Application of rice alpha-isopropyl malate synthase gene
A technology of malate synthase and isopropyl, which is applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, acyltransferase, etc., and can solve the problem of few varieties or resource applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1: Gene Cloning
[0035] The sequence of the OsIPMS1 gene was cloned by PCR using the japonica rice variety Nipponbare cDNA as a template. The sequence of the upstream primer is shown in SEQ ID NO.3 in the sequence table, and the sequence of the downstream primer is shown in SEQ ID NO.4 in the sequence table. The nucleotide sequence and amino acid sequence of the rice OsIPMS1 gene are obtained, the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1 in the sequence table, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2.
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2: Mutant construction
[0037] Analyze the target gene, find NGG (N is A, T, C or G) in the CDs region sequence of the gene, preferably AGG, take the 20bp in front of NGG as the target sequence, clone the target fragment, and the upstream primer sequence As shown in the sequence listing SEQ ID NO.5, the downstream primer sequence is shown in the sequence listing SEQ ID NO.6. T4 ligase was used to connect the 20 bp target fragment in the above OsIPMS1 gene to the CH vector to obtain the CH-Target recombination vector. The pCAMBIA1300 and CH-target vectors were digested with EcoRI HF and Hind III respectively, and the digested products were detected by 1.2% agarose gel, and the vector pCAMBIA1300 and fragment CH-target were recovered by cutting the gel respectively; p1300-CH-Target recombination was obtained by using T4Ligase carrier.
[0038] The constructed rice OsIPMS1CRISPR / Cas9 mutant gRNA target sequence is shown in the sequence table as SEQ ID NO.7; the ...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Example 3: Phenotype Analysis of Gene Mutants
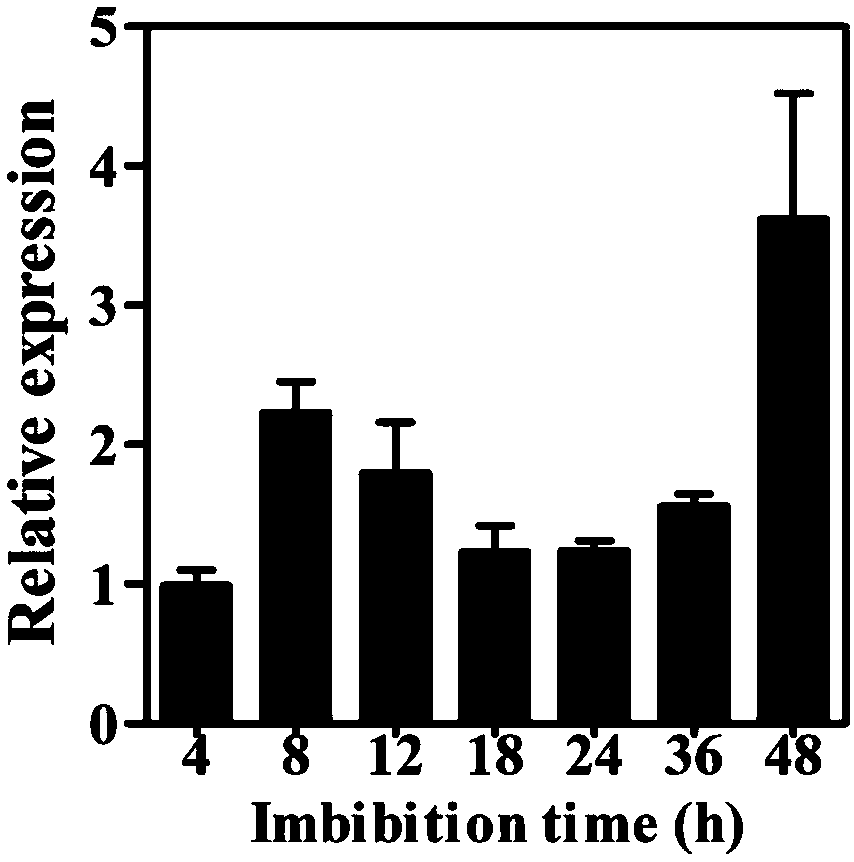
[0040]Seed germination experiments were carried out using the constructed OsIPMS1CRISPR / Cas9 mutant osipms1a, osipms1b seeds, and wild-type Nipponbare (WT) rice varieties. The specific method is as follows: each time repeatedly select 50 healthy and plump seeds, sterilize the surface with 0.1% mercuric chloride solution for 5 minutes, rinse with distilled water for 3 times, dry the surface of the seeds, and place them on a petri dish with two layers of filter paper (diameter 9 cm), add 10 mL of distilled water, place at 30°C under light / dark conditions for 12 hours and culture for 5 days, and finally count the seedling rate. The experiment was repeated 3 times. The results showed that compared with the control seeds, the germination speed of the mutant seeds was slow and uneven, and the seedling growth was significantly weaker ( figure 1 ). It can be seen that the gene plays an important role in improving the germinatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com