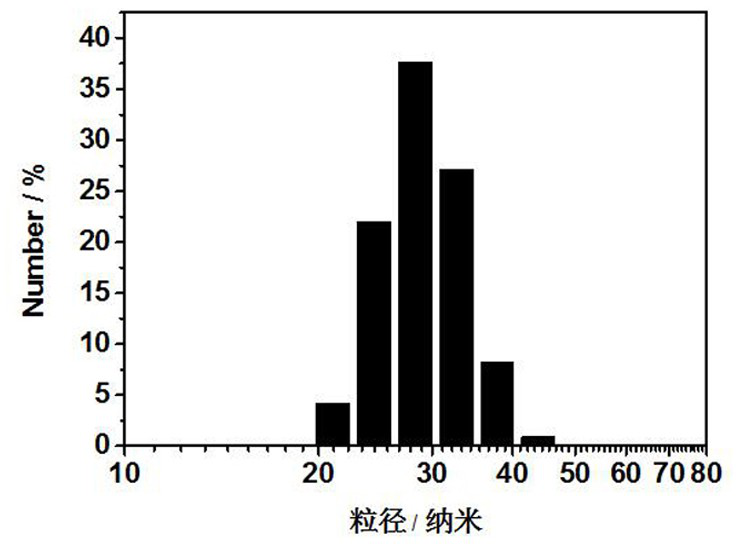
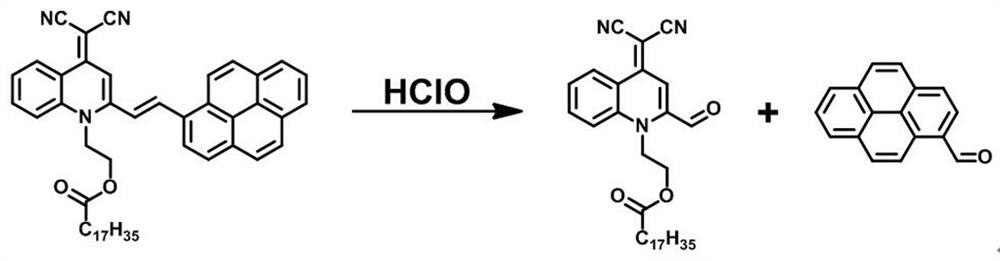
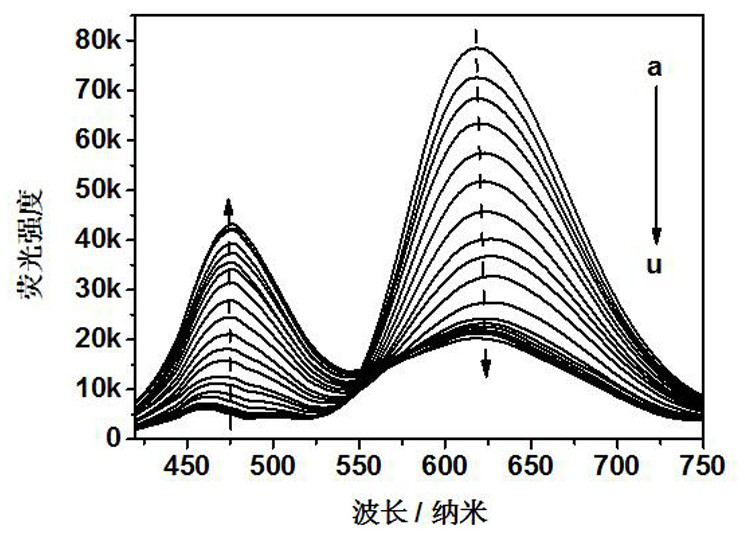
Aie-based polymer ratiometric fluorescent sensor capable of rapidly detecting hypochlorous acid and its preparation method and application
A technology for detecting hypochlorous acid and ratiometric fluorescence, applied in the field of preparation of AIE fluorescence sensors, can solve the problems of reduced feasibility, limited applicability, and unresolved ACQ
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027]Example 1: A preparation of a polymer ratio fluorescence sensor based on AIE-based polyethylene chloric acid, specific steps:
[0028](1) 2- (1- (2-hydroxyethyl) -2-methyl quinoline-4 (1) prepared according to the prior artH) - subunit) proprialonitrile (2 mmol) and hard ester chloride (3 mmol) were dissolved in 25 mL of tetrahydrofuran, triethylamine (3 mmol) was added, placed in N.2Under the conditions of protecting and expanding light, at room temperature 24 h, the reaction was rotated after the reaction was completed, and most (85 to 95%) of the solvent was removed, the column was separated from the pure product, dried in vacuo, and product 1;
[0029](2) The product 1 (0.387 mmol) and hydrocetaldehyde (0.774 mmol) were dissolved in a mixed solution of acetonitrile (15 mL) and tetrahydrofuran (15 mL), and a small amount of piperidine (5 droplets) was added to N.2Under the conditions of protecting and expanding light, the reflux 24 h, and the reaction was rotated after the reacti...
Embodiment 2
[0031]Example 2: An AIE-based speed detecting hypochlorous acid polymer ratio fluorescence sensor is prepared, and the specific steps are:
[0032](1) 2- (1- (2-hydroxyethyl) -2-methyl quinoline-4 (1) prepared according to the prior artH) - subunit) proprialonitrile (1.5 mmol) and hard ester chloride (3 mmol) were dissolved in 20 mL of tetrahydrofuran, triethylamine (3 mmol) was added, placed in N.2Under the conditions of protecting and expanding light, at room temperature 24 h, the reaction was rotated after the reaction was completed, and most (85 to 95%) of the solvent was removed, the column was separated from the pure product, dried in vacuo, and product 1;
[0033](2) The product 1 (0.25 mmol) and hydrocetaldehyde (0.774 mmol) were dissolved in a mixed solution of acetonitrile (10 mL) and tetrahydrofuran (10 mL), and a small amount of piperidine (2 droplets) was added to N.2Under the conditions of protecting and expanding light, reflux 20 h, and the reaction was evaporated after the...
Embodiment 3
[0035]Example 3: An AIE-based faster detection hypochlorous acid-based polymer ratio fluorescence sensor, specific steps:
[0036](1) 2- (1- (2-hydroxyethyl) -2-methyl quinoline-4 (1) prepared according to the prior artH) - subunit) propennitrile (3 mmol) and hard ester chloride (3 mmol) were dissolved in 30 mL of tetrahydrofuran, triethylamine (3 mmol) was added, placed in N2Under the conditions of protecting and expanding light, at room temperature 24 h, the reaction was rotated after the reaction was completed, and most (85 to 95%) of the solvent was removed, the column was separated from the pure product, dried in vacuo, and product 1;
[0037](2) The product 1 (0.5 mmol) and hydrocetaldehyde (0.774 mmol) were dissolved in a mixed solution of acetonitrile (20 mL) and tetrahydrofuran (20 mL), and a small amount of piperidine (10 droplets) was added to N.2Under the conditions of protecting and protected, refluxed 30 h, and the reaction was rotated after the reaction was evaporated, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com