Sub-wavelength layered three-dimensional broadband absorbing structure based on a loss type frequency selective surface
A frequency-selective surface, sub-wavelength technology, applied in the field of electromagnetic fields and microwaves, can solve the problems of difficult low-frequency absorption performance, complex preparation process, poor absorption effect, etc., and achieve the effect of light weight, thin thickness, and wide operating frequency band.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and specific embodiment, further illustrate the present invention, should be understood that these embodiments are only for illustrating the present invention and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention, after having read the present invention, those skilled in the art will understand various aspects of the present invention Modifications in equivalent forms all fall within the scope defined by the appended claims of this application.
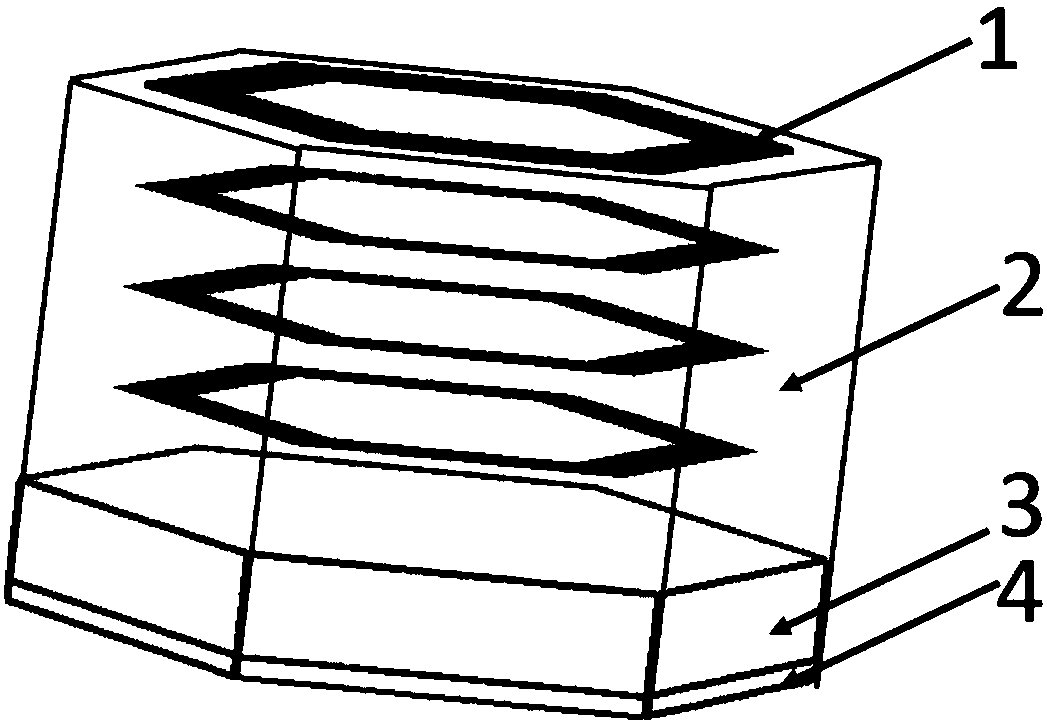
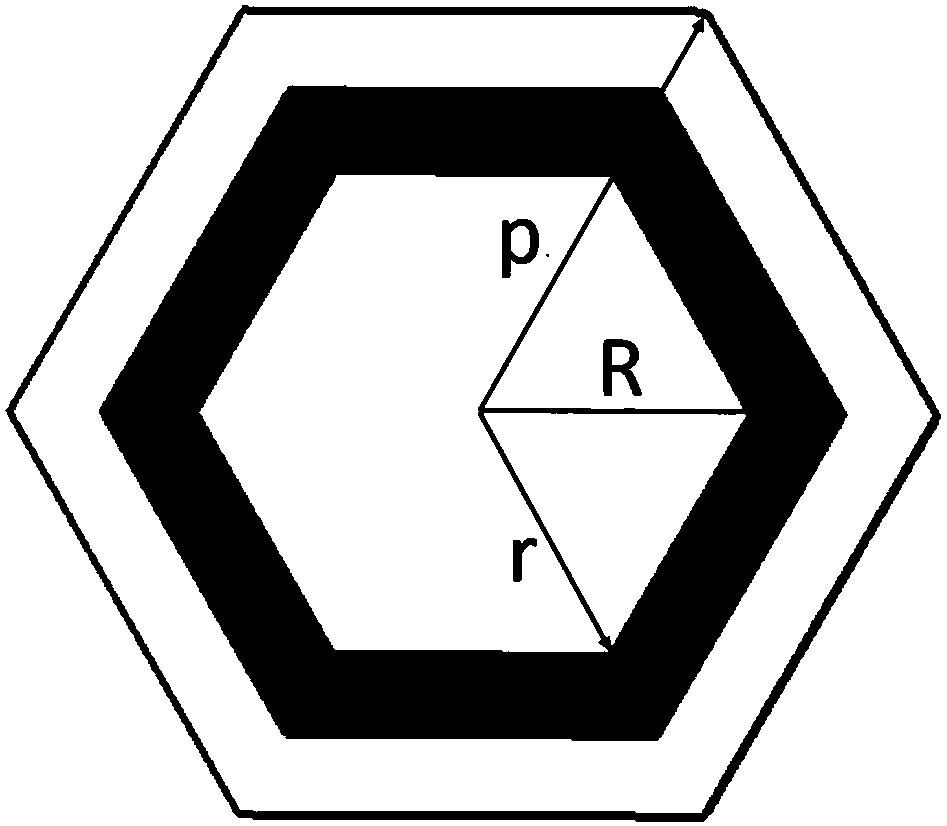
[0021] Figure 1-Figure 4 A schematic diagram showing a sub-wavelength layered three-dimensional broadband absorbing structure based on a lossy frequency selective surface according to an embodiment of the present invention. In this embodiment, the broadband absorbing structure is a periodic array structure composed of multiple structural units, where each structural unit, such as figure 1 , 2 As shown, it includes four ring-shaped loss-type frequency selective surface...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The inside diameter of | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com