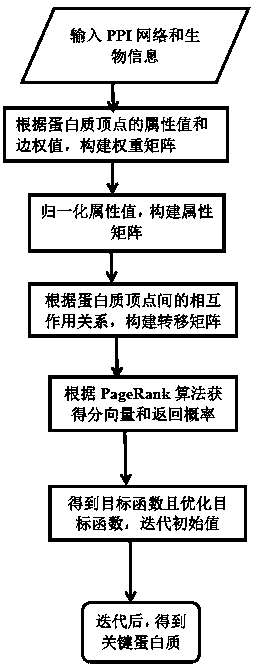
Key protein identification method based on Markov random walk
A random walk and identification method technology, applied in the field of bioinformatics, can solve problems such as false positives in protein interaction data, neglect of protein biological characteristics, and noise in PPI networks, so as to expand the application range and practicability, and overcome data noise High, efficiency-enhancing effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
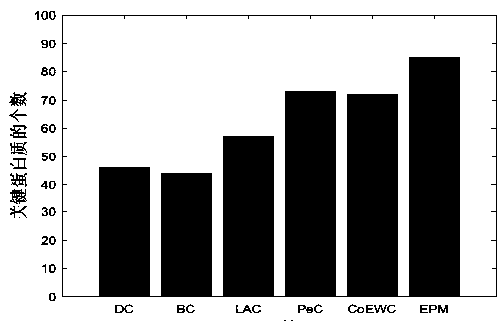
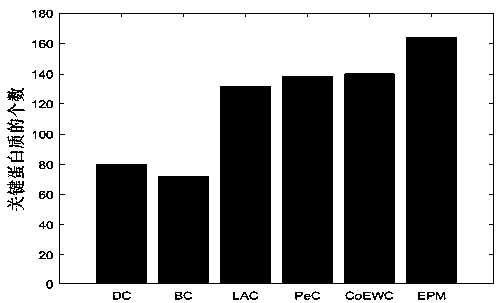
[0076] To verify the performance of the proposed algorithm EPM in this chapter, we compared the number of key proteins identified with other five methods (DC, BC, LAC, PeC and CoEWC). For each method, we select the protein recognition results of top100, top200, top300, top400, top500, and top600 as candidate sets, and then intersect the proteins in each candidate set with the standard key protein set to obtain the real key in the candidate set The amount of protein, the experimental results are shown in Figure 2.
[0077] from Figure 2a , 2b , 2c, 2d, 2e, and 2f, it can be seen that in the yeast PPI network, the algorithm EPM proposed by us can achieve better results than other methods in identifying key proteins. When the top500 and top600 key proteins are used as candidate sets, the number of proteins identified by the algorithm proposed in this chapter is significantly higher than other methods. Among them, compared with the PeC method, when extracting the top100, top20...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com