Method for evaluating restoration effect of polluted sediment used for limnodrilus hoffmeisteri
A technology for polluting sediment and waterworms, which is applied in the direction of material inspection products, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to characterize the restoration effect of sediments, and achieve the effect of easy collection and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
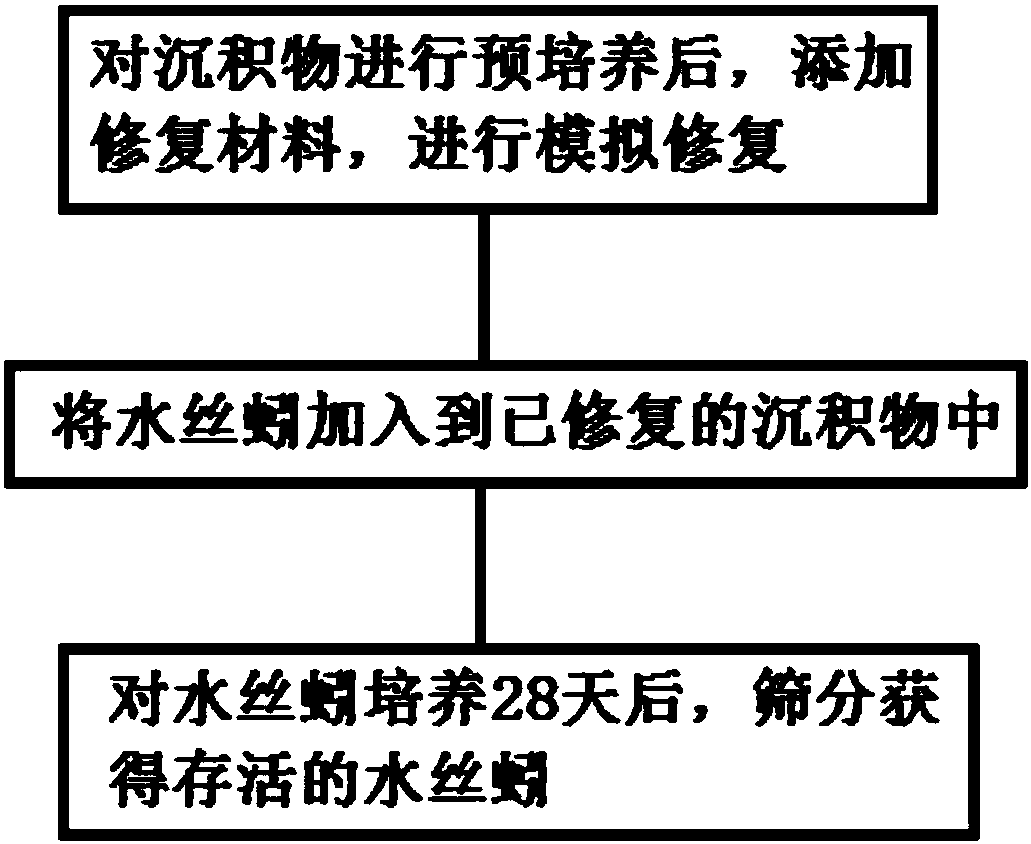
[0052] Take 20g of sediment from a heavily polluted section of a river, put it into a glass container, add 100ml of tap water after 24 hours of aeration, mix the sediment and water for 2 days, add repair materials for another 5 days. Restoration materials are added in an amount of 0-15% of the dry weight of the sediment.
[0053] Waterworms can be isolated from natural water sediments. After separation, they should be cultivated in the laboratory for more than 30 days, and then suitable waterworms should be selected for testing. The weight of selected waterworms is 8 ± 1 mg; the length is 3-5 cm.
[0054] Waterworms were added to culture for 28 days, and then the sediments of waterworms were separated with an 80-mesh sieve. Cultivate at room temperature; no feeding and water changes are performed during the cultivation process. The biomass change was determined by the total mass of water silk worms before and after cultivation.
Embodiment 2
[0056] Different from Example 1, the restoration effect index is the survival rate, and the survival rate is determined by the number of waterworms before and after cultivation.
Embodiment 3
[0058] Different from Example 1, the restoration effect index is the reproduction rate, and the reproduction rate is determined by the ratio of the number of waterworm larvae after the cultivation to the initial dosage of waterworm.
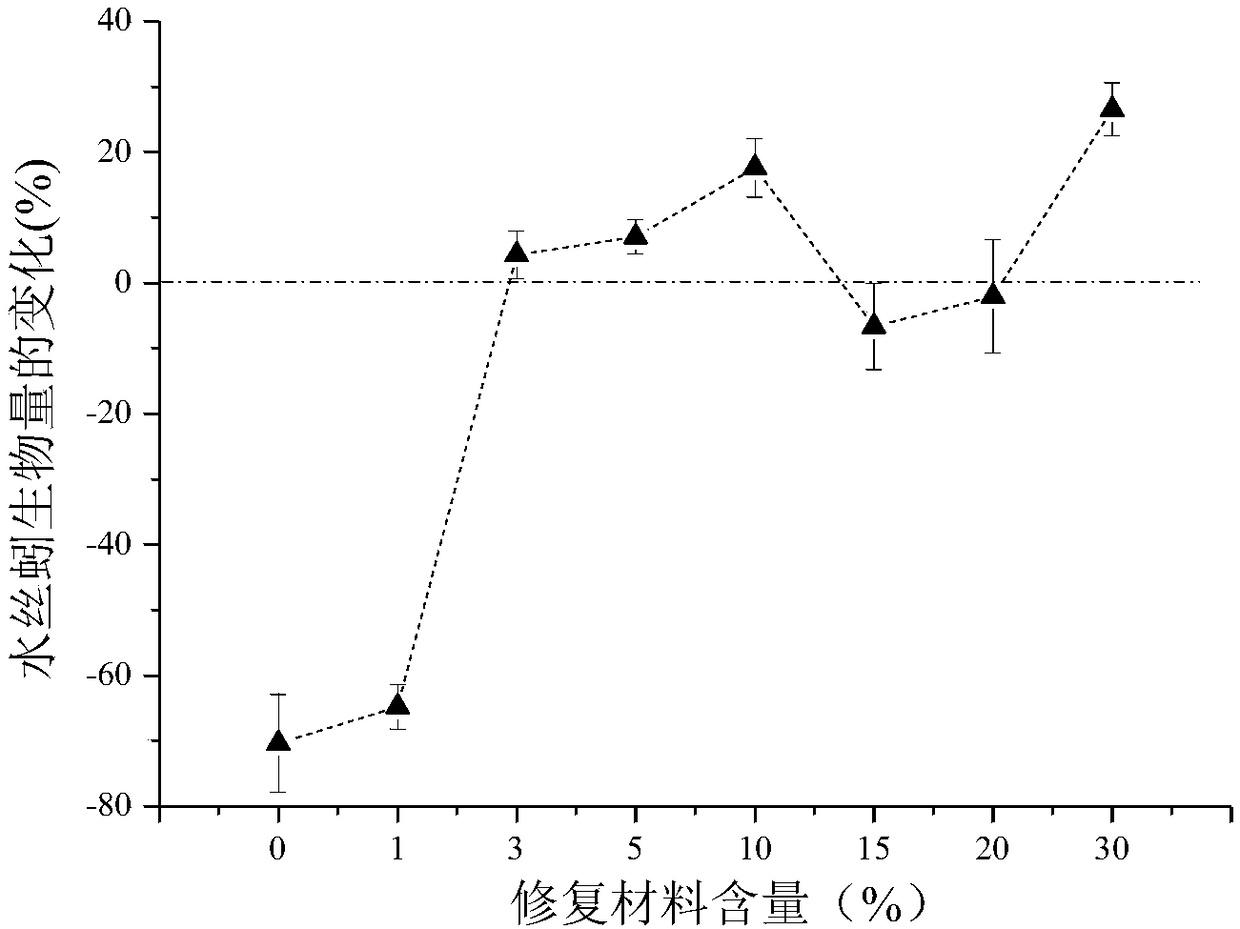
[0059] In the above-mentioned embodiment 1, after adding exogenous repair materials, the biomass change rate of water silk worms showed negative growth before no repair materials were added, and when the amount of repair materials added exceeded 3%, the change rate of water silkworm biomass increased. With the addition of restoration materials, the growth environment of waterworms was improved, and the growth rate of waterworms was significantly increased.
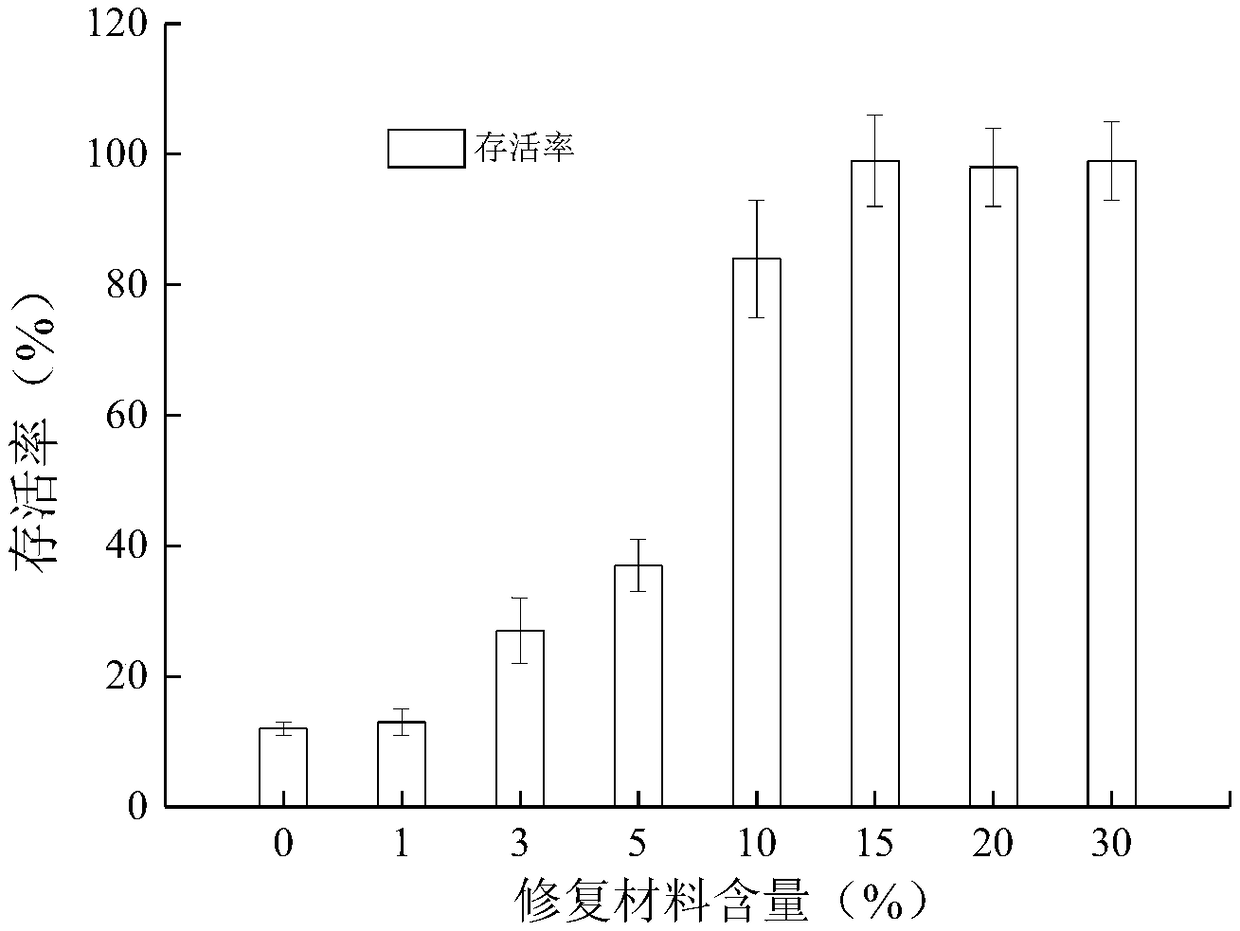
[0060] In the second embodiment above, after adding exogenous repairing materials, the survival rate of waterworms was as low as 11% before no repairing materials were added. When the amount of repairing materials added exceeded 10%, the survival rate of waterworms was over 90%. With the additi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com