Method for calculating carbon energy of urban residential building system
A technology for building systems and cities, applied in computing, instrumentation, data processing applications, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to characterize the energy consumption and carbon emissions of the building system, the inability to scientifically and rationally select the measurement points, and the inaccurate data of energy consumption and carbon emissions. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
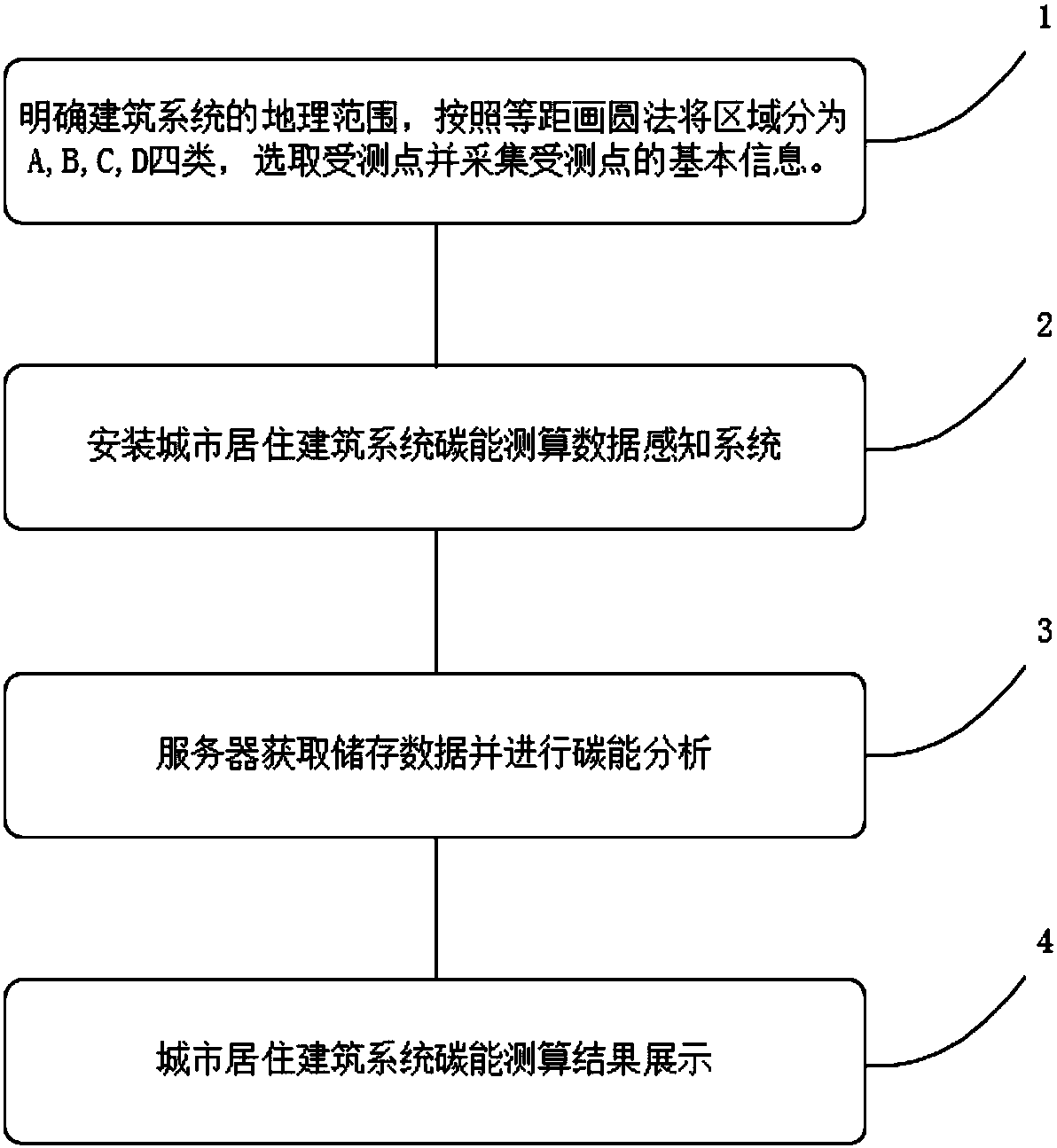
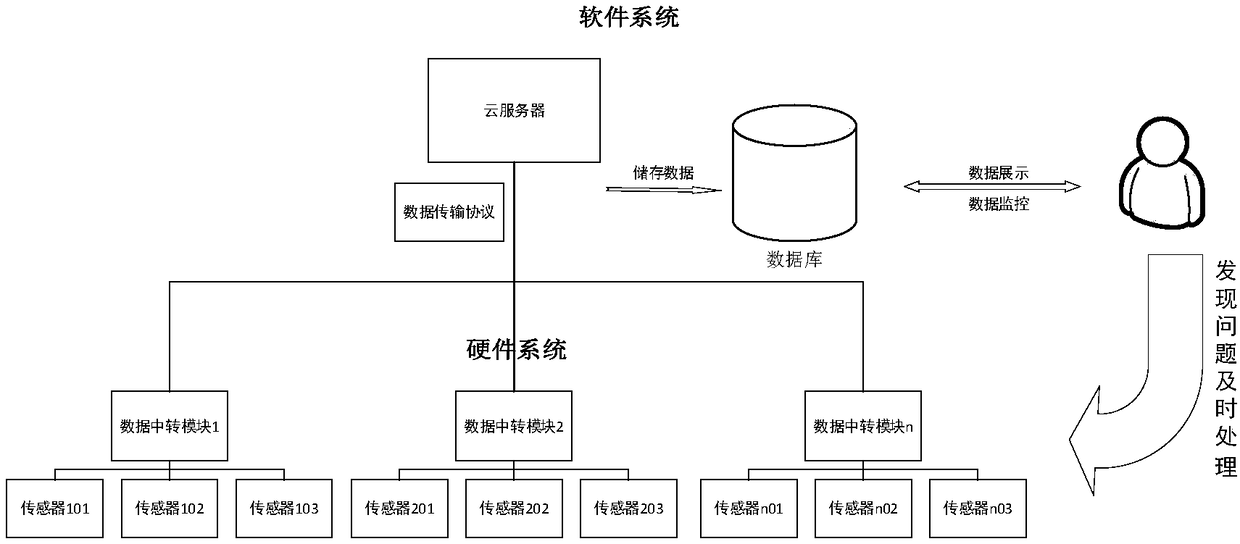
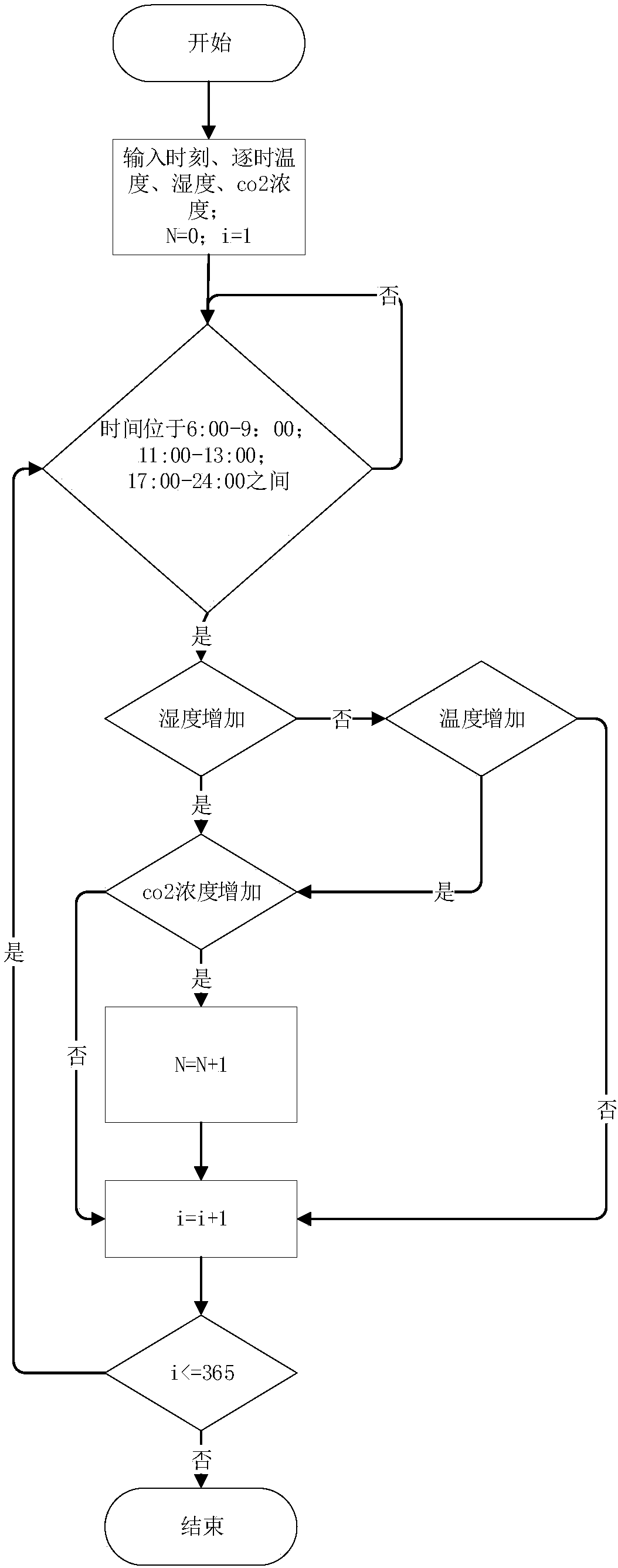
[0076] A residential area in Beilin District, Xi'an City was selected as a building system, and the carbon energy of this system was measured and calculated. The methods include:
[0077] (1) Define the geographic scope of the urban residential building system to be monitored and draw the outline on the map, then find out the winter heating and heat exchange stations within the area occupied by the system or close to the area, and use each exchange station The heat station is the center of the circle, draw a circle with a radius of 100m, 300m, and 500m respectively, and divide the area into A (100m) area, B (300m) area, C (500m) area, and D (more than 500m) area. The distance determines that the user needs to consume energy in the transmission of the heating pipe network when the temperature is adjusted in winter. At least 5 measured points are randomly selected in each type of area, and finally the floor plan is drawn for the building units of each measured point And survey, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com