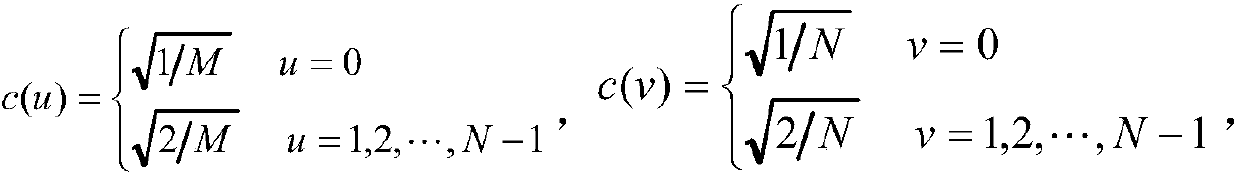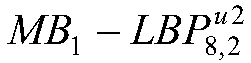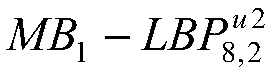Face recognition method based on MBLBP and DCT-MB2DPCA
A technology of DCT-BM2DPCA and face recognition, which is applied in the direction of character and pattern recognition, instruments, computer parts, etc., can solve the problem of low recognition rate, achieve the effect of improving recognition accuracy, reducing time, and improving recognition accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0030] Specific Embodiment 1: The face recognition method based on multi-scale block local binary pattern and discrete cosine transform bidirectional module two-dimensional principal component analysis described in this embodiment, such as figure 1 As shown, it is implemented according to the following steps:
[0031] Step 1, convert the face image from the spatial domain to the frequency domain by DCT, and then reconstruct the face image by IDCT;
[0032] Step 2. Use The operator performs feature extraction on the face image reconstructed by IDCT to obtain matrix B;
[0033] Step 3, obtain the characteristic matrix through BM2DPCA;
[0034] Step 4: Use the nearest neighbor classifier to identify the test samples.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0035] Specific implementation mode two: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one is: if figure 2 (a) and figure 2 Shown in (b), described in step 1, the human face image is converted from the spatial domain to the frequency domain by DCT, and then the reconstruction of the human face image by IDCT is realized according to the following steps:
[0036] Step 1 (1), the face image is converted to the frequency domain by DCT, the input image is first decomposed into 8×8 blocks, and then DCT is performed on each block, and the DCT transformation formula is as follows:
[0037]
[0038] In the formula M×N is the image block size obtained after the input image is transformed by DCT.
[0039] Step one (two), the face image is reconstructed by IDCT, because after the discrete cosine transform, the main information of the image is concentrated in the low-frequency component, so select 10 in the upper left corner of each image block in...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0044] Specific implementation mode three: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one or two is: the use described in step two The operator performs feature extraction on the face image reconstructed by IDCT to obtain matrix B, where, Indicates that the size of the pixel block is 1×1, and the circular 8-neighborhood LBP operator with a radius of 2 is realized according to the following steps:
[0045] Step 2 (1), the face image reconstructed by IDCT is divided into 1 * 1 pixel blocks;
[0046] Step 2 (2), obtain the mapping matrix by calculating the average gray value of each pixel block;
[0047] Step 2 (3), obtain the feature matrix represented by the low resolution of the pixel block by calculating the uniform (8,2) LBP feature of the mapping matrix;
[0048] Step two (four), restore the feature matrix represented by the low resolution, that is, expand each pixel in the matrix into a 1×1 block, and the gray value of each pixel in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com