Weight learning based stack shape planning method
A stack-shaped and weighted technology, applied in the field of logistics, can solve the problems of low efficiency, lack of macro planning, low degree of automation, etc., and achieve the effect of simple use and clear parameters.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019] The technical solution of this patent will be further described in detail below in conjunction with specific embodiments.
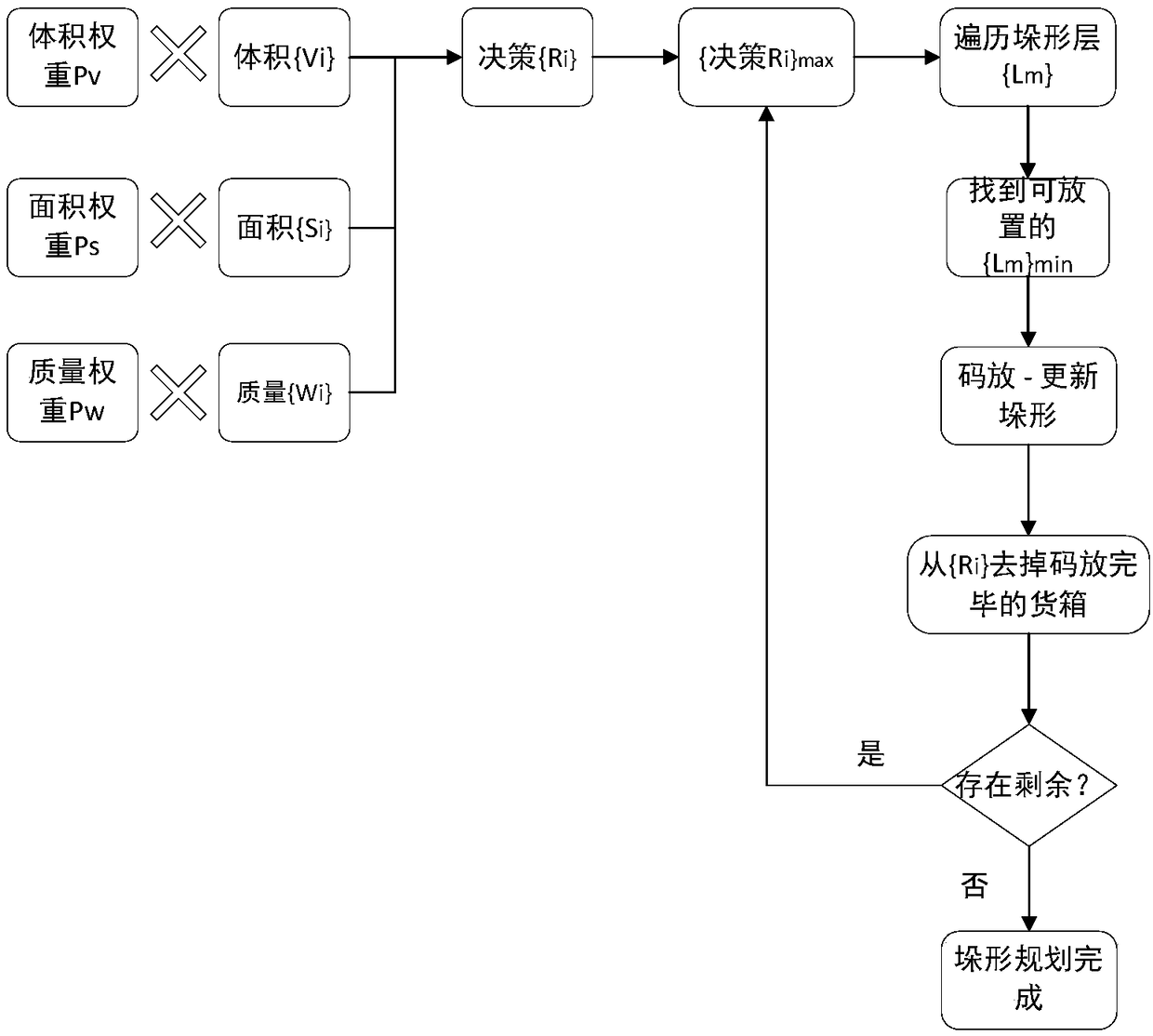
[0020] Cut Figure 1-3 , a stack planning method based on weight learning, the specific steps are as follows:
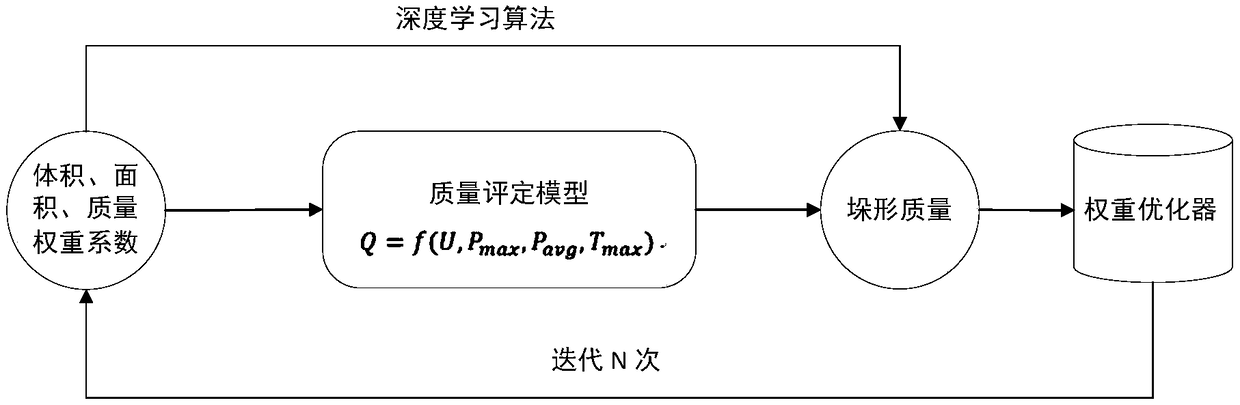
[0021] Step 1, automatic stacking planning: calculate the priority rate of stacking for all boxes to be stacked{R i},R i =P v V i +P s S i +P w W i , where P V is the volume weight, V i is the volume of the container, P S is the area weight, S i is the area of the container, P w is the mass weight, W i is the quality of the container, where i∈[1,n] represents the number of the container;
[0022] Step two, the R i Arrange in order from large to small, that is, to get the stacking order of the container;
[0023] Step 3, take the current {R i}max container, try to put it into L 1 to L k , until a stackable layer L is found m , L m is the number of layers of the container stack, m ∈ [1, k], indicating the number of la...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com