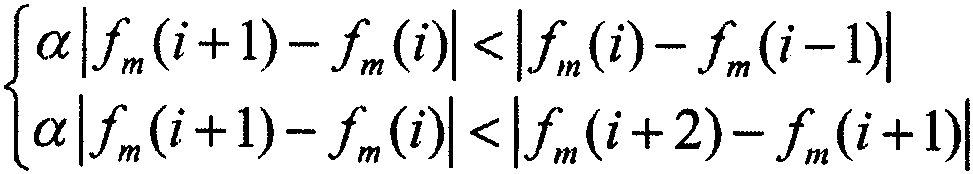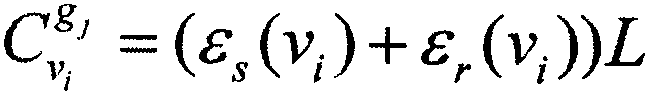Deployment method for a plurality of water surface sink nodes of underwater wireless sensor network
A wireless sensor and sensor node technology, applied in the field of monitoring, can solve the problems of limiting the application of underwater wireless sensor networks, limited battery energy, affecting the life cycle of underwater wireless sensor networks, etc., so as to reduce network transmission delay and reduce energy consumption. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
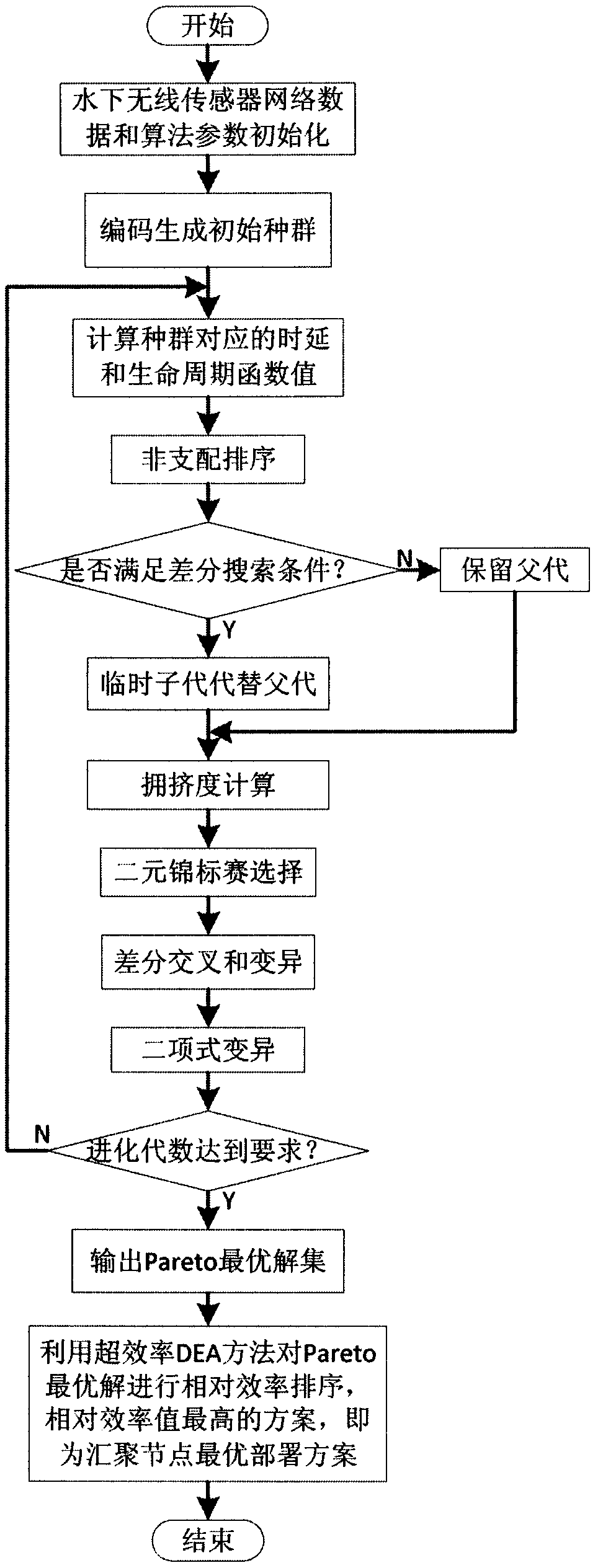
[0039] A method for deploying multiple aggregation nodes on the water surface of an underwater wireless sensor network, comprising the following steps:
[0040] 1. According to the energy consumption of sending data between the nodes of the underwater wireless sensor network, the energy consumption of receiving data and the initial energy of the nodes, the life cycle model of the underwater wireless sensor network is established.
[0041] Let the initial energy of each sensor node be the same and both be q 0 , the unit is J, ignoring the energy consumption of sensor nodes in idle state, only considering the energy consumption of nodes when sending and receiving data. ε s represents the sensor node v i The power required to send each packet, ε r represents the sensor node v i The power required to receive each packet, then node v i assigned to sink node g j The energy consumed by forwarding a packet of length L when for:
[0042]
[0043] then node v i has a life c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com