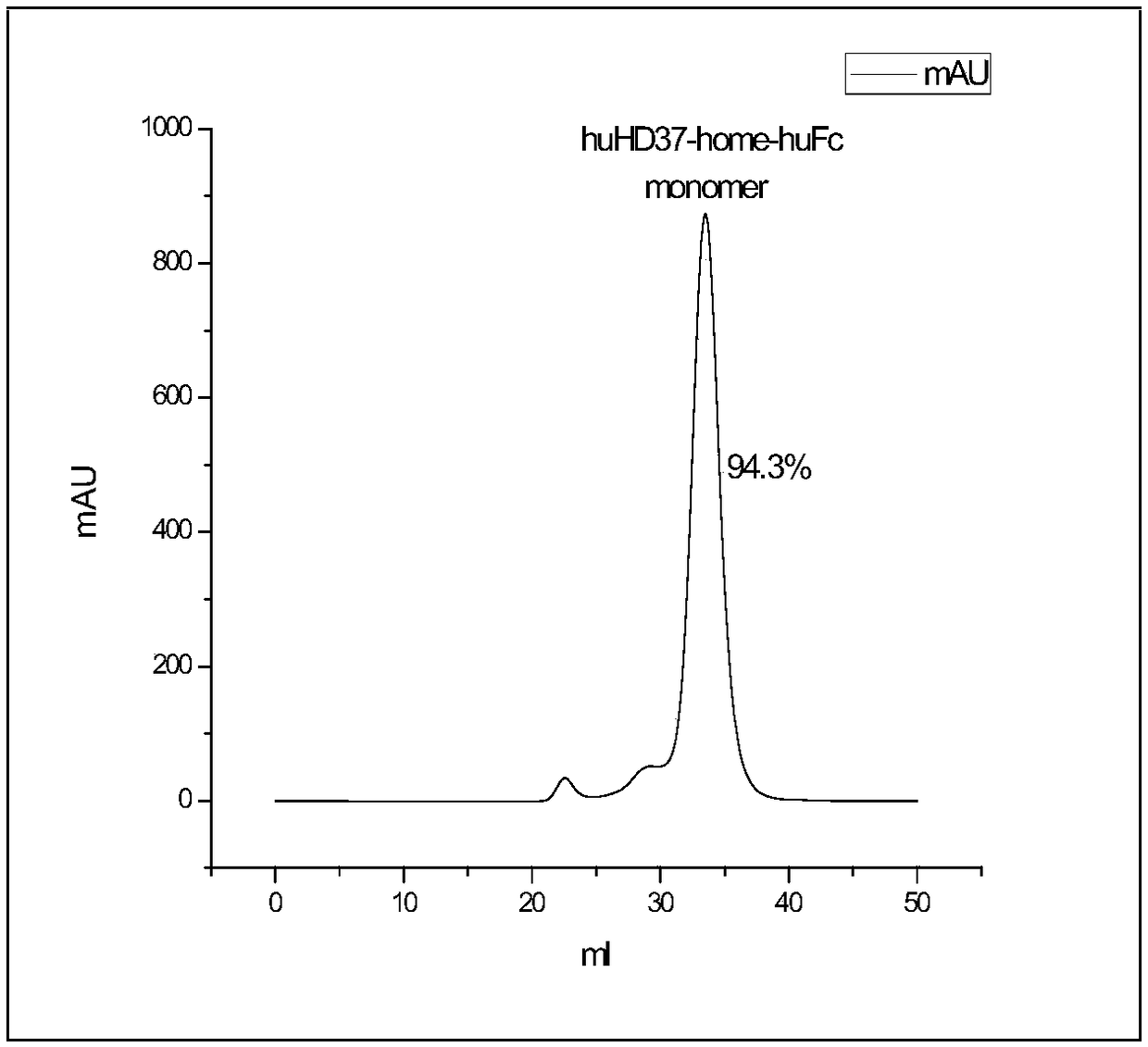
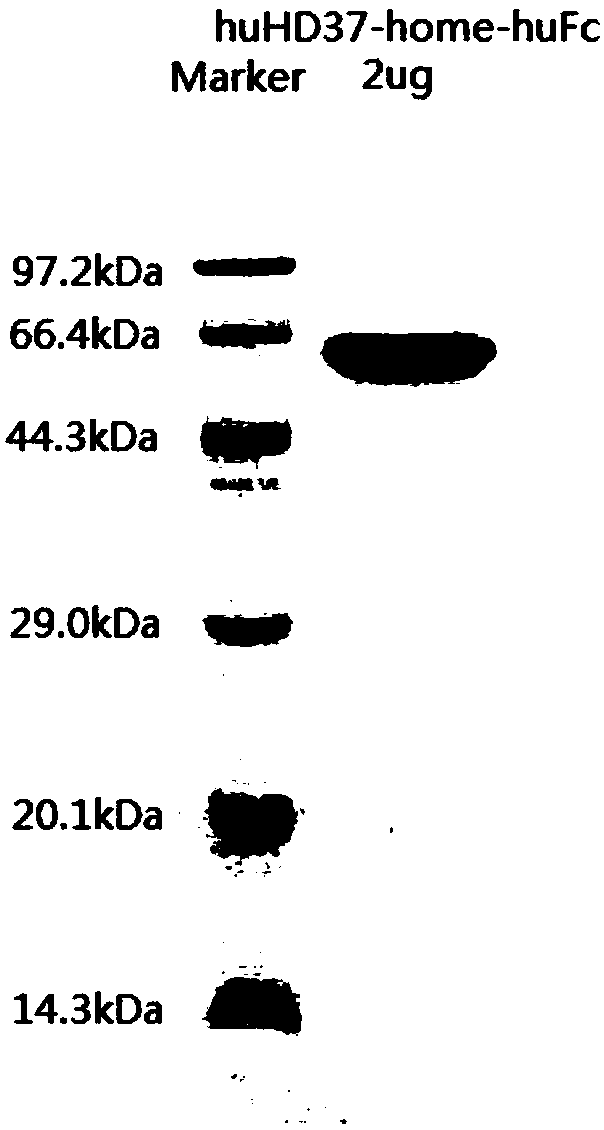
Humanized antibody against CD19 and immune effector cells targeting to CD19
A technology of humanized antibodies and antibodies, applied to genetically modified cells, cells modified by introducing foreign genetic material, animal cells, etc., can solve the problems of antibody affinity and specificity reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0143] Example 1. Preparation of humanized antibody huHD37 of anti-CD19 antibody HD37
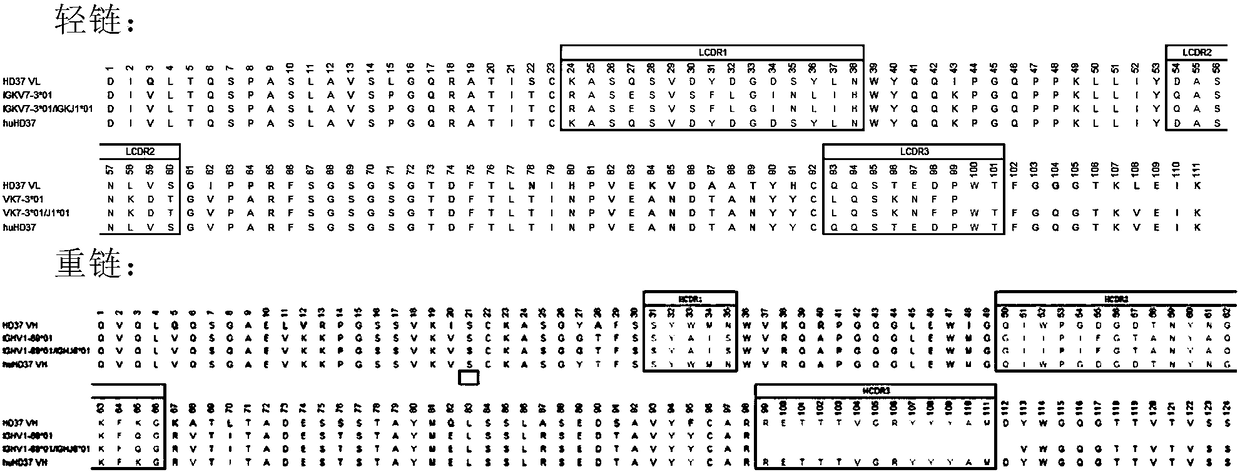
[0144] In this embodiment, mouse anti-HD37 (J Immunol.1987May 1; 138(9):2793-9) is used as the parental antibody. Mouse anti-HD37 has the light chain variable region shown in SEQ ID NO: 19 and SEQ ID NO: The heavy chain variable region shown in 20 combined the nomenclature of Kabat, Chothia and IMGT three antibody CDR regions, and determined the six CDR region sequences of the antibody light chain and heavy chain:
[0145] Light chain variable region (SEQ ID NO: 19), CDR regions are underlined.
[0146] DIQLTQSPASLAVSLGQRATISC KASQSVDYDGDSYLN WYQQIPGQPPKLLIY DASN LVS GIPPRFSGSGSGTDFTLNIHPVEKVDAATYHC QQSTEDPWT FGGGTKLEIKR
[0147] Heavy chain variable region (SEQ ID NO: 20) CDR regions are underlined
[0148] QVQLQQSGAELVRPGSSVKISCKASGYAFS SYWMN WVKQRPGQGLEWIG QIWPGDGDTNYNGKFKG KATLTADESSSTAYMQLSSLASEDSAVYFCAR RETTTVGRYYYAM DYWGQGTTVTVSS
[0149] a. Selection of Antibody Templ...
Embodiment 2
[0165] The transformation of embodiment 2.huHD37
[0166] In this example, huHD37 was used as the parental antibody, and huHD37 was transformed by the method of phage display. The construction of the phage library based on the humanized antibody huHD37 retained the CDR3 region of the light chain and the heavy chain. Two phage libraries were constructed by randomizing the CDR1 and CDR2 of the light chain or the CDR1 and CDR2 of the heavy chain respectively through degenerate primers. Primer information is shown in the table below.
[0167] No.
name
sequence
Length
1
LMF
CAGGAAACAGCTATGACCATGATTAC
26
2
C37H1R
CACTCCAGGCCCTGGCCGGGGGCCTGCCGCACCCAMNNMNNMNNMNNMNNMNNGAAGGTGTAGCCGCTGGCCT
73
3
C37H2F
ccggccagggcctggagtggatgggcNNKATCNNKCCNNKNNKGGCNNKACCNNKtacaacggcaagttcaagggc
77
4
Fd
GACGTTAGTAAATGAATTTTCTGTATGAGG
30
5
C37L1R
CTGGCCGGGCTTCTGCTGGTACCAMNNMNNNGTAMNNMNNMNNMNNMNNMNNMNNGCTM...
Embodiment 3
[0175] Example 3. Construction of anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor plasmid (CAR)
[0176] 3.1 Construction of humanized antibody chimeric antigen receptor plasmid (CAR)
[0177] Using PRRLSIN-cPPT.EF-1α as the vector, the lentiviral plasmids expressing the second and fourth generation chimeric antigen receptors of humanized antibody huHD37 were constructed, including PRRLSIN-cPPT.EF-1α-huHD37-28Z, PRRLSIN- cPPT.EF-1α-huHD37-BBZ, PRRLSIN-cPPT.EF-1α-huHD37-28Z&IFNb and PRRLSIN-cPPT.EF-1α-huHD37-BBZ&IFNb ( Figure 10 ). The huHD37-28Z sequence consists of CD8α signal peptide (SEQ ID NO: 23), huHD37scFV, CD8hinge (SEQ ID NO: 25), CD28 transmembrane domain (SEQ ID NO: 27) and intracellular signaling domain (SEQ ID NO: 29 ) and the intracellular segment CD3ξ (SEQ ID NO: 31) of CD3; the huHD37-BBZ sequence consists of CD8α signal peptide (SEQ ID NO: 23), huHD37scFV, CD8hinge (SEQ ID NO: 25) and transmembrane domain (SEQ ID NO: 33), CD137 intracellular signaling domain (SEQ ID N...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com