Vehicle steady-state intelligent control method and device
A technology of intelligent control and steady-state control, applied in the field of automobiles, can solve problems such as driving safety hazards and reducing driving comfort
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
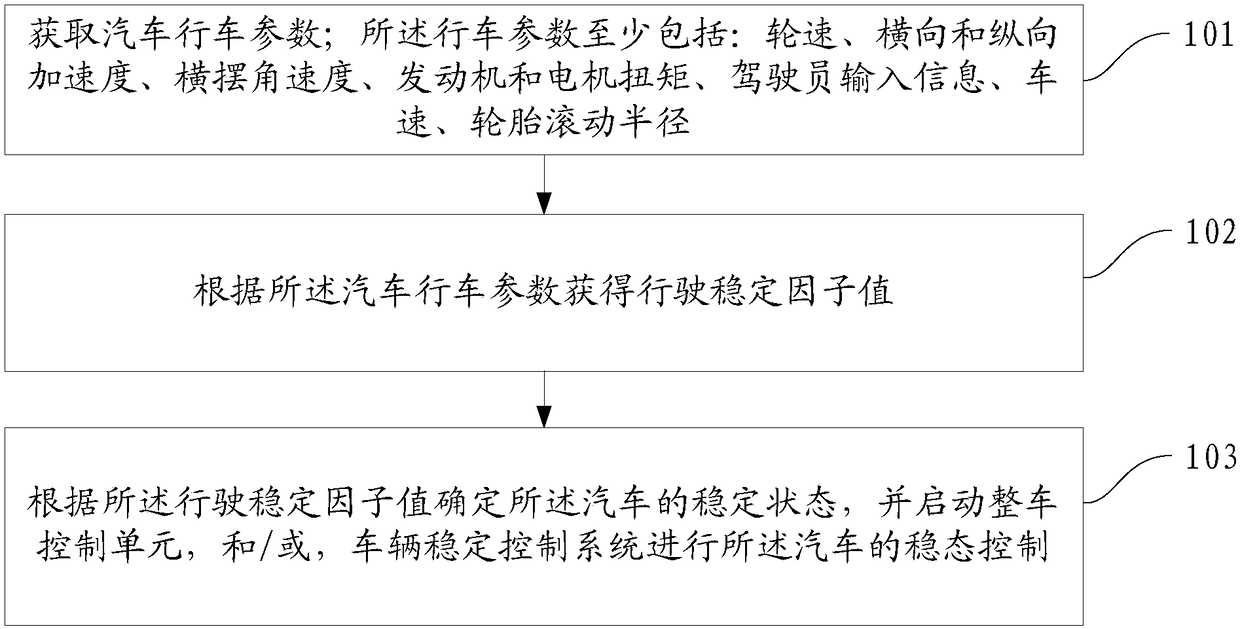
[0043] refer to figure 1 , which is a flow chart of a vehicle steady-state intelligent control method described in an embodiment of the present invention, may specifically include the following steps:
[0044]Step 101 , obtain vehicle driving parameters; the driving parameters at least include: wheel speed, lateral and longitudinal acceleration, yaw rate, engine and motor torque, driver input information, vehicle speed, and tire rolling radius.
[0045] In the embodiment of the present invention, a hybrid vehicle refers to a vehicle that can be driven by fuel or electricity. Usually, the VSC system and the yaw rate sensor are used to measure the yaw rate, the lateral accelerometer to measure the lateral acceleration, and the longitudinal accelerometer to measure the yaw rate. Measure the longitudinal acceleration, the wheel speed sensor measures the wheel speed, the steering wheel angle sensor measures the value of the driver input information such as the steering wheel angle,...
Embodiment 2
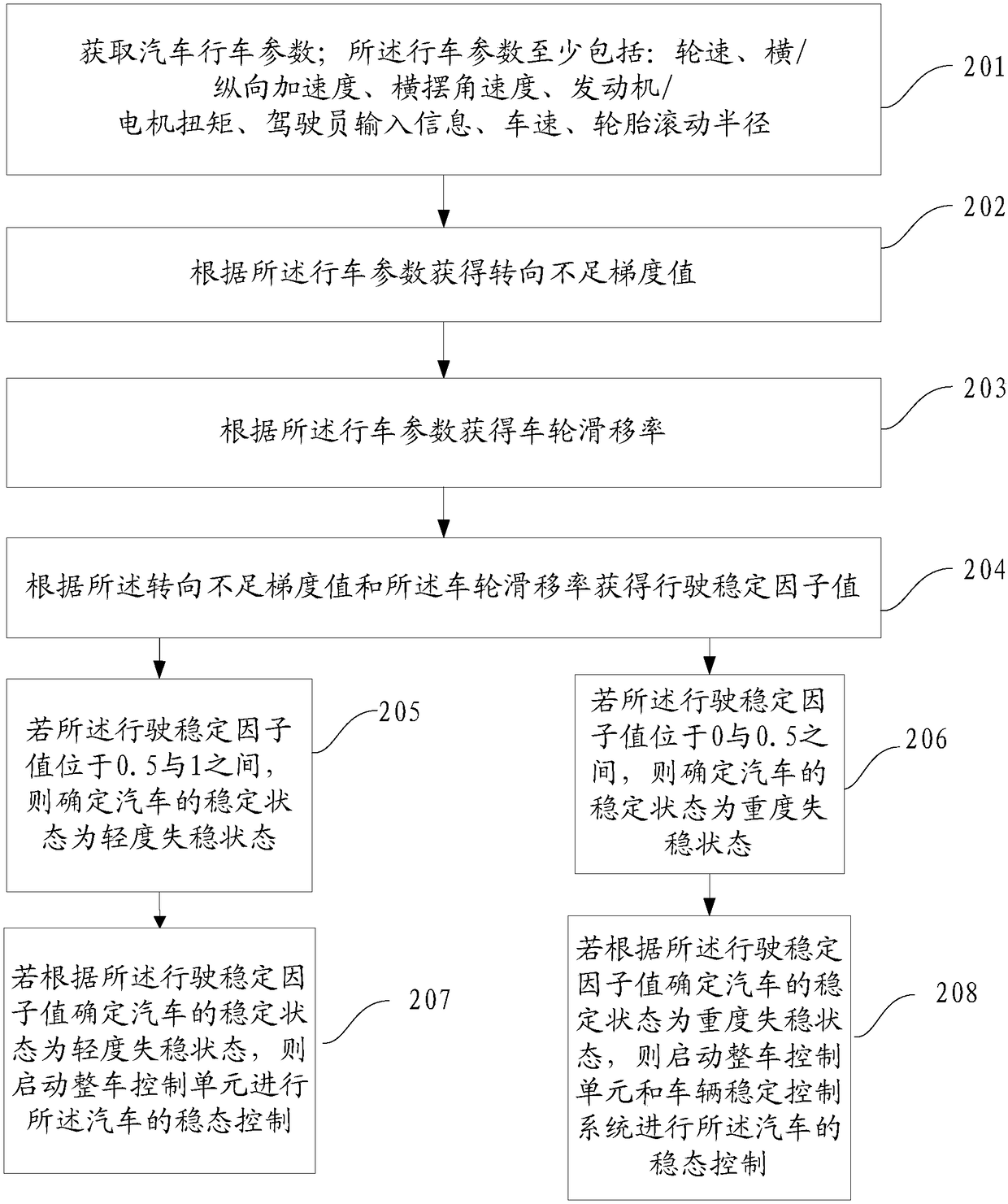
[0055] refer to image 3 , which is a flow chart of a vehicle steady-state intelligent control method described in an embodiment of the present invention, may specifically include the following steps:
[0056] Step 201, acquiring vehicle driving parameters; the driving parameters at least include: wheel speed, lateral and longitudinal acceleration, yaw rate, engine and motor torque, driver input information, vehicle speed, and tire rolling radius.
[0057] This step is the same as step 101, and will not be described in detail again.
[0058] Step 202, obtaining an understeer gradient value according to the driving parameters.
[0059] In the embodiment of the present invention, such as Figure 4 As shown in the schematic diagram of the steady-state motion characteristics, the VSC system monitors and controls vehicle stability using sensors that measure values such as yaw rate, lateral acceleration, wheel speed, steering wheel angle, brake pedal and accelerator pedal positi...
Embodiment 3
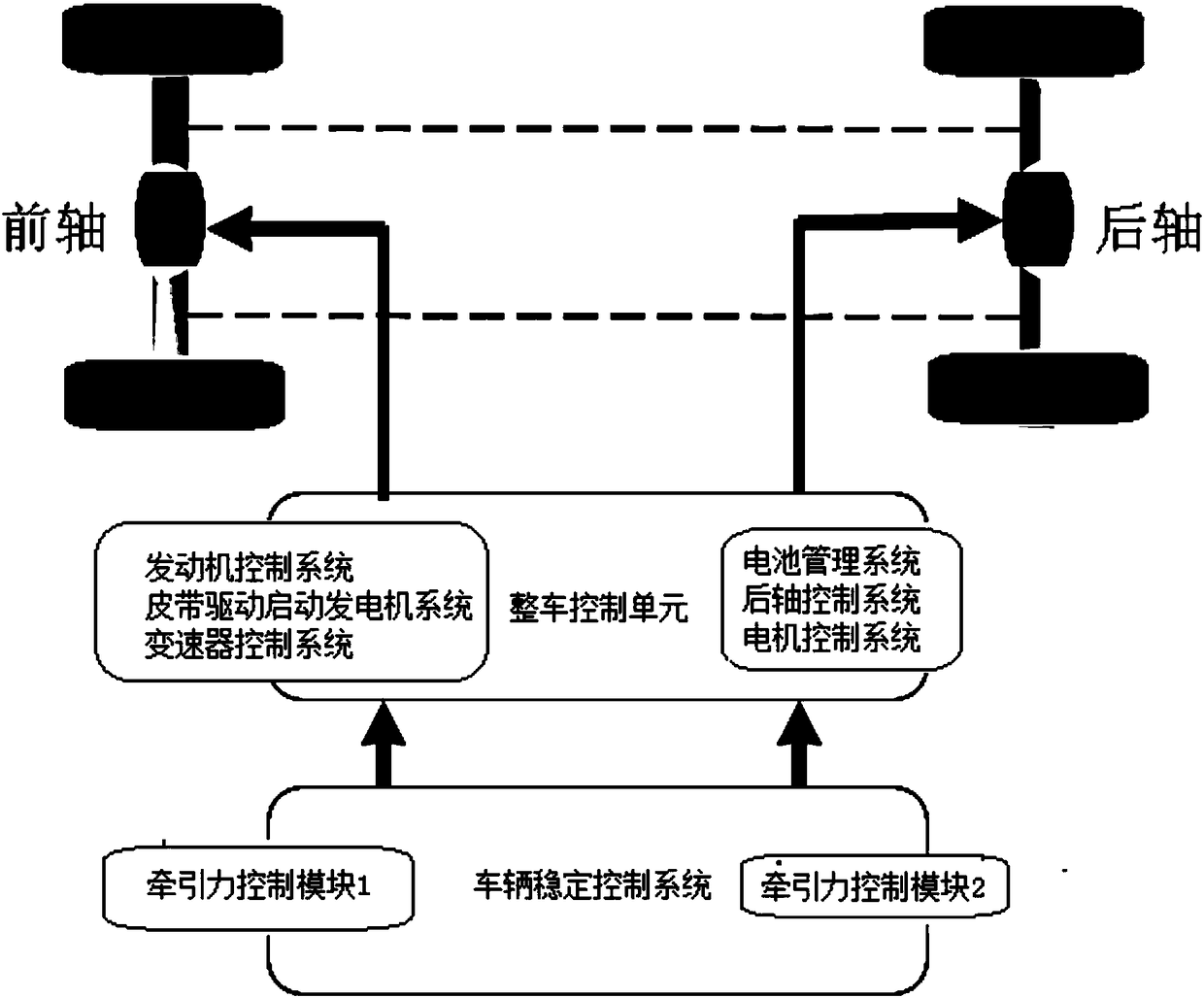
[0114] refer to Figure 16 , is a structural block diagram of a vehicle steady-state intelligent control device according to an embodiment of the present invention.
[0115] A driving parameter acquisition module 401 , a stability factor value acquisition module 402 , and a steady state control module 403 .
[0116] refer to Figure 17 , the function of each module and the interaction relationship between each module are introduced in detail below.
[0117] The driving parameter acquisition module 401 is used to acquire the driving parameters of the vehicle; the driving parameters at least include: wheel speed, lateral and longitudinal acceleration, yaw rate, engine and motor torque, driver input information, vehicle speed, tire rolling radius;
[0118] Stability factor value acquisition module 402, used to obtain the driving stability factor value according to the vehicle driving parameters;
[0119] Preferably, the stability factor value acquisition module 402 specificall...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com