Storing and queuing method for blockchain transaction
A blockchain and transaction technology, applied in the blockchain field, can solve the problems of not setting transaction queuing mode, unable to change transaction queuing priority, consuming a lot of time and computing power, etc., to speed up storage speed and verification speed, Prevent zero-cost malicious swiping and improve flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Embodiment 1: This embodiment specifically illustrates the content of the storage and queuing method of blockchain transactions, as follows:
[0036] The store and queue method includes the following steps:
[0037] Step S1: Generate transaction hash value:
[0038] The blockchain system generates a transaction hash value for each transaction, and the transaction hash value is a random number with a length of 64 characters (hexadecimal);
[0039] Step S2: Write the transaction to the bitmap:
[0040] The bitmap is a list composed of multiple storage bits; each storage bit includes status code, storage space and bit number; the bit number is a random number with a length of 3 characters (hexadecimal), only the first three characters and The transaction corresponding to the transaction hash value with the same bit number is the transaction that meets the conditions; the storage space is used to store transactions, and each storage space can only store one transaction th...
Embodiment 2
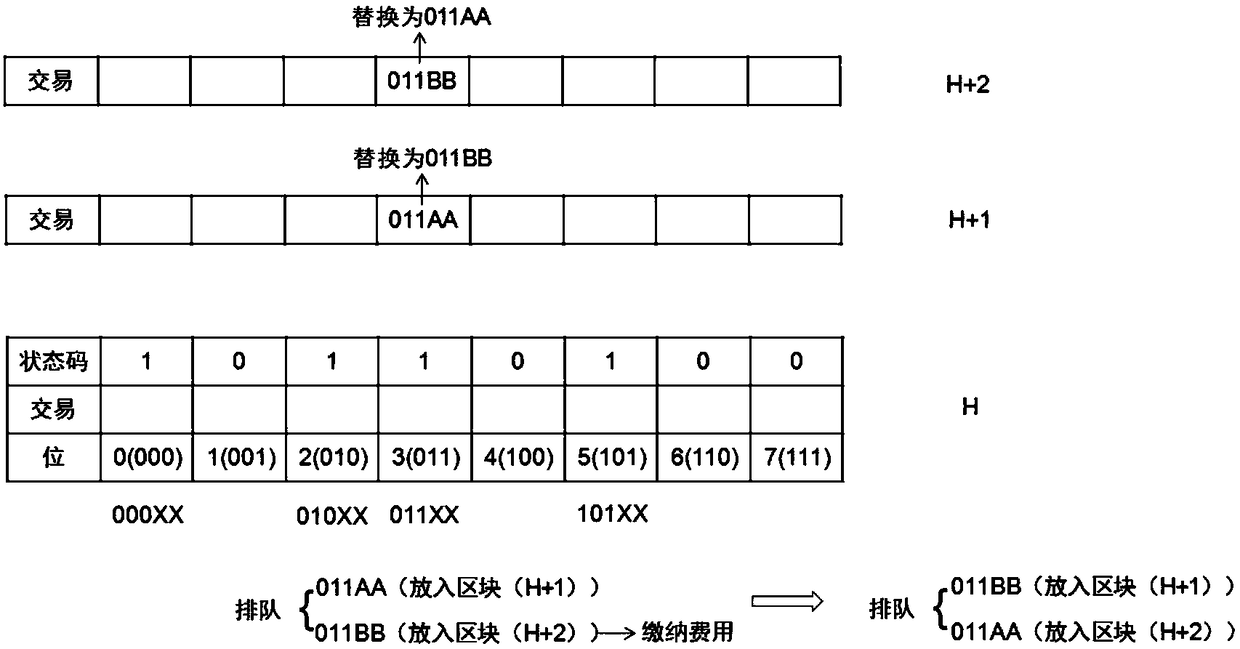
[0059] Embodiment 2: This embodiment illustrates the storage of blockchain transactions and the processing process of the queuing method, such as figure 1 and figure 2 :
[0060] Step S1: Each transaction will generate a transaction hash value.
[0061] Step S2: One bit can only store one transaction hash value that meets the conditions, and other transactions that meet the conditions will be queued, for example: the bit of 3 (011) can only store transactions with the first three transaction hash values of 011.
[0062] Step S3: The status code of the bit stored in the transaction is changed from 0 to 1, and the status code of the bit not stored in the transaction is always 0.
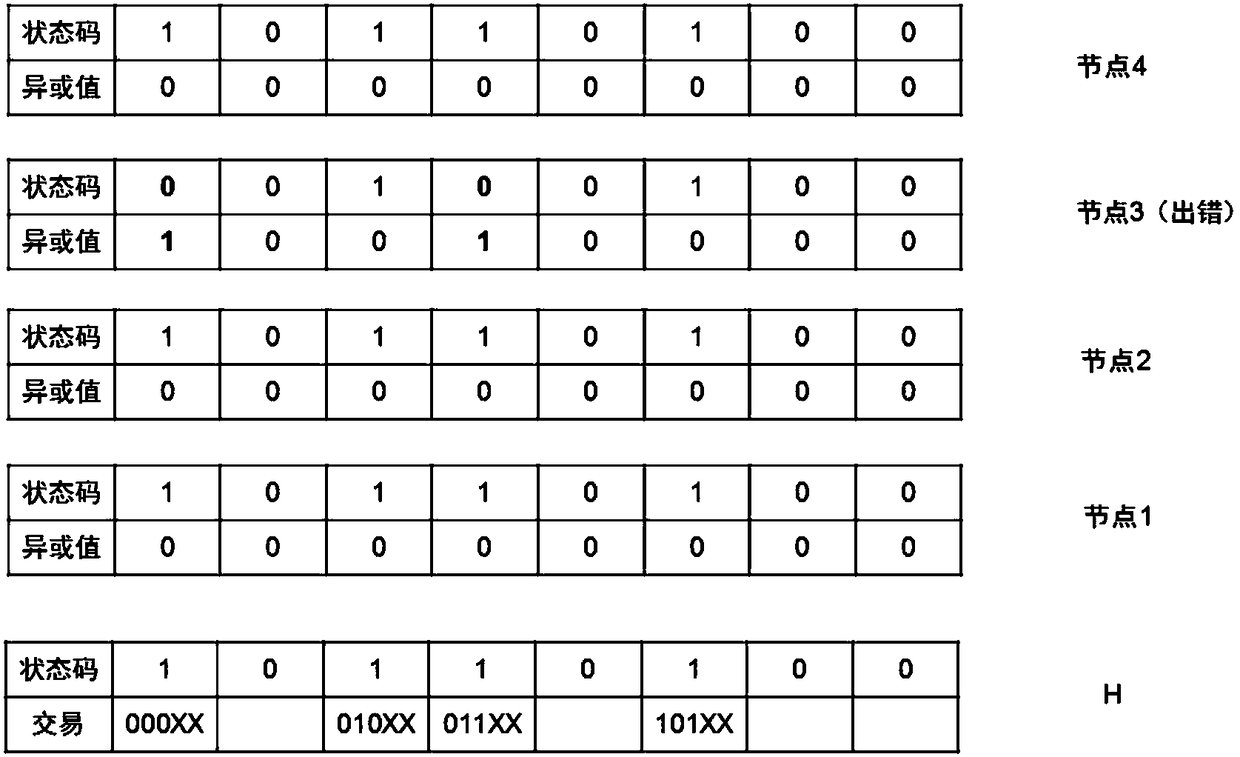
[0063] Step S4: Consensus nodes perform mining, and the consensus node N that first calculates the Merkle root hash value broadcasts the Merkle root hash value and its own bitmap to other consensus nodes.
[0064] Step S5: The remaining consensus nodes calculate the Merkle root hash value. If the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com