Cradle rotation insensitive inertial navigation
A rotation matrix and inertial sensor technology, applied in navigation, surveying and navigation, navigation through speed/acceleration measurement, etc., can solve the problems of weakened reliability of position estimates, inaccurate misalignment calibration, increased offset, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
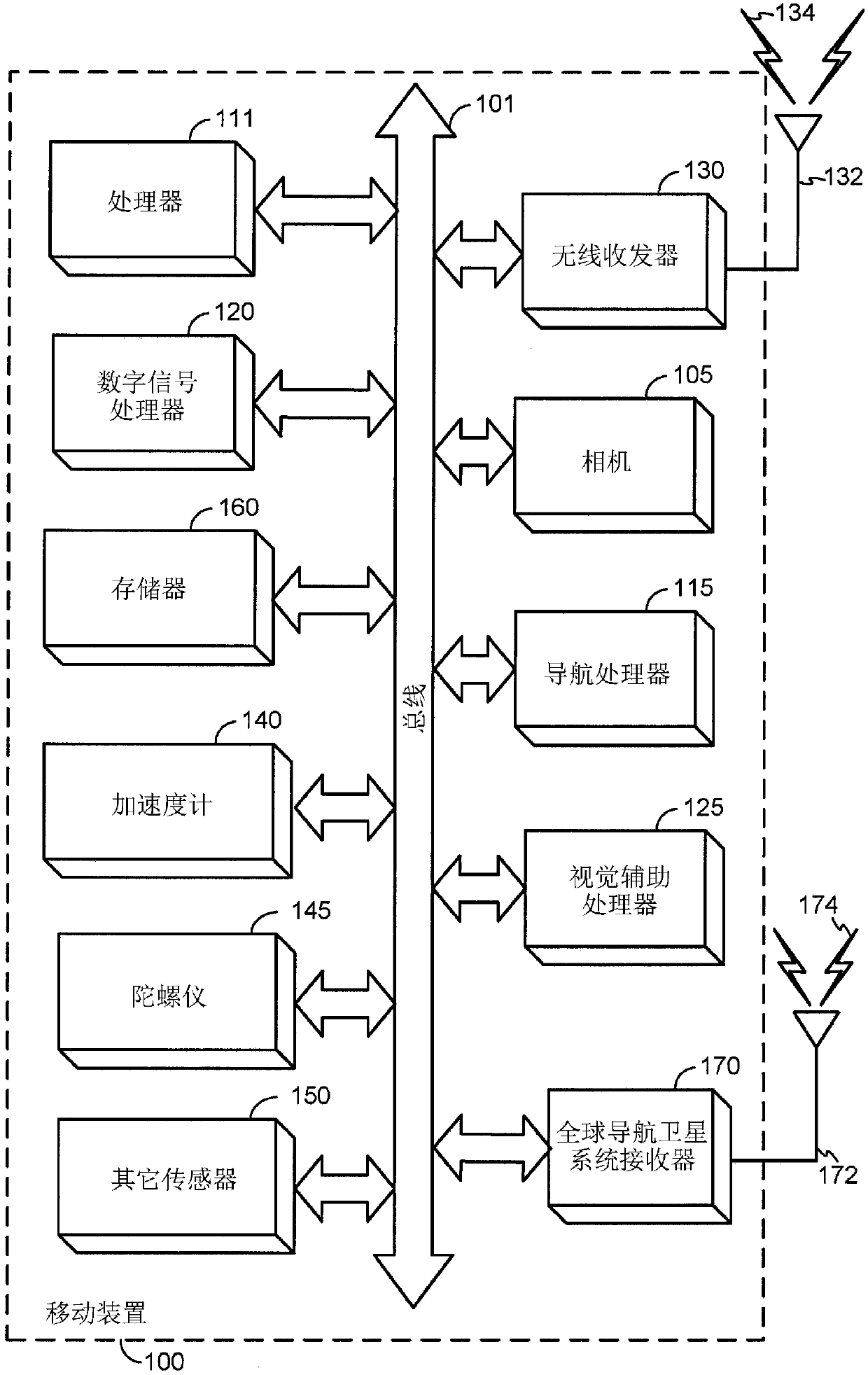
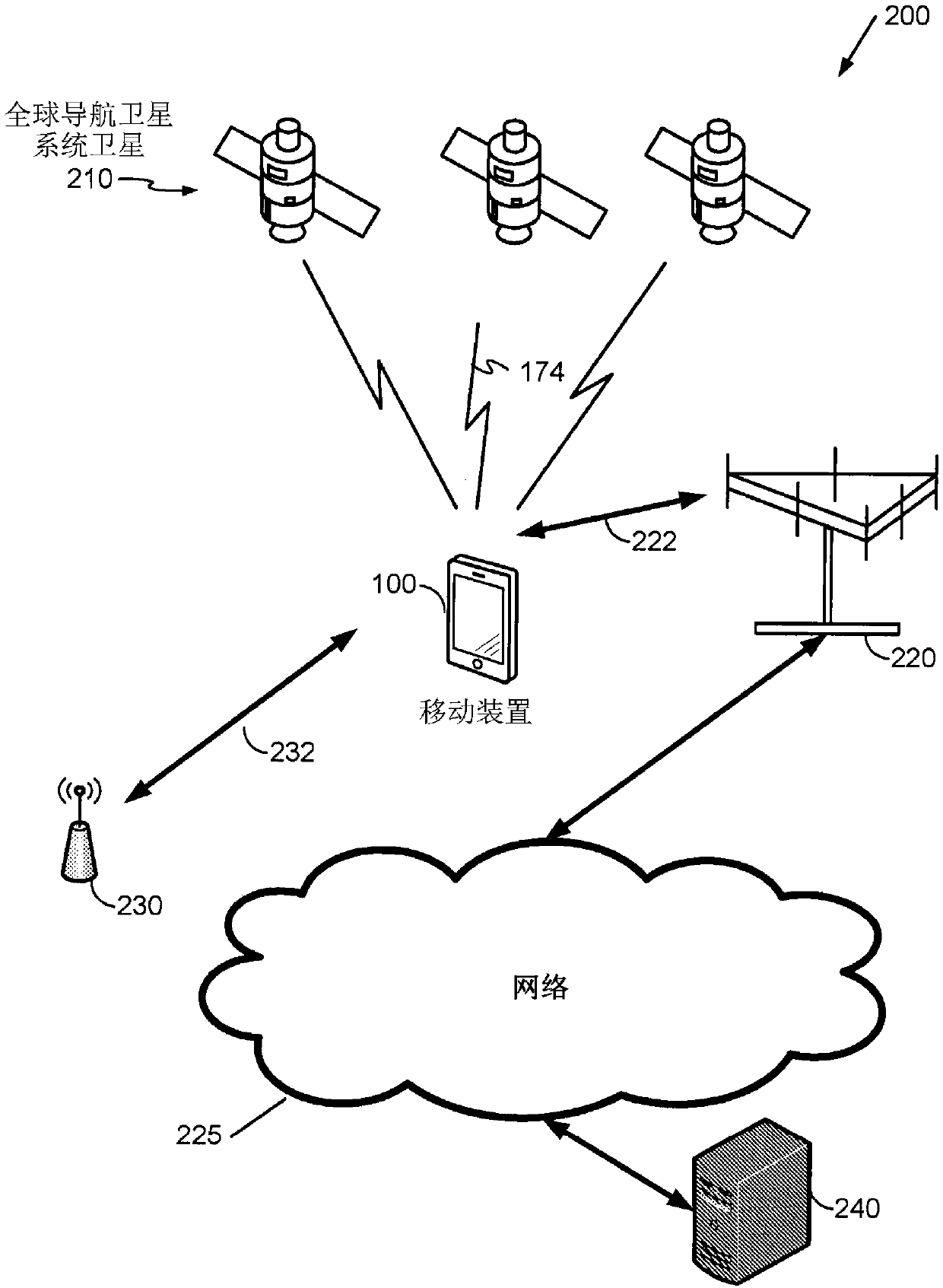
[0023]Presented herein are some example techniques that may be implemented in various methods and apparatuses in mobile devices, potentially providing or otherwise supporting cradle rotation insensitive inertial navigation. Many vehicles (eg, automobiles, bicycles, boats, recreational vehicles, etc.) include brackets configured to secure a mobile device to the vehicle. However, these brackets may allow the relative orientation between the mobile device and the vehicle to change over time. That is, the mechanical assembly within the bracket may be slack and allow the mobile device to move, or the bracket may be configured to allow the mobile device to rotate or otherwise adjust to improve the viewing angle for the user. In many systems that support GNSS and INS, misalignment between the vehicle frame (eg, v-frame) and the moving subject frame (b-frame) can be calibrated prior to using the INS. Once calibrated, in the event of a change in orientation between the v-frame and b-f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com