Constant voltage output circuit
A constant voltage, output circuit technology, applied to electrical components, adjusting electrical variables, power oscillators, etc., can solve problems such as changes in bias current values, and achieve the effects of reducing output voltage deviation and low power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach )
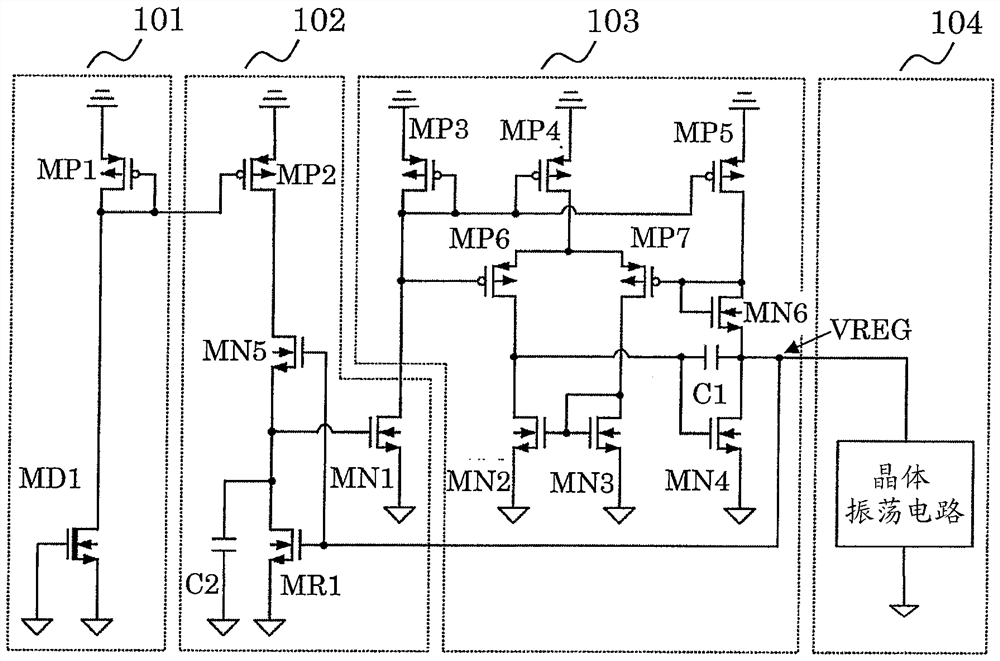
[0019] exist figure 1 The first embodiment of the constant voltage output circuit of the present invention is shown in . The constant voltage output circuit of this embodiment is as figure 1 As shown, a constant current circuit 101, a bias current control circuit 102, and a constant voltage circuit 103 are provided. The constant current circuit 101 is composed of an N-channel depletion transistor (depletion transistor) MD1 and a PMOS transistor MP1. Bias current control circuit 102 is composed of PMOS transistor MP2 and NMOS transistors MN1, MN5, and MR1. The constant voltage circuit 103 is composed of PMOS transistors MP3, MP4, MP5, MP6, MP7 and NMOS transistors MN2, MN3, MN4, MN6. Let the output node of the constant voltage circuit 103 be the VREG node, and let the voltage between the power supply and the VREG node be the voltage of the VREG node.
[0020] The connection of the constant current circuit 101 will be described. Connect the source terminal of transistor M...
no. 2 approach )
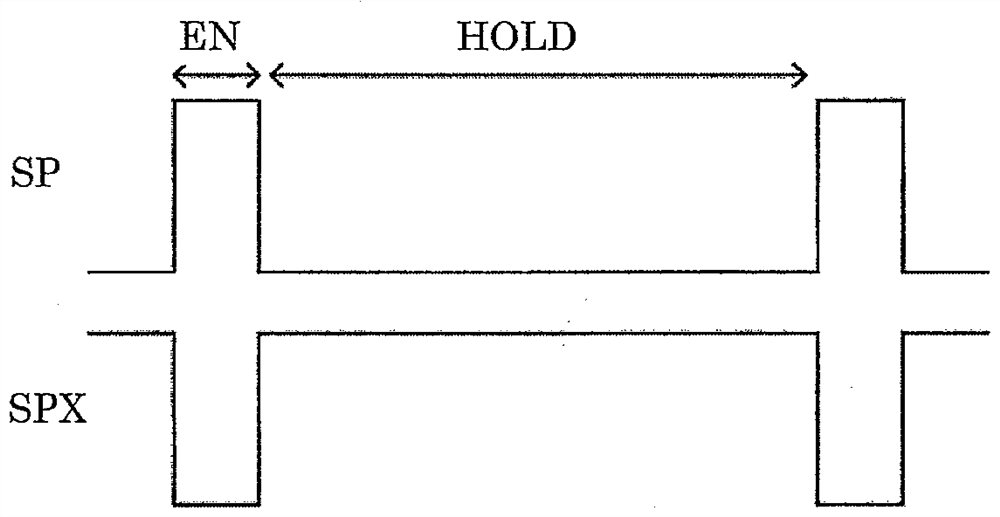
[0029] exist figure 2 A second embodiment of the constant voltage output circuit of the present invention is shown in . This circuit structure is used to reduce the power consumption of the constant voltage output circuit itself. In this embodiment, a switch for performing a sample-and-hold operation, a sample-and-hold signal generating circuit for generating a signal for causing the switch to perform the sample-and-hold operation, and a hold circuit are provided. generate image 3 The shown sample-and-hold signal is applied to the switch, and the operation of the constant voltage circuit is stopped to maintain the state when it is enabled, thereby reducing power consumption.
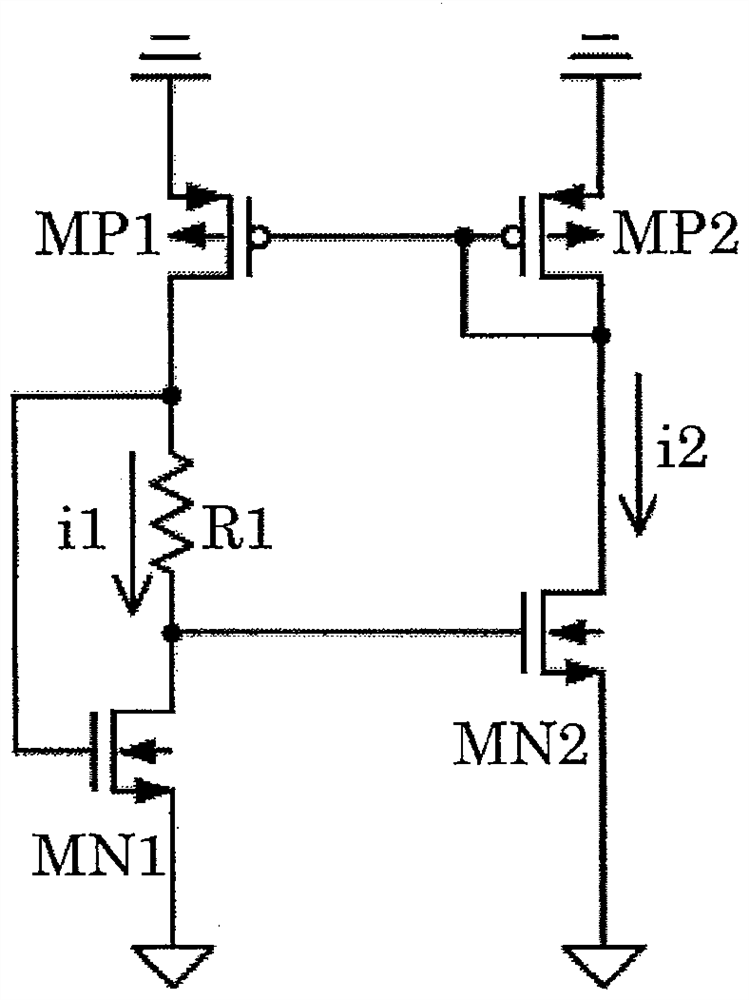
[0030] Differences in configuration between the second embodiment and the first embodiment will be described. Such as figure 2 As shown, the constant current circuit 101 and the bias current control circuit 102 are the same as those of the first embodiment.
[0031] Differences in the configurati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com