Method for quickly judging whether retired battery can be subjected to cascading utilization
A step-by-step, fast technology, applied in the field of rapid judgment of whether decommissioned batteries can be used in steps, can solve problems such as the inability to realize fast regrouping and the inability to quickly judge the re-use of retired batteries, so as to save resources, judge accuracy, and reduce wasteful effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
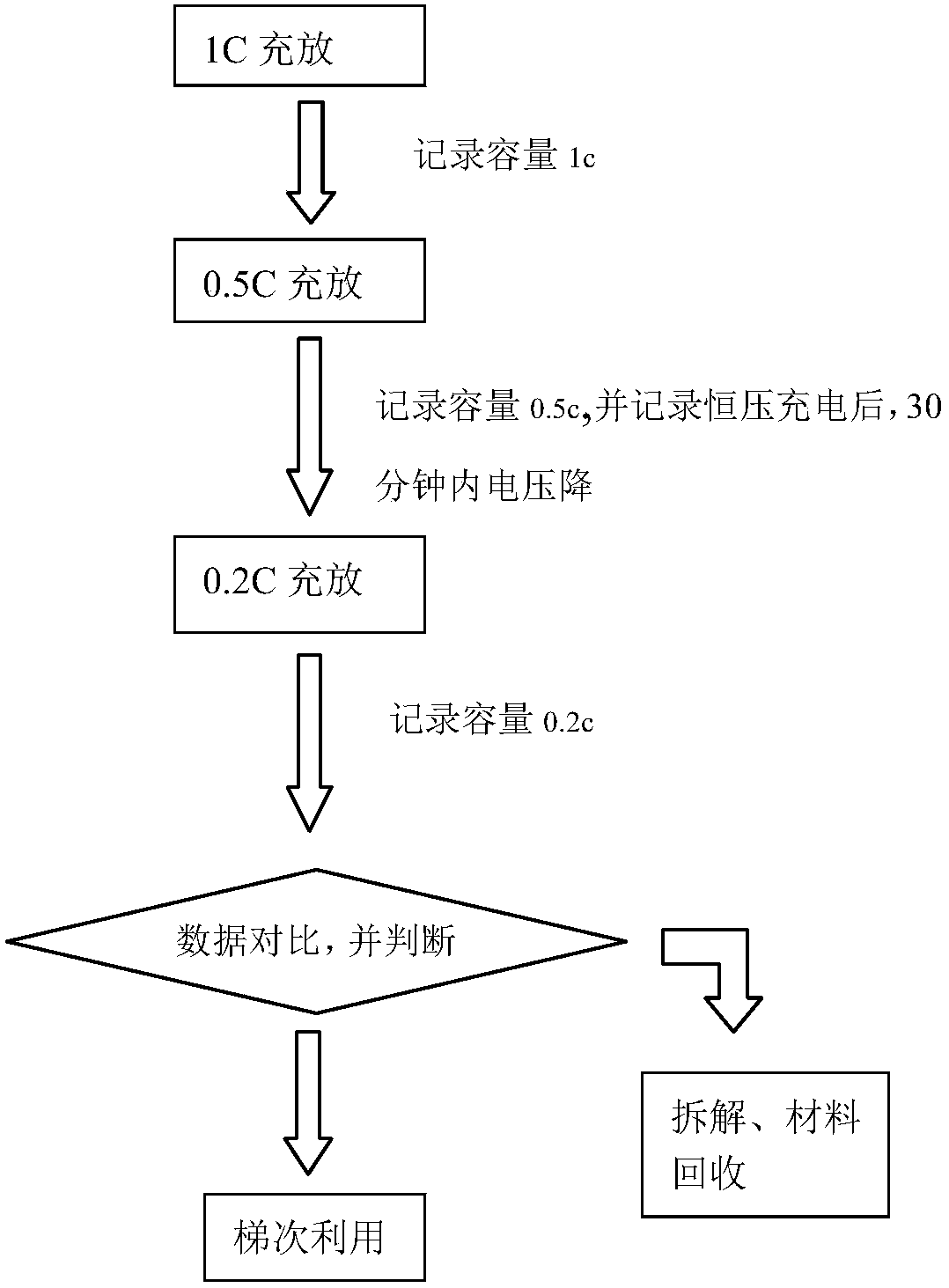
[0025] In this example, 4 batteries (ternary) were subjected to 1C, 0.5C, 0.2C normal temperature cycles respectively, and the capacity and voltage drop within 30 minutes after charging at 0.5C constant current and constant voltage were recorded;
[0026] 1# cell: capacity 1C ≈Capacity 0.5C ≈Capacity 0.2C ; 30 minutes after 0.5C constant current and constant voltage charging, the voltage drop > 0.06V, discarded; dismantling found that the battery core was seriously decomposed of lithium, and the electrolyte was dry;
[0027] 2# cell: capacity 1C ≈Capacity 0.5C ≈Capacity 0.2C ;After charging at 0.5C constant current and constant voltage within 30 minutes, the voltage drop > 0.1V, discarded; after the cycle, the battery cell swelled significantly, dismantling found that the battery cell was seriously decomposed of lithium, the pole pieces turned dark red, and the electrolyte dried up;
[0028] 3# cell: capacity 1C 0.5C 0.2C ; After 0.5C constant current and constant voltag...
Embodiment 2
[0032] In this example, 4 batteries (lithium iron) were subjected to 1C, 0.5C, and 0.2C normal temperature cycles respectively, and the capacity and voltage drop within 30 minutes after charging at 0.5C constant current and constant voltage were recorded;
[0033] 1# cell: capacity 1C ≈Capacity 0.5C ≈Capacity 0 .2C; 0.5C constant-current constant-voltage charging within 30 minutes after the voltage drop > 0.2V, discarded; dismantling found serious lithium deposition in the battery cell, and the electrolyte dried up;
[0034] 2# cell: capacity 1C ≈Capacity 0.5C ≈Capacity 0.2C ; 30 minutes after 0.5C constant current and constant voltage charging, the voltage drop > 0.5V, discarded; after the cycle, the battery cell swelled significantly, dismantling found that the battery cell was seriously decomposed of lithium, the pole pieces turned dark red, and the electrolyte dried up;
[0035] 3# cell: capacity 1C 0.5C 0.2C ; After 0.5C constant current and constant voltage chargin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com