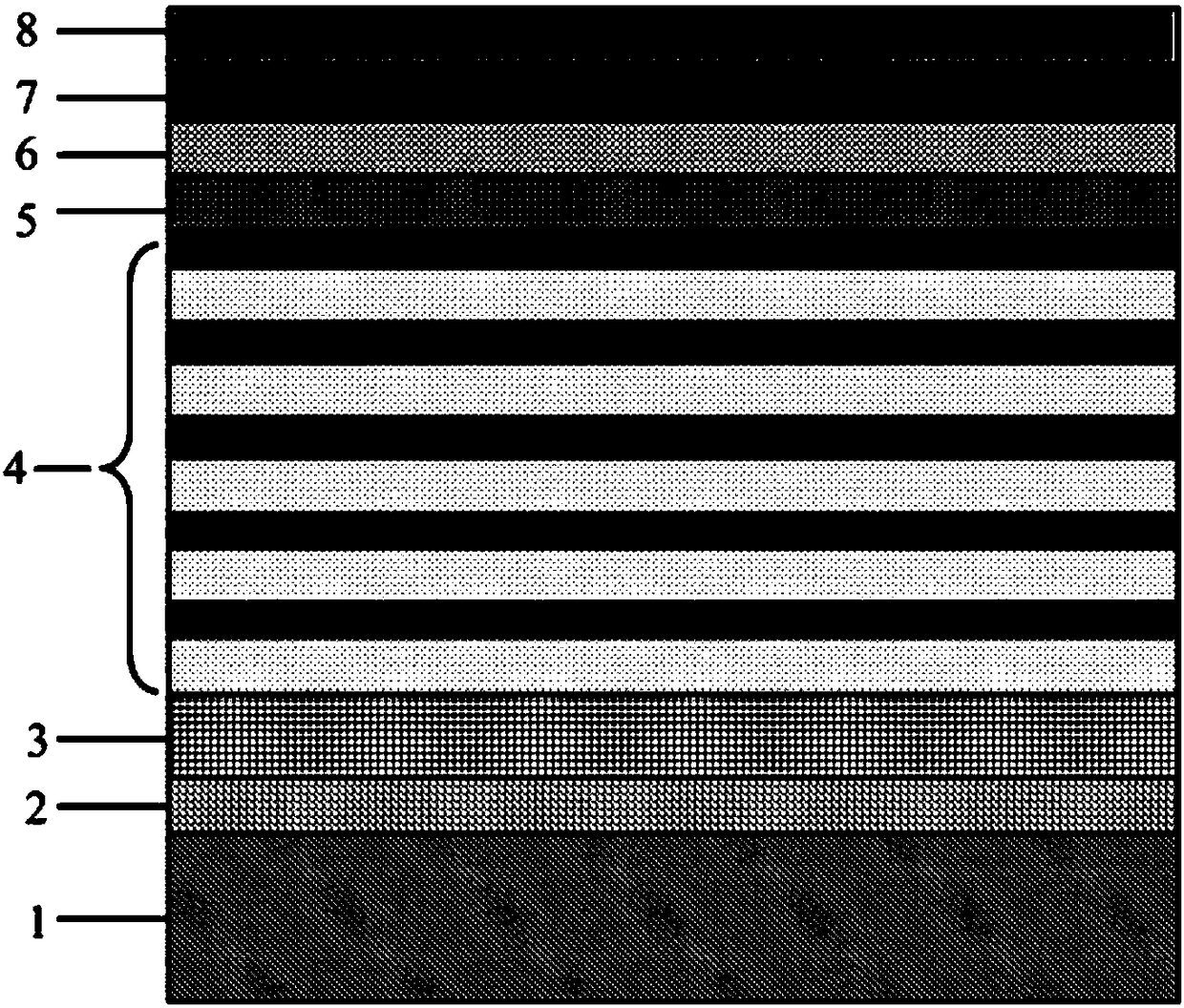
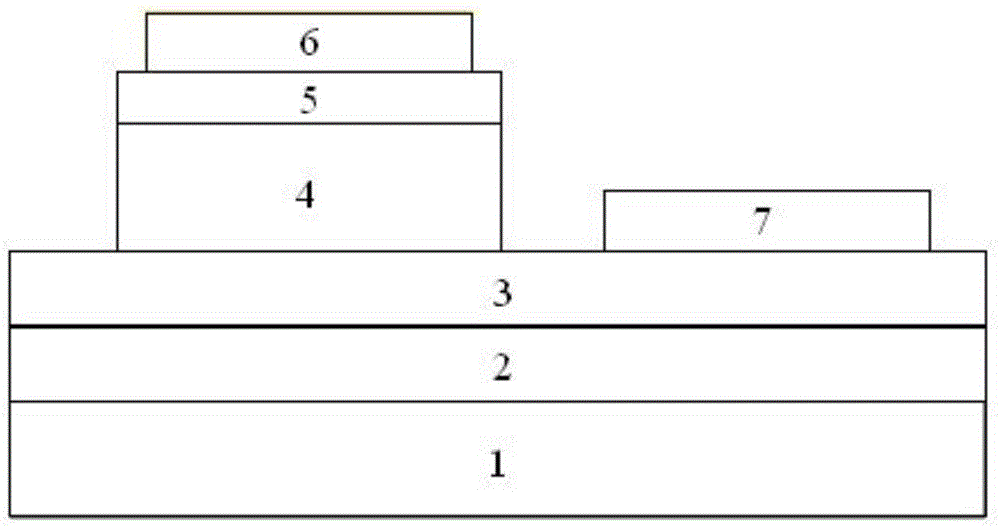
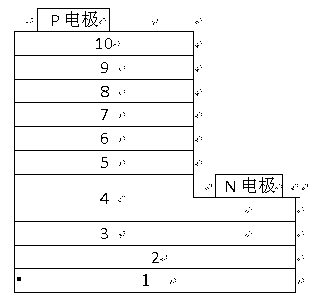
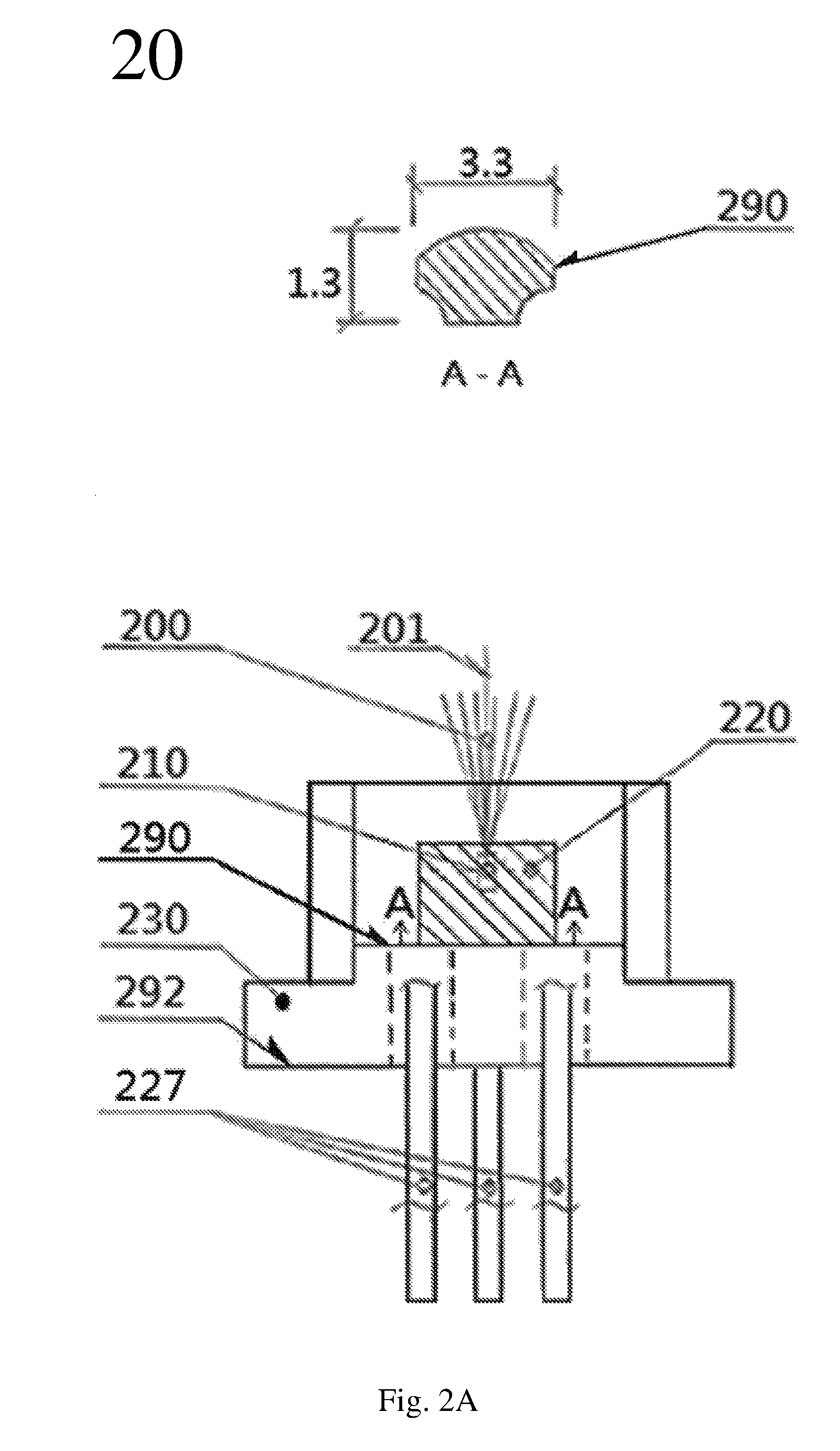
A III-V group compound semiconductor light-emitting diode, containing a substrate 1 having plural crystal planes, and a grown layer formed on the substrate by epitaxial growth, the grown layer at least including a barrier layer 2 and 3 and an active layer 8, wherein at least the active layer of the grown layer has plural crystal planes each having a different bandgap energy in the in-plane direction, and an Ohmic electrode 4 for current injection is formed on a crystal plane (3) having a higher bandgap energy among the plural crystal planes.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Active optical phase conjugating method and apparatus
InactiveCN1932565ARealize automatic and precise adjustmentSimple structureCoupling light guidesWaveguideWaveguide array
The invention relates to the active optics phase conjugate method and the imaging device, the optical switch. It constructs the mode separation / integration convertor by the optical waveguide array which is set together at one end, the optics field couples with each other; it is set separately in the other end. It leads the optical wave into the separating optical waveguide by the separation / integration convertor, then to achieve the active optics phase conjugate by adjusting the phase and the swing. It can solves the imaging problem in many limit condition such as big size, high quality, super quick focal variation, long distance and so on. So it can be used in the field of the computer-human conversation, the robot optics, the integrate circuit photoetching, information storage, the military affairs, the energy source, the biology and the light communication network.
Owner:李志扬
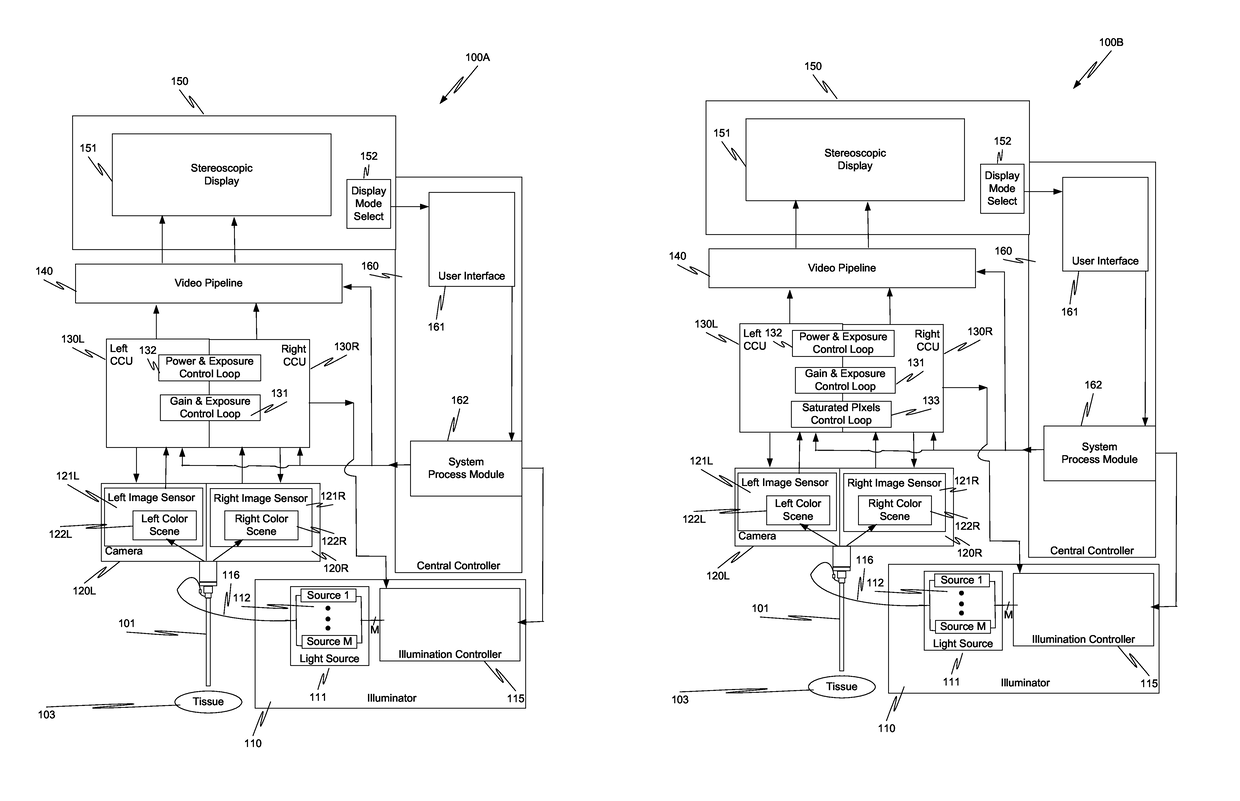
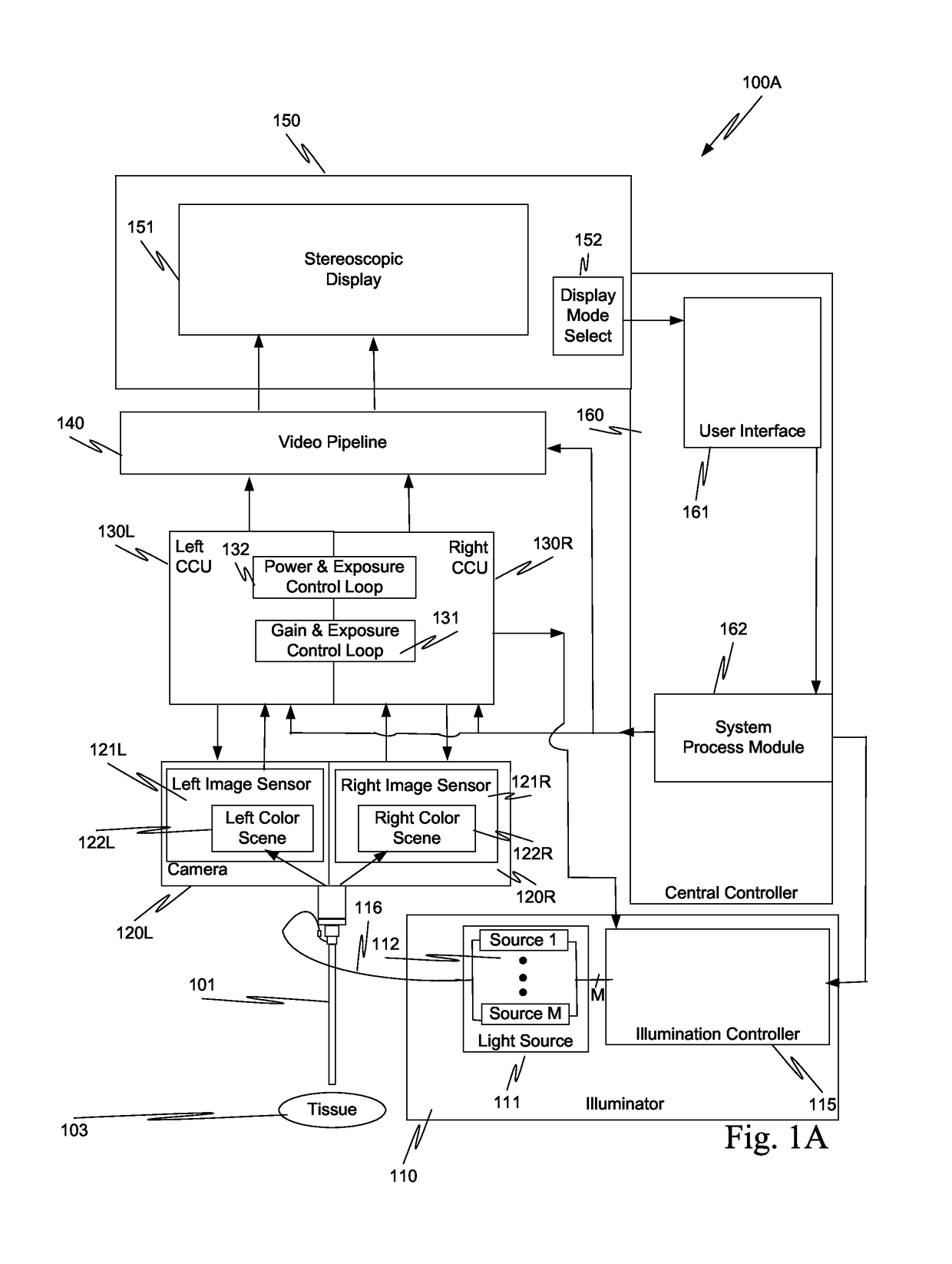
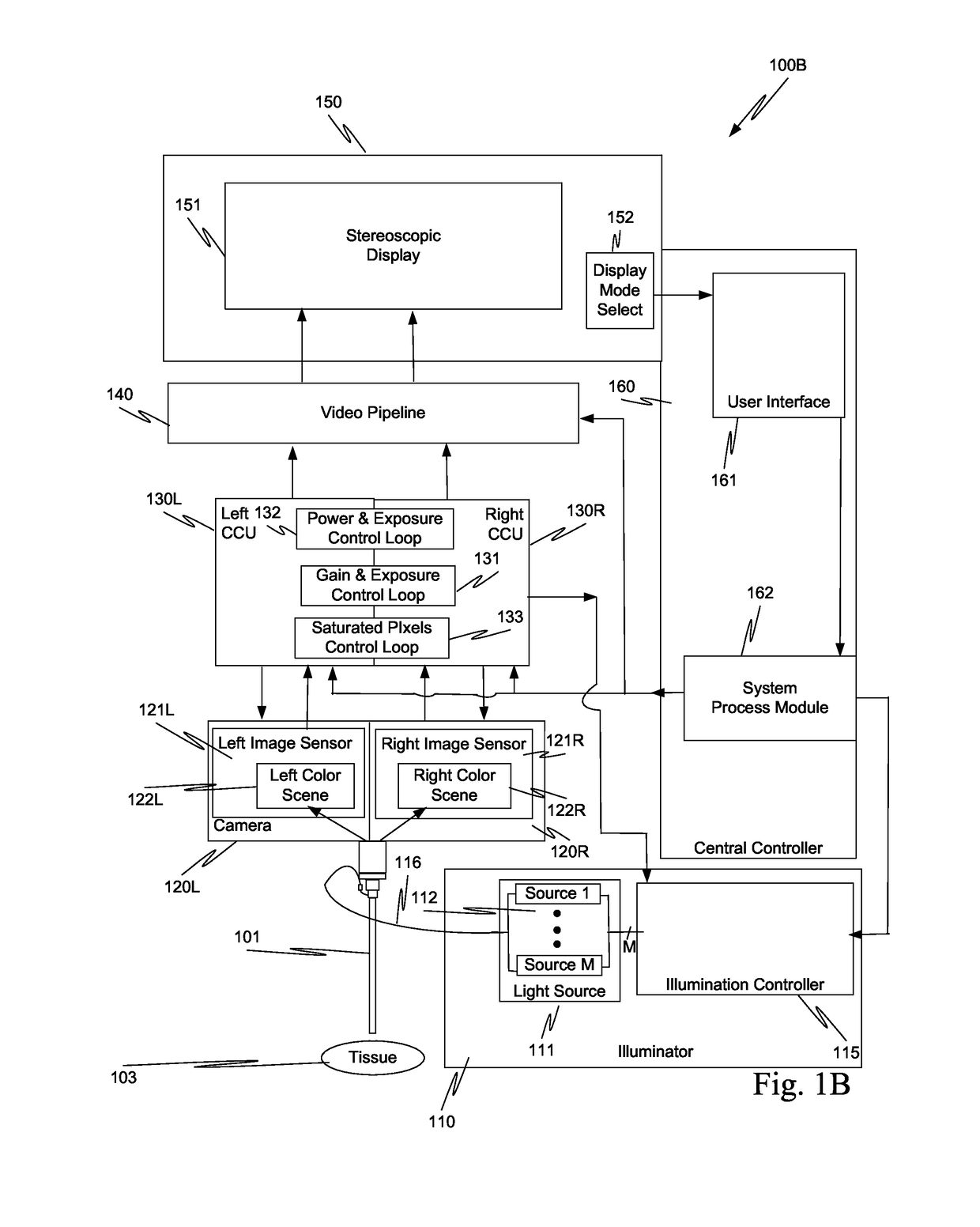
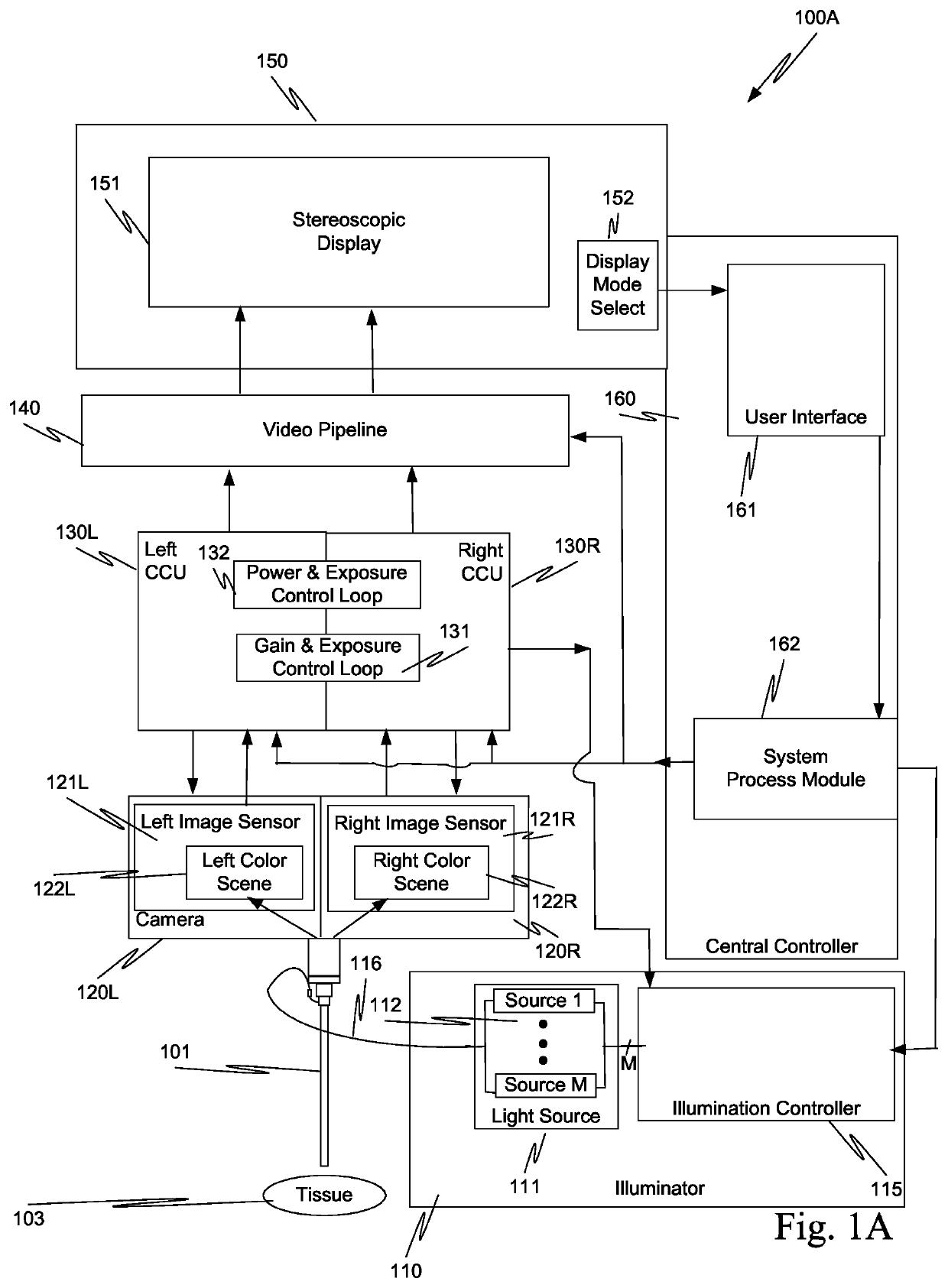
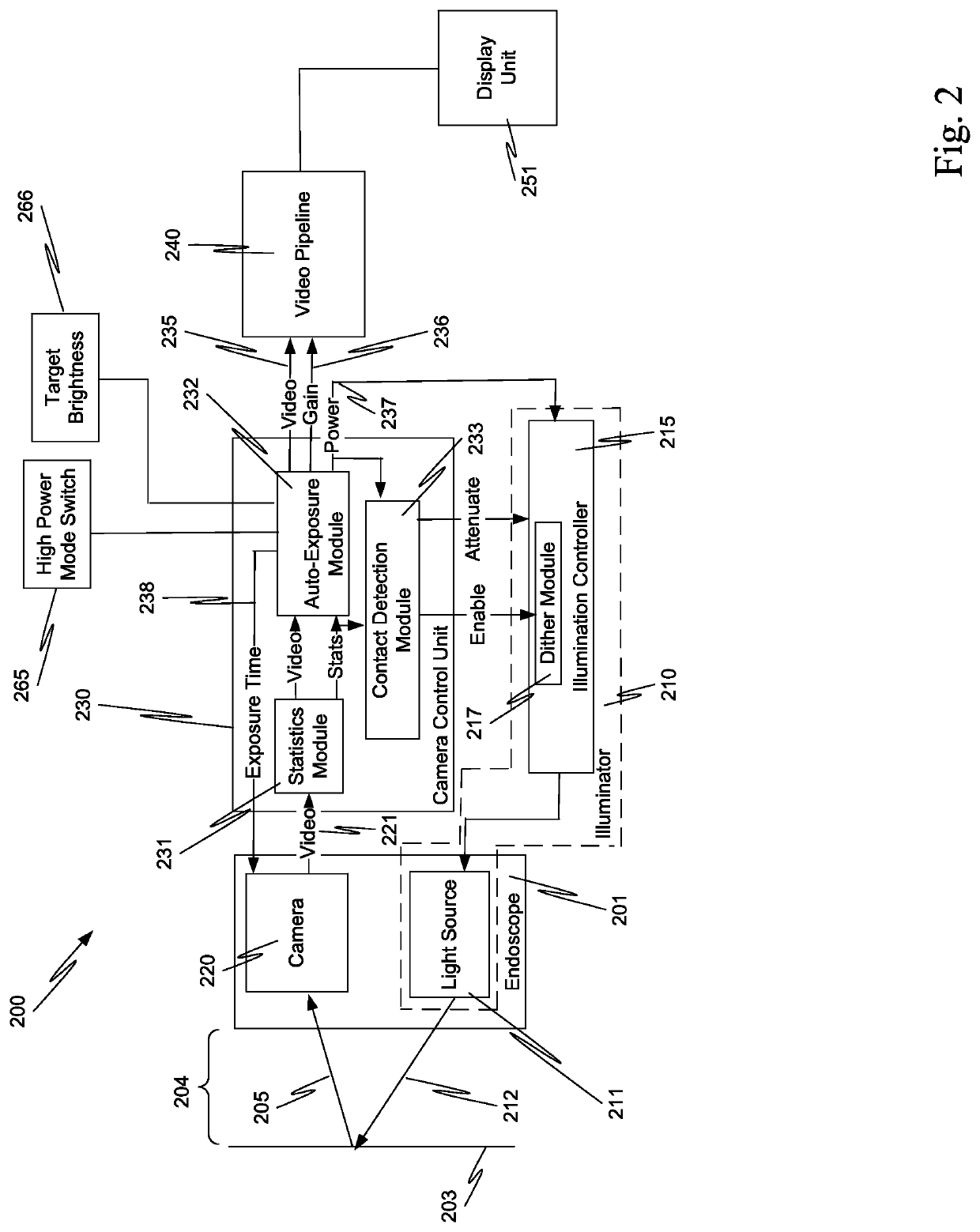
System and method for tissue contact detection and for auto-exposure and illumination control
ActiveUS20170095297A1Reduces target brightnessCompensation changesEndoscopesSurgical robotsMedicineOptical power
Scenes captured with an endoscope (201) of a teleoperated surgical system (200) and displayed on a display unit (251) maintain a consistent brightness even though optical output power of an illuminator (210) changes, and working distance (204) between tissue (203) and the distal tip of the endoscope changes. Teleoperated surgical system (200) also automatically detects when endoscope (201) contacts tissue (203) and adjusts the output optical power of illuminator (210) so that tissue damage does not occur.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Hybrid silicon-based whispering gallery mode microcavity laser
InactiveCN103117510ASimple structureIncrease output optical powerLaser optical resonator constructionWhispering gallerySilicon dioxide
The invention discloses a hybrid silicon-based whispering gallery mode microcavity laser which adapts to a light source part of a silicon-based photonic integrated circuit. The hybrid silicon-based whispering gallery mode microcavity laser comprises a silicon-based waveguide part and an III-V semiconductor gain part. The III-V semiconductor gain part is formed on the silicon-based waveguide part. The silicon-based waveguide part is in an SOI (silicon-on-insulator) structure with silicon, silicon dioxide and silicon. The silicon-based waveguide part is made into a triangular, rectangular, circular or waveguide-coupled output form to allow for longitudinal mode control. The III-V semiconductor gain part made of gain material is bonded to the SOI structure directly and matches with the SOI structure to form evanescent field coupling output. The hybrid silicon-based whispering gallery mode microcavity laser has the advantages that single-mode output of laser source on a silicon-based semiconductor surface is achieved by a right-triangular, square or round whispering gallery mode microcavity, cavity surface need not be split, large-scale processing is facilitated, optical coupling output and single longitudinal mode operation are easy to implement, and the laser is simpler in process and higher in practicality than the conventional single-mode lasers.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Quantum-dot laser diode
InactiveUS20110313407A1Minimal absorptionEasily transportable-andLaser detailsNanoopticsPhotodynamic therapyLaser technology
Aspects of the present disclosure relate to the field of laser technology, specifically semiconductor lasers, and to novel biomedical applications of such lasers, including novel methods of photodynamic therapy. Exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure include a semiconductor laser diode having an active region having a gain medium with one or more InGaAs / InAs quantum dot layers; and wherein the laser diode can be arranged in operation to emit laser light having a central wavelength within spectral range of wave lengths. The present embodiments further include a method of directly forming a reactive oxygen species (ROS), the method including exposing a medium having a potential source of ROS to a semiconductor laser diode, the semiconductor laser diode configured to emit laser light having a central wavelength within the spectral range.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DUNDEE
AlGa-based semiconductor ultraviolet device for improving luminous efficiency and preparation method thereof
PendingCN108231960AHigh light efficiencyReduce contentSemiconductor devicesQuantum efficiencyQuantum well
The present invention provides an AlGa-based semiconductor ultraviolet device for improving luminous efficiency and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the technical field of semiconductors.The epitaxial structure of the device comprises a substrate, an AlN buffer layer, an n-type AlGaN layer, an AlxGa1-xN / AlyGa1-yN luminescence active region, the last one AlGaN quantum barrier layer, ap-type AlGaN electron blocking layer, a p-type AlGaN layer and a contact layer, wherein 0.01<=x and y<=1. The luminescence active region comprises a plurality of quantum well layers and a plurality ofquantum barrier layers, the quantum well layers and the quantum barrier layers are alternately arranged, and the last one AlGaN quantum barrier layer is an aluminium ingredient gradient layer. The last one AlGaN quantum barrier layer of aluminium ingredient gradient is introduced in the ultraviolet device to optimize the energy band structure of the device, effectively improve the electron restriction effect and enhance the cavity injection efficiency so as to improve the quantum efficiency and the luminescence efficiency of the semiconductor ultraviolet device.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF SEMICON IND TECH
Terahertz quantum cascade laser of multiple-mode interface structure and manufacturing method thereof
The invention relates to a terahertz quantum cascade laser of a multiple-mode interface structure. The terahertz quantum cascade laser comprises a multiple-mode interference wave guiding structure. The multiple-mode interference wave guiding structure comprises a semi-insulating substrate, a buffer layer, a lower contact layer, an active region, an upper contact layer and an upper metal layer in the perpendicular direction from bottom to top in sequence, wherein the active region, the upper contact layer and the upper metal layer form a ridge type structure on the lower contact layer; lower metal layers are arranged on the two sides of the ridge type structure; the upper metal layer forms a multiple-mode wave guide and output wave guides through the wet etching method; the output wave guides are single-mode wave guides and located at the centers of the two ends of the multiple-mode wave guide, and the width of each output wave guide is smaller than that of the multiple-mode wave guide. The invention further relates to a manufacturing method of the THz QCL. By the adoption of the THz QCL of the multiple-mode interface structure and the manufacturing method of the THz QCL, the light-emitting power of the THz QCL can be increased, the quality of an emitted light beam is not reduced, collection efficiency is not reduced, the device is kept small, and cost is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Epitaxial structure for improving illumination efficiency of high-power GaN-base LED (light emitting diode) and growth method
InactiveCN103247729AQuality improvementPrevent leakageSemiconductor devicesContact layerElectron blocking layer
The invention discloses an epitaxial structure for improving the illumination efficiency of a high-power GaN-base LED (light emitting diode) and a growth method. The epitaxial structure sequentially comprises a substrate, a low-temperature GaN buffer layer, a GaN non-doping layer, an N type GaN layer, a multiple quantum well layer, a luminescent quantum well layer, a low-temperature P type GaN layer, a PAlGaN / PInGaN current blocking layer, a high-temperature P type GaN layer and a P type contact layer from bottom to top, wherein the growth of the PAlGaN / PInGaN electron blocking layer is completed through nine steps. An optimized PAlGaN / PInGaN structure layer is introduced between the epitaxial structure L-PGaN and H-PGaN, and a general electron blocking layer is replaced for further improving the electron leakage stopping effect. Through the structure, the performance of the InGaN / GaN base LED can be greatly improved in case of high-current-density injection.
Owner:江苏华功半导体有限公司
Mopa laser source with wavelength control
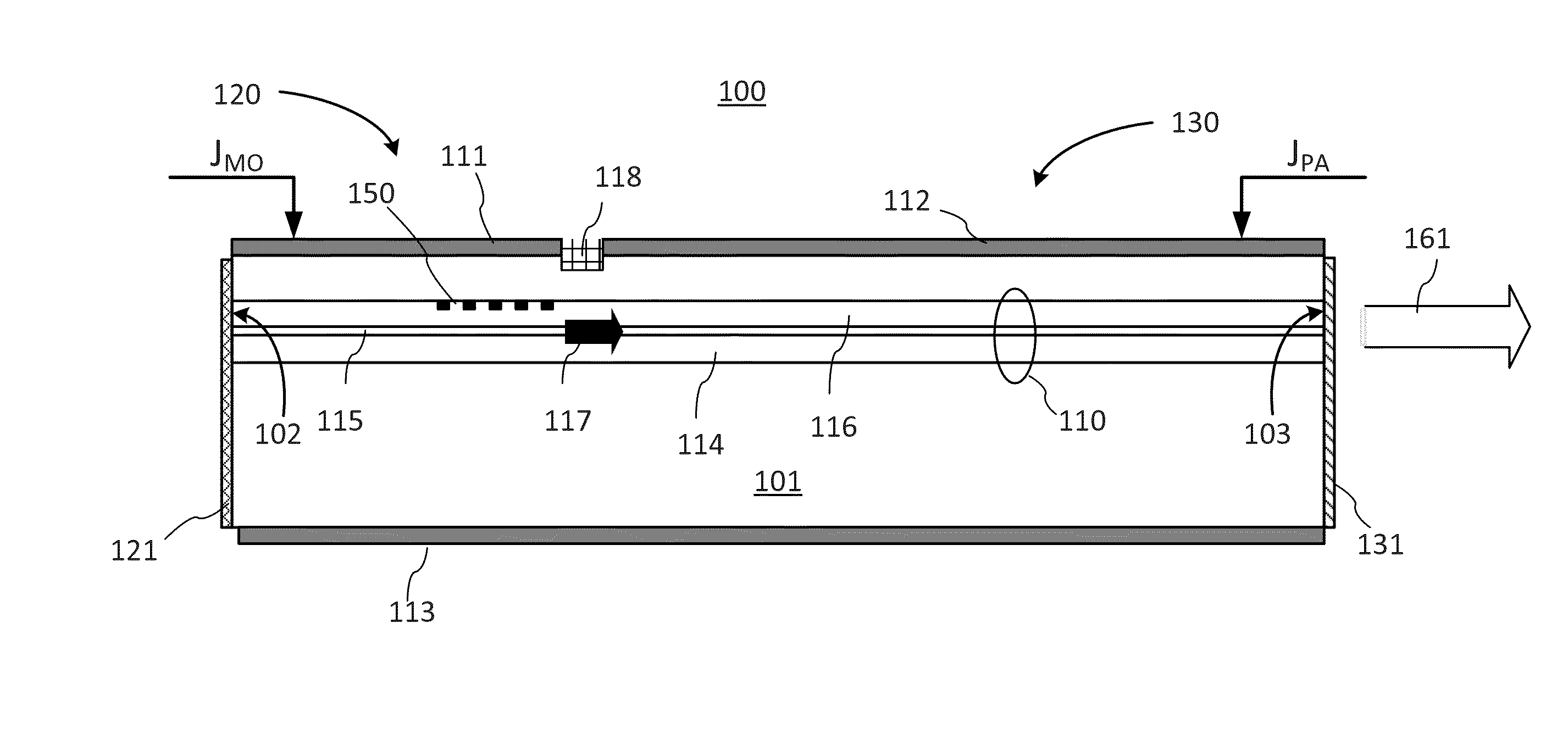
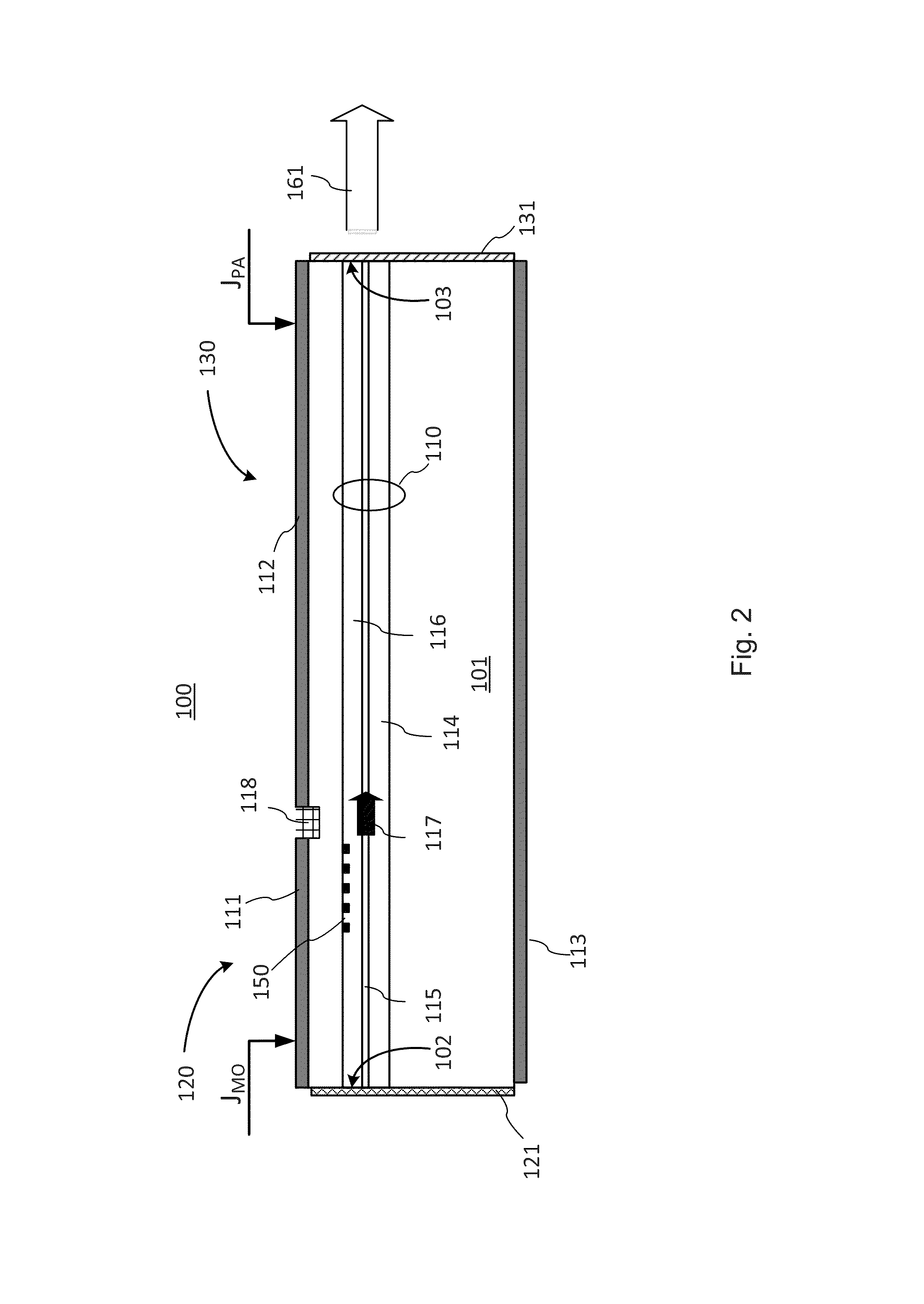
ActiveUS20150092800A1ConstantIncrease output optical powerLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersGratingPower flow
The invention provides a wavelength-controlled pump MOPA laser and a method of operation thereof. A monolithic semiconductor MOPA laser chip has a DFB-laser based MO (master oscillator) and PA (power amplifier) sections formed in a same monolithic waveguide, and separate MO and PA electrodes for individual control of current injection into the MO and PA sections. The laser wavelength is defined by the DFB grating and is kept fixed by suitably controlling the MO current to compensate for a thermal crosstalk from the PA section, or tuned by suitably changing the MO current or direct heating of the DFB region.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Flip-chip structure micro-size photonic crystal LED array chip and preparation method thereof
PendingCN109216399AIncrease compound rateHigh communication rateSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesPhotonic crystalInsulation layer
The invention discloses a flip-chip structure micro-size photonic crystal LED array chip and a preparation method thereof. The LED array chip of the invention has four light emitting units connected in parallel, the metal connecting line of the positive electrode and the semiconductor material are separated by a dielectric insulation layer, and the negative electrode is directly covered on the upper surface of the semiconductor material. The active region of the light-emitting unit has a photonic crystal with periodic distribution, and the depth of the photonic crystal exceeds the depth of theactive layer. Except electrode pad, DBR is distributed on the whole chip surface. Metal electrodes form metal mirrors. The preparation method of the invention adopts the scheme that an ohmic contactlayer and an electrode are firstly prepared and then a photonic crystal is etched without planarizing and the like traditional process flow; Using thick strip dielectric insulating layer to insulate the electrode from semiconductor material and thin dielectric mask layer and adhesive mask layer to etch together is conducive to the deposition of DBR and the rapid escape of photon mode. The processflow of the invention is simple and reliable.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
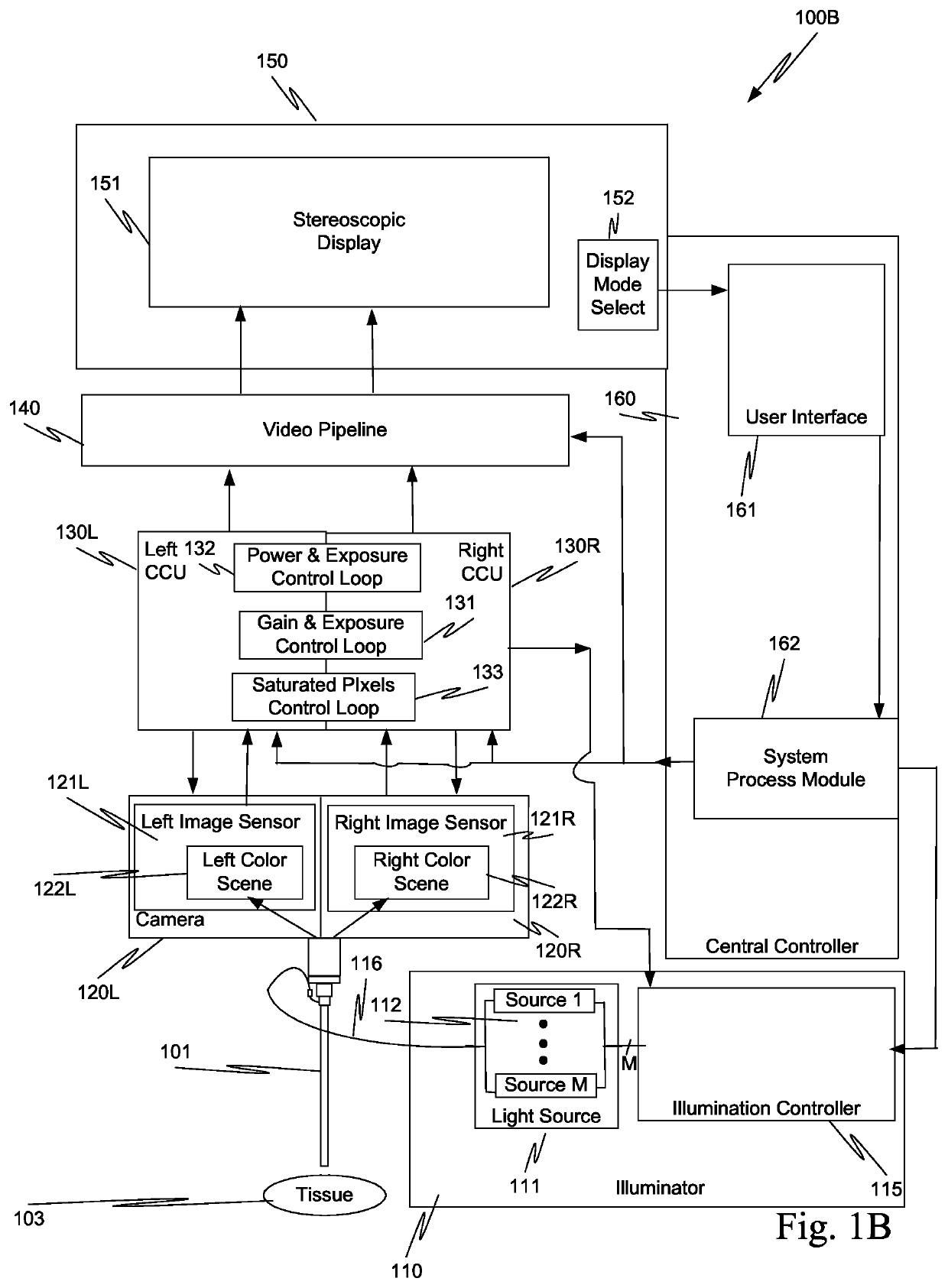
System and method for tissue contact detection and for auto-exposure and illumination control
ActiveUS10512512B2Increase output optical powerReduce exposure timeEndoscopesSurgical robotsOptical powerEndoscope
Scenes captured with an endoscope (201) of a teleoperated surgical system (200) and displayed on a display unit (251) maintain a consistent brightness even though optical output power of an illuminator (210) changes, and working distance (204) between tissue (203) and the distal tip of the endoscope changes. Teleoperated surgical system (200) also automatically detects when endoscope (201) contacts tissue (203) and adjusts the output optical power of illuminator (210) so that tissue damage does not occur.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Production method for P type gallium nitride electrode
InactiveCN101174660AImprove transmittanceImprove reflectivitySemiconductor devicesContact layerGallium nitride
The present invention relates to the preparation method of P-typed gallium nitride electrode, the present invention comprises the procedures that the external Mg on a sapphire substrate is mixed with P-typed gallium nitride kinetosome; a semi-transparent electrode ohm contact layer Ru / Ni is evaporated on the P-GaN kinetosome mixed with Mg through an electronic beam; an adhesion layer Ni is evaporated on the semi-transparent electrode ohm contact layer Ru / Ni through an electronic layer; a layer of high launching mirror Ag is evaporated on the adhesive layer Ni through an electronic beam; a layer of blocking layer Pt is evaporated on the high launching mirror Ag through an electronic beam; a protection layer Au is bonded on the blocking layer Pt so as to prevent the oxidation and the pollution of the metal electrode, thereby completing the preparation of the P-typed gallium nitride electrode.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Packaging Structure For A Laser Diode
ActiveUS20160294157A1Efficiently and rapidly conductEfficiently and rapidly and dissipateSemiconductor laser arrangementsSolid-state devicesHeat conductingElectrical connection
The invention relates to a packaging structure for a laser diode, comprising an electrically insulated, heat-conducting board having an electronic circuit thereon; a laser diode chip mounted on the electronic circuit of the electrically insulated, heat-conducting board and having an anode and a cathode, respectively connected to an external soldering pad for external electrical connections; and a heat-conducting base installed on a surface of the electrically insulated, heat-conducting board to conduct the heat generated by the laser diode chip to the heat-conducting base through the electrically insulated, heat-conducting board, wherein the laser diode chip emits the light from an edge of the electrically insulated, heat-conducting board and the area of a faying plane between the electrically insulated, heat-conducting board and the heat-conducting base is adjusted depending on the power requirements of the laser diode, and the area of the faying plane is from 6 to 5,000 mm2.
Owner:LEE HOU CHIEH
Multi-wavelength laser, its production method and use
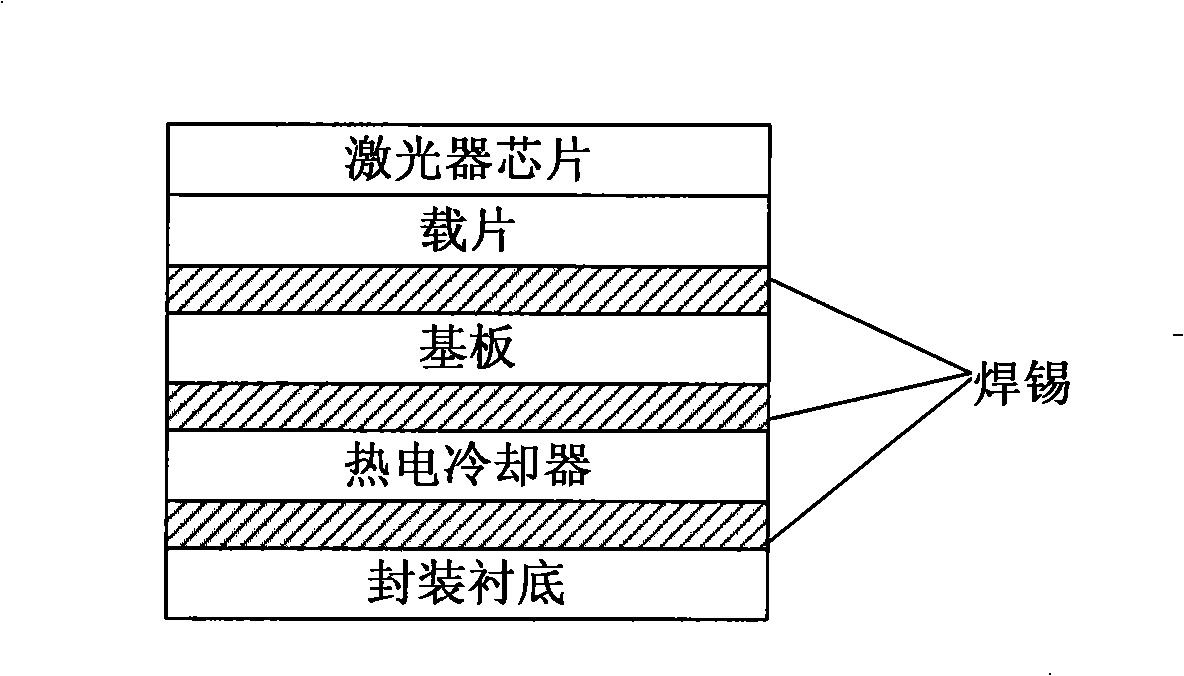
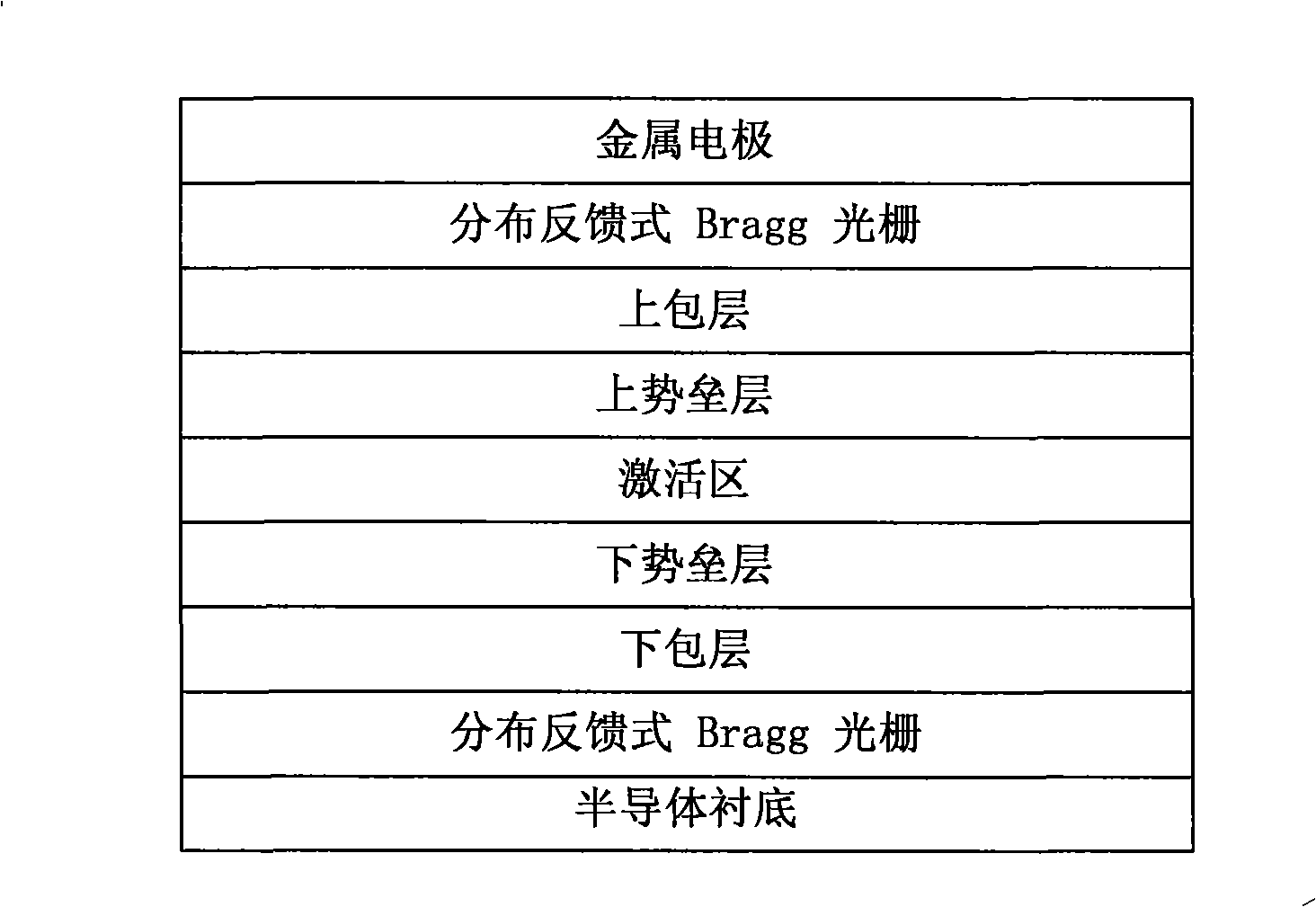
InactiveCN101404384AGood wavelength selectivityIncrease output optical powerMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsQuantum efficiencyGrating
The invention discloses a multi-wavelength laser, a preparation method and the application thereof. The multi-wavelength laser is at least composed of an encapsulation substrate, a thermoelectric cooler, a base plate, a piece of slide glass and a laser chip, wherein, the laser chip at least consists of a semiconductor substrate, distributed feedback Bragg raster display, a lower cladding, a lower barrier layer, an active region, an upper barrier layer, an upper cladding, the distributed feedback Bragg raster display and a metal electrode in sequence; the active region is internally provided with an active gain medium which is formed by a plurality of preconcerted quantum dot belts which are made of semiconductor dielectric material and have modulatory components and sizes, and each of the quantum dot belts internally contains a plurality of quantum dots having the same size and uniform distribution; the quantum dots are arranged in line, each of the quantum dot belts is corresponding to different lasing wavelengths, and the sizes of the quantum dots in the quantum dot belts are not the same as each other; the invention is characterized by good wavelength selectivity, high conversion quantum efficiency, high light output power, etc.
Owner:SUOOTER TECH BEIJING LTD
Micron-sized diode chip and preparation method
ActiveCN110061107AReduce areaRestricted shipping routesSemiconductor devicesQuantum wellThermal expansion
The invention provides a micron-sized diode chip. The micron-sized diode chip comprises a first table surface, a second table surface, a gallium nitride layer, an n-GaN layer, a stress release layer,a multi-quantum-well light-emitting layer, a p-GaN layer, a first electrode, a second electrode and an insulating layer, wherein the sizes of the first table surface and the second table surface are different. The technical problems that an original LED is low in output light power and large in mismatch with GaN in thermal expansion rate and lattice constant are avoided; and the technical effectsof integration of multiple functions of communication, illumination, detection and the like on the same chip, and high light extraction efficiency are achieved.
Owner:纳微朗科技(深圳)有限公司
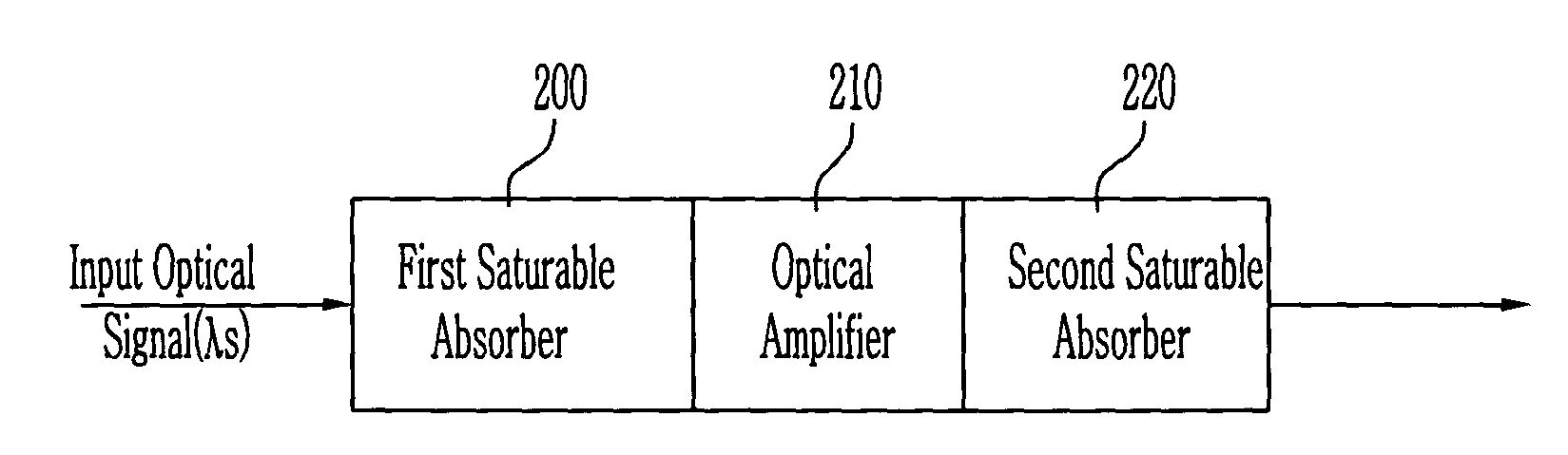
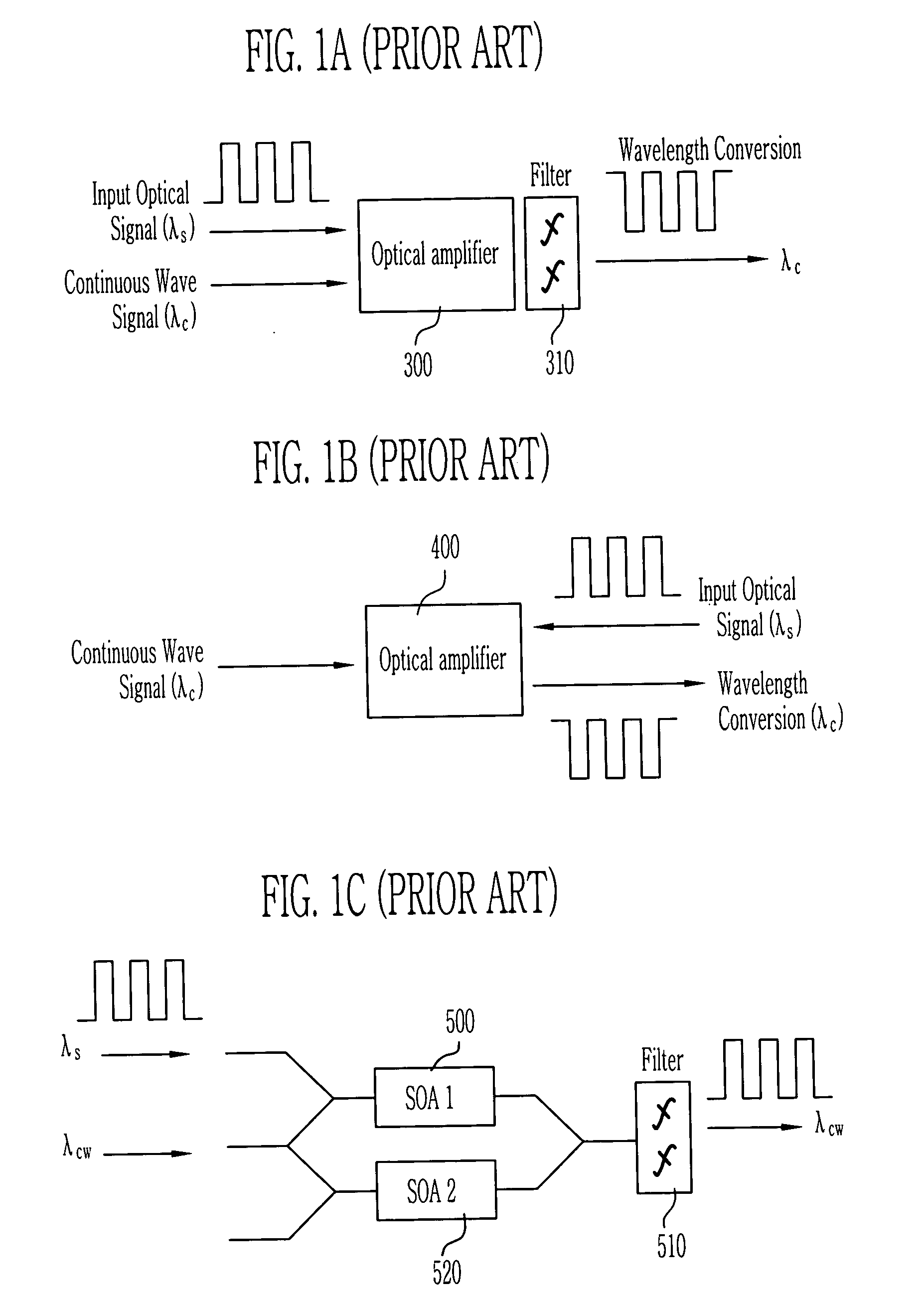
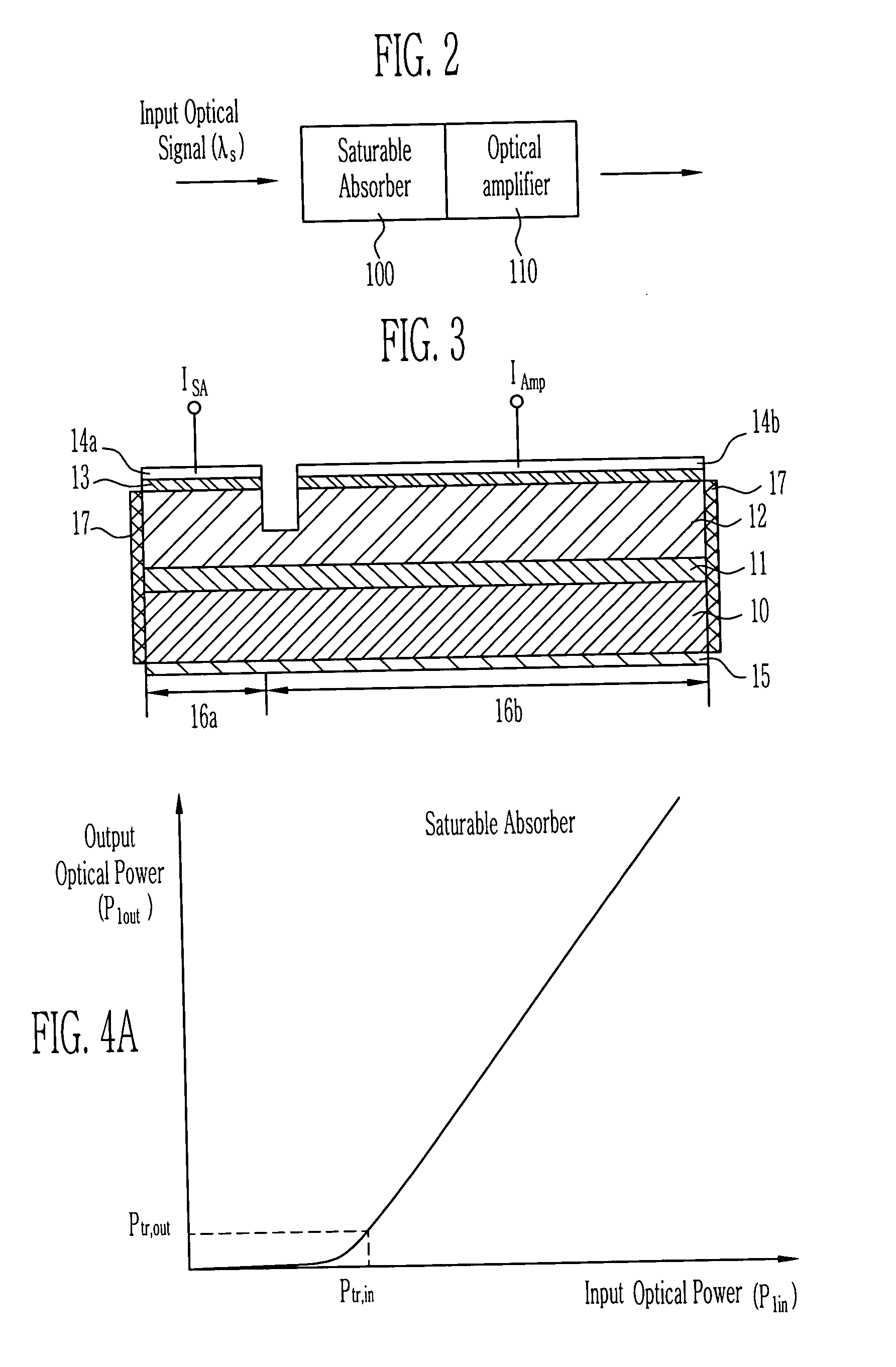
Optical signal processing element using saturable absorber and optical amplifier
InactiveUS20040075890A1Cancel noiseIncrease output optical powerLaser detailsFibre transmissionOptical powerLength wave
The present invention relates to an optical signal processing element capable of performing various functions of equalization of output power, wavelength converting, reshaping or reamplifying an input optical signal using an optical amplifier in which saturable absorbers are integrated, the saturable absorbers being used as an optical gate to improve the extinction ratio of the input optical signal. The saturable absorber and the optical amplifier are connected in series, and a transparent output optical power outputted from the saturable absorber is not less than a saturation input optical power of the optical amplifier.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Optical module
InactiveCN110474688ASimplify the assembly processImprove reliabilityFibre transmissionElectromagnetic transceiversFiberUltrasound attenuation
The invention discloses an optical module. The optical module comprises a tube shell, a light emitting assembly, a light receiving assembly, a light emitting interface and a light receiving interface,the light emitting assembly and the light receiving assembly are arranged in the tube shell, the light emitting interface and the light receiving interface are arranged on the tube shell, an output optical fiber is arranged on the side of the light emitting assembly, and an input optical fiber is arranged on the side of the light receiving assembly; the output optical fiber is wound around the light emitting assembly and the light receiving assembly and then is connected with the light emitting interface; the input optical fiber is wound around the light emitting assembly and the light receiving assembly and then is connected with the light receiving interface. The light receiving assembly and the light emitting assembly are flexibly connected with the corresponding interfaces through theoptical fibers, so that the coupling difficulty is reduced, and the light receiving assembly and the light emitting assembly can be placed flexibly. Attenuation of the optical module is mainly generated by the optical fiber, attenuation generated by optical port pressure in an optical port integration scheme is avoided, attenuation can be reduced, and output optical power and receiving sensitivity are improved.
Owner:WUHAN ACCELINK TECH CO LTD
Electro-optical modulation device
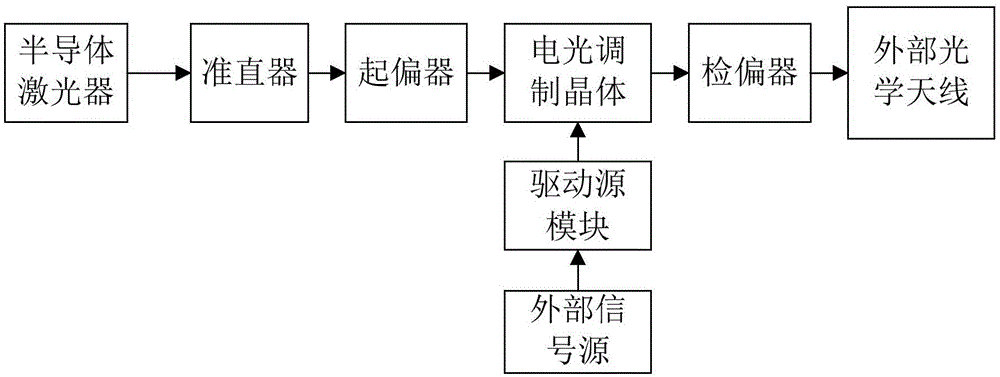
InactiveCN106019642AEfficient couplingIncrease output optical powerNon-linear opticsOperating pointPolarizer
An electro-optic modulation device provided by the present invention includes a semiconductor laser, a collimator, a polarizer, a driving source module, an electro-optic modulation crystal, and a polarizer. This device is mainly aimed at the 800nm band, the modulation rate is 100Mbps to 500Mbps, and the maximum optical power output is greater than 0.5w. The semiconductor laser is connected to the collimator through an optical fiber. The laser light passing through the collimator becomes polarized light after passing through the polarizer. The polarized light is modulated after passing through the electro-optic modulation crystal. Use the unit. The external signal source and the driving source module are connected with a high-frequency coaxial cable, the external signal source provides a high-frequency, high-power square wave AC signal for the driving source module, and the electro-optical modulation crystal and the driving source module are connected by a high-frequency coaxial The cable is connected, the output signal of the driving source module is sent to the electro-optic modulation crystal through the high-frequency coaxial cable and the traveling wave electrode, and the optical feedback signal of the electro-optic modulation crystal realizes the real-time control of the static working point.
Owner:GUILIN TRYIN TECH CO LTD
Multi-junction distributed feedback semiconductor laser and preparation method thereof
PendingCN113422295AEvenly distributedSmall cross-sectional area of effective light fieldLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionGratingPhysical chemistry
The invention provides a multi-junction distributed feedback semiconductor laser. The laser comprises a substrate and a laser DFB-LD functional layer growing on the surface of the substrate; the DFB-LD functional layer comprises a plurality of semiconductor PN junctions and a grating; the plurality of semiconductor PN junctions are distributed up and down and are electrically connected with each other, and a junction region of each PN junction is provided with a light-emitting region; and the grating is positioned on any one of the semiconductor PN junctions or a connecting layer between the semiconductor PN junctions. According to the DFB-LD, the effective light emitting area of the laser can be increased, the symmetry of the transverse light field distribution of the waveguide cross section is improved, and the parasitic capacitance parameter of the laser is reduced, so that the laser has the advantages of high power, high modulation rate and high optical fiber coupling efficiency.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
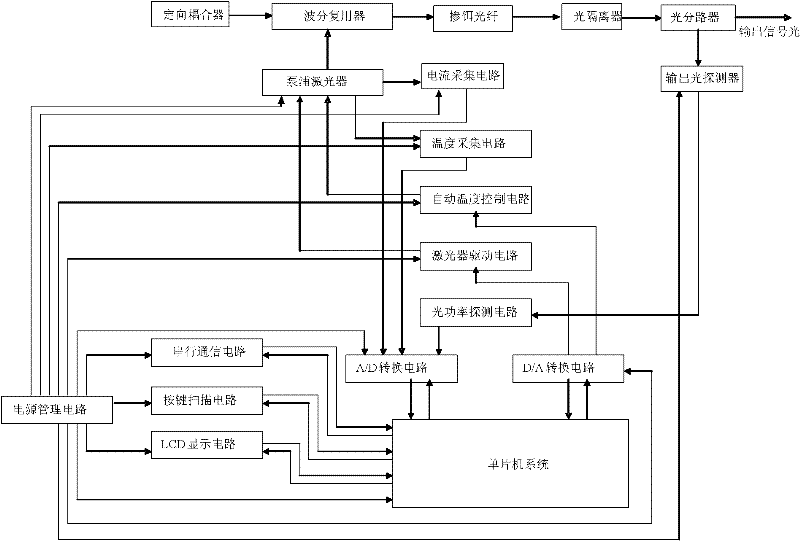
Amplified spontaneous emission light source device
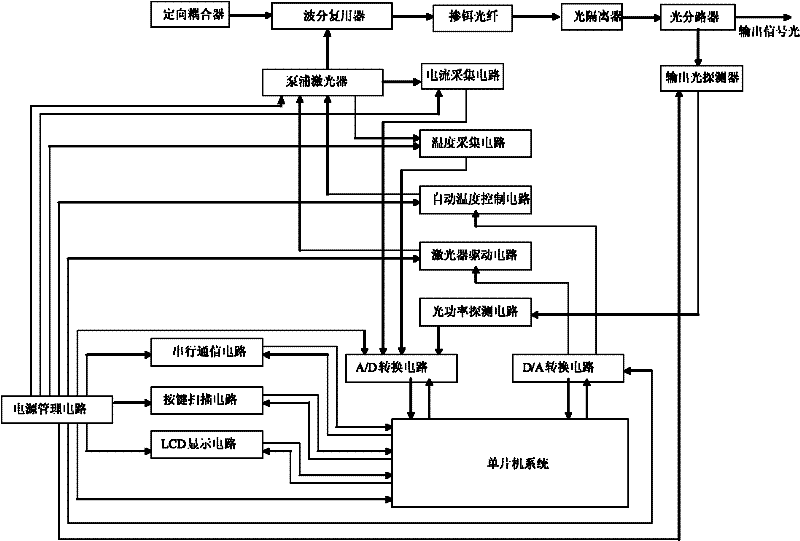
The invention discloses an amplified spontaneous emission light source device, which comprises a circuit part and a light path part. Light emitted by a pump laser enters an erbium-doped fiber after passing through a wavelength division multiplexer to generate primary forward amplified spontaneously emitted light and backward amplified spontaneously emitted light. An A / D conversion circuit is connected with an output light power detection circuit, a current acquisition circuit and a temperature acquisition circuit. The pump laser is connected with an automatic temperature control circuit, a laser drive circuit, the temperature acquisition circuit and the current acquisition circuit. The laser drive circuit is connected with a D / A conversion circuit. A singlechip system is connected with the A / D conversion circuit, the D / A conversion circuit, a serial communication circuit, a liquid crystal display (LCD) circuit and a key scanning circuit. A power management circuit supplies power to each circuit. The amplified spontaneous emission light source device provided by the invention is convenient to use and high in working performance and output light power.
Owner:上海光家仪器设备有限公司 +1
Asymmetrically-structured phase-shifting grating and DFB (distributed feedback) semiconductor laser
InactiveCN108233173AAchieving an asymmetrical outputIncrease output optical powerLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionNon symmetricPhase shifted
The present application discloses an asymmetrically-structured phase-shifting grating and a DFB (distributed feedback) semiconductor laser. The phase-shifting grating comprises a phase-shifting structure, a first grating and a second grating, wherein the phase-shifting structure is located at the non-center position of the phase-shifting grating, and the first grating and the second grating are located at two sides of the phase-shifting structure; the etching depth of the first grating is equal to the etching depth of the second grating; the grating duty ratio of the first grating is equal tothe grating duty ratio of the second grating, or the sum of the grating duty ratios of the first grating and second grating is equal to 1; the length of the first grating is different from the lengthof the second grating; two sides in the first grating and the second grating, which are adjacent to the phase-shifting structure, are a first chirp grating and a second chirp grating respectively; thefirst chirp grating and the second chirp grating are symmetrically distributed along the phase-shifting structure; and the grating period of the first chirp grating and the second chirp grating gradually changes along the direction of the phase-shifting structure. With the asymmetrically-structured phase-shifting grating of the invention adopted, the asymmetric output of optical power can be realized, so that the output optical power of the laser can be improved; and refractive index modulation near the phase-shifting structure can be decreased, and therefore, the influence of a spatial hole-burning effect can be effectively reduced, and the single-mode stability of the laser can be improved.
Owner:INNOLIGHT TECHNOLOGY (SUZHOU) LTD
Bragg grating external cavity semiconductor laser module beam combining device
ActiveCN112531462AReduce usageLow costLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsGratingLight beam
The invention relates to a Bragg grating external cavity semiconductor laser module beam combining device, and the device comprises at least one light emitting module; the light emitting module comprises at least two light emitting units; at least one conduction optical fiber which is arranged on an output light path of the light-emitting module; a Bragg grating is arranged on an output light pathof the conduction optical fiber, the Bragg grating and the output end of the light-emitting module form an outer cavity, laser output through the conduction optical fiber vertically enters the incident end face of the Bragg grating, part of the laser is transmitted to serve as output light to be output, and part of the laser is reflected to serve as feedback light to return into the light-emitting module along the original path to achieve wavelength locking. An outer cavity is formed by one Bragg grating and a plurality of light-emitting modules, so that the cost of the beam combining deviceis reduced. The Bragg grating only feeds back part of light beams perpendicular to the incident end face, the output light power is improved, the light intensity fed back by the Bragg grating is ensured by limiting the core diameter of the conduction optical fiber and the distance between the conduction optical fiber and the Bragg grating, and a better locking effect is achieved.
Owner:SUZHOU EVERBRIGHT PHOTONICS CO LTD +1
Fiber welding method and device
ActiveCN105116493AReduce the impact of different batchesReduce the chance of higher order modesCoupling light guidesFiberMechanical engineering
In an embodiment, the application provides a fiber welding method, comprising the steps of: employing a welding machine to align fiber claddings; after aligning the fiber claddings, fixing any fiber, selecting another fiber to scan the cross section axis of the cross section of the fixed fiber, and adjusting a fiber position according to scanning results; and welding the fiber after position adjustment. The method realizes fiber core alignment by scanning fiber end faces, reduces high-order mode generation opportunities, and reduces the influence caused by fiber different batches.
Owner:武汉创鑫激光科技有限公司
Mixed silicon single mode annular cavity laser based on microstructural silicon waveguide frequency selection
InactiveCN102856789BImprove efficiencyReduced reflected energy lossOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionGratingHigh density
The invention discloses a mixed silicon single mode annular cavity laser based on microstructural silicon waveguide frequency selection, comprising a silicon substrate, a silicon dioxide layer formed on the silicon substrate, a silicon annular waveguide layer formed on the silicon dioxide layer, a bonding buffer layer formed on the silicon waveguide layer, an N type contact layer formed on the bonding buffer layer, an N type electrode formed in the middle on the N type contact layer, an annular quantum well active region formed in an annular part of the N type electrode on the N type contact layer, a P type annular contact layer formed on the annular quantum well active region, a P type annular cover layer formed on the P type annular contact layer and a P type electrode formed on the P type annular cover layer. The structure is in high density integration, single longitudinal mode working and high-efficiency coupling outputting; and more importantly, according to the mixed silicon single mode annular cavity laser disclosed by the invention, technological steps of conventional DFB distributed feedback grating manufacturing, III-V group material secondary epitaxy and the like are saved in technological processing, and the complexity is lowered.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Asymmetric micro-cavity edge emitting semiconductor laser array
ActiveCN109921284AConsistent light directionClosely arrangedLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser arrayCoupling
The invention discloses an asymmetric micro-cavity edge emitting semiconductor laser array, and belongs to the technical field of semiconductor lasers. An existing semiconductor laser stack array faces multiple technical problems in beam shaping and output coupling. According to the asymmetric micro-cavity edge emitting semiconductor laser array, laser single tubes forming the laser array are asymmetric micro-cavity edge emitting semiconductor lasers; a front row of laser linear arrays and a back row of laser linear arrays are located on the same substrate; in the front row of the laser lineararrays, the 3-4 laser single tubes are linearly arranged according to the same geometric center distance; in the back row of the laser linear arrays, the 2-4 laser single tubes are linearly arrangedaccording to the same geometric center distance; the geometric center distance of each laser single tube in the front row of the laser linear arrays is the same as the geometric center distance of each laser single tube in the back row of the laser linear arrays; the laser single tubes are same in light-emitting direction, and are forward; and an optical axis of light emitted by each laser singletube in the back row of the laser linear arrays is away from the geometric center of the closest laser single tube in the front row of the laser linear arrays for 1 / 2 of the geometric center distance.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Multi-wavelength high-power modulation light source for optical fiber sensing network and use method thereof
ActiveCN101714900AImprove applicabilityIncrease flexibilityElectromagnetic transmissionLighting spectrumTime-division multiplexing
The invention provides a multi-wavelength high-power modulation light source for an optical fiber sensing network and a use method thereof. The light source comprises an intelligent signal generation module, a driving module, a superradiation diode, a multi-wavelength filter, a first Er-doped optical fiber amplifier, a wideband filter and a second Er-doped optical fiber amplifier which are connected in sequence. The use method comprises the steps of generating digital waveform, internally modulating the light source, segmenting wideband modulation light source and light spectrum and amplifying two-stage power. The invention is especially suitable for high-capacity optical fiber sensing network based on the wavelength division and time division multiplexing technology. Meanwhile, the invention has important significance on improving the cost performance of an optical fiber sensing network system and generalizing the optical fiber sensing network with lower realizing cost.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Distributed optical fiber temperature sensing system and application thereof
InactiveCN112213000AImprove detection accuracySignal widthThermometers using physical/chemical changesConverting sensor output opticallyPhotovoltaic detectorsFilter (signal processing)
The invention discloses a distributed optical fiber temperature sensing system, which comprises a pulse light source, a modulator, a circulator, a band-pass filter, a first photoelectric detector, a second photoelectric detector, a signal processing device and a driver, and an optical fiber amplifier is connected between the modulator and the circulator, and the input end of the optical fiber amplifier is connected with the light output end of the modulator; and the first light input end of the modulator is connected with the output end of the pulse light source, and the output end of the optical fiber amplifier is connected with the input end of the circulator. The system can be applied to long-distance temperature detection, the detection precision of signal light is high, the temperature detection range is wide, and the problems that a distributed optical fiber temperature sensing system in the prior art is short in detection distance and low in temperature detection precision are solved.
Owner:姚峰
Light source apparatus, optical amplifier and optical communication system
InactiveUS6856455B2Increase powerIncrease output optical powerOptical resonator shape and constructionCoupling light guidesCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
An apparatus has first and second light sources, a plurality of filters, and an optical switch. The light sources output a light beam having a spectrum determined by a gain band thereof. The plurality of filters each have a reflection band included in the gain band. The optical switch selectively couples the filters to the light source. The first and second light sources provide pumping light to a single transmission line. The first and second filters are configured so as to not reflect signal light to be amplified.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Packaging structure for a laser diode
ActiveUS9496679B2Efficiently and rapidly conductEfficiently and rapidly and dissipateSemiconductor laser arrangementsSolid-state devicesElectricityHeat conducting
The invention relates to a packaging structure for a laser diode, comprising an electrically insulated, heat-conducting board having an electronic circuit thereon; a laser diode chip mounted on the electronic circuit of the electrically insulated, heat-conducting board and having an anode and a cathode, respectively connected to an external soldering pad for external electrical connections; and a heat-conducting base installed on a surface of the electrically insulated, heat-conducting board to conduct the heat generated by the laser diode chip to the heat-conducting base through the electrically insulated, heat-conducting board, wherein the laser diode chip emits the light from an edge of the electrically insulated, heat-conducting board and the area of a faying plane between the electrically insulated, heat-conducting board and the heat-conducting base is adjusted depending on the power requirements of the laser diode, and the area of the faying plane is from 6 to 5,000 mm2.
Owner:LEE HOU CHIEH
Electrically pumped random laser device based on dual SiO2-ZnO structure and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102931583BLower threshold currentIncrease output optical powerLaser detailsLaser active region structureRandom laserCMOS
The invention provides an electrically pumped random laser device based on a dual SiO2-ZnO structure and a preparation method and application thereof. The electrically pumped random laser device comprises a first ZnO thin film, a first SiO2 thin film, a second ZnO thin film, a second SiO2 thin film and a semi-transparent electrode which are sequentially deposited on the front face of a silicon substrate from bottom to top, wherein an ohmic contact electrode is deposited on the back face of the silicon substrate. The invention also provides a preparation method of the laser device. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: 1) depositing the first ZnO thin film on the front face of the silicon substrate; 2) depositing the first SiO2 thin film on the first ZnO thin film; 3) depositing the second ZnO thin film on the first SiO2 thin film; 4) depositing the second SiO2 thin film on the second ZnO thin film; 5) sputtering the semi-transparent electrode on the second SiO2 thin film, and sputtering the ohmic contact electrode on the back face of the silicon substrate, thus obtaining the electrically pumped random laser device based on the dual SiO2-ZnO structure. According to the electrically pumped random laser device based on the dual SiO2-ZnO structure, the threshold current of is obviously reduced and the light output power is obviously improved. Moreover, the preparation method is simple, can be compatible with the conventional complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) process and is favorable for large-scale production and application of devices.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com