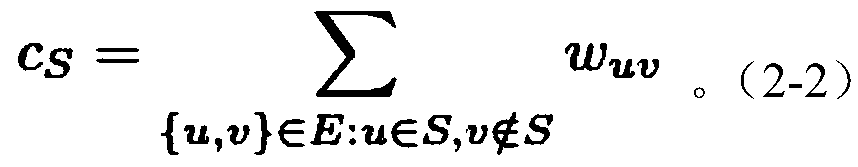Large-scale complex network oriented dense overlapping community division method
A technology of complex networks and overlapping communities, applied in the field of dense and overlapping community division, it can solve the problems of complex computing, loss of useful information, and difficulty in estimating the number of large networks, and achieve the effect of low algorithm complexity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
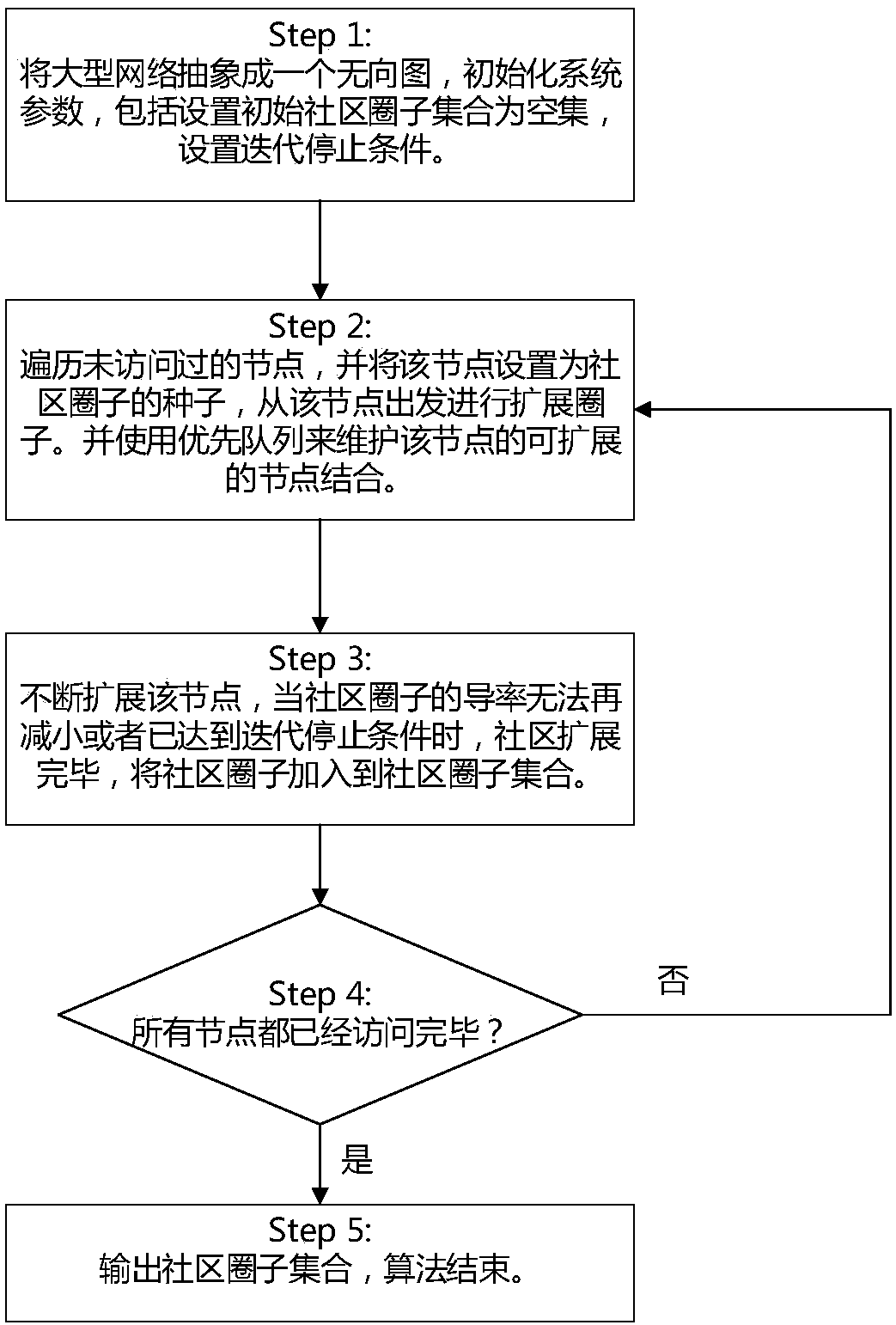
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] First, use G=(V, E) to abstractly represent a network, which is composed of undirected edges, where V represents the combination of nodes in the network, and E represents the set of edges in the network. If two nodes u, v ∈ V, if there is an edge between these two nodes, then it can be expressed as (u, v) ∈ E. Using ωuv to represent the weight between nodes, the present invention mainly considers the undirected graph, so w uv =1.
[0019] The present invention uses S to represent a collection of several nodes, and defines m S Indicates the weight of the edge in S, then:
[0020]
[0021] Define the weight of the cutting edge of S as c S , then c S defined as:
[0022]
[0023] Define N(S) as the set of neighbor nodes of S. For a neighbor node u∈N(S), the outgoing weight of node u can be defined as:
[0024]
[0025] And the inward weight of node u is:
[0026]
[0027] In the existing community mining, there are many indicators, among which Conductanc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com