Magnetic resonance imaging method and device, equipment and storage medium
A magnetic resonance imaging, target object technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve the problems of short data sampling time, difficult balance, high image quality, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
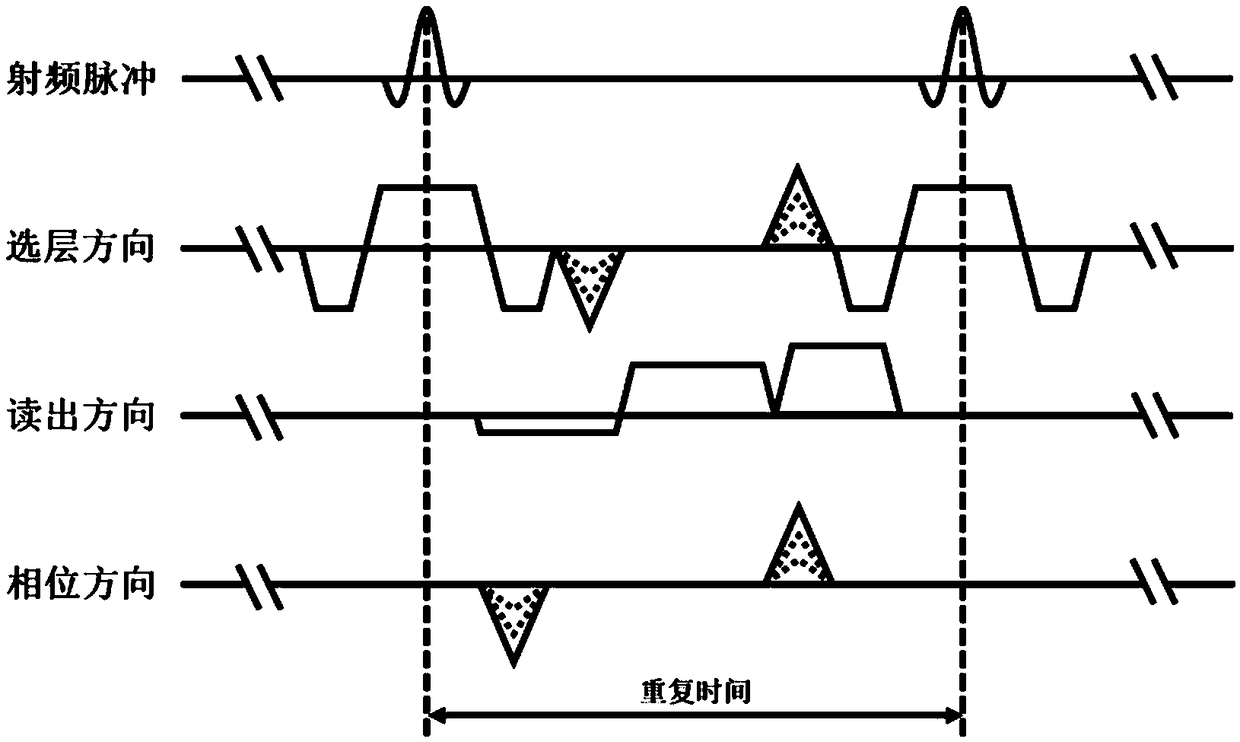
[0045] figure 1 It is a flow chart of the magnetic resonance imaging method provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention. The technical solution of this embodiment is suitable for shortening the data acquisition time without affecting the quality of magnetic resonance imaging. The method can be executed by the magnetic resonance apparatus provided by the embodiment of the present invention, and the apparatus can be realized by software and / or hardware, and configured to be applied in a processor. Such as figure 1 As shown, the method specifically includes the following steps:
[0046] S101. Acquire a three-dimensional point spread function of a target object.
[0047] The three-dimensional point spread function of the target object is obtained, and the frequency-domain space (k-space) sampling trajectory is corrected by the three-dimensional point spread function (PSF).
[0048] S102. Acquire a sensitivity map of the target object.
[0049] In order to speed up the d...
Embodiment 2
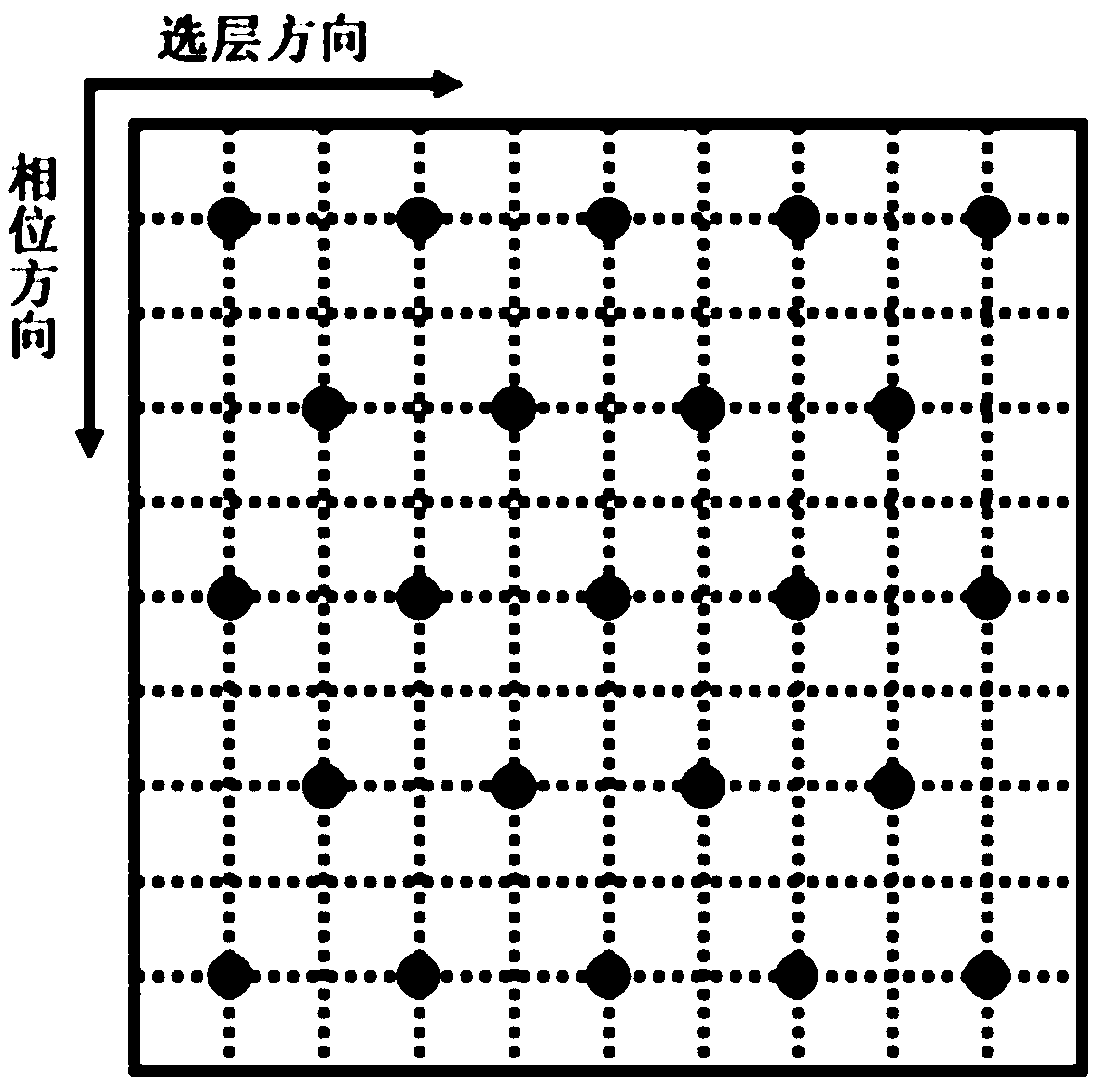
[0066] Image 6 It is a flow chart of the method for obtaining a three-dimensional point spread function provided by Embodiment 2 of the present invention. On the basis of the foregoing embodiments, the embodiment of the present invention optimizes the acquisition of the three-dimensional point spread function of the target object.
[0067] Correspondingly, the method of this embodiment includes:
[0068] S1011. Acquire the mapping data of the target object based on the balanced steady-state free precession pulse sequence.
[0069] Based on the two-dimensional equilibrium steady-state free precession pulse sequence, the two-dimensional mapping data of the target object in the layer selection direction and phase direction are obtained. Specifically: if Figure 7 As shown, based on the two-dimensional equilibrium steady-state free precession pulse sequence in the layer selection direction, the two-dimensional mapping data of the target object in the layer selection direction,...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Embodiment 3 of the present invention has carried out phantom and human brain tests on the medical magnetic resonance imaging system (3.0T MAGNETOM of Siemens AG, Erlangen, Germany) of 3.0 Tesla, has confirmed the magnetic resonance imaging described in the foregoing arbitrary embodiments of the present invention. Feasibility of the resonance imaging method.
[0081] Figure 11 with Figure 12 For the phantom test results, the scanning parameters are as follows: echo time (TE) = 2.41ms, repetition time (TR) = 4.81ms, flip angle (FA for short) = 50°, bandwidth (bandwidth) = 579Hz / pixel , voxel size (voxel size) = 1 × 1 × 1mm3, scan matrix size = 192 × 192 × 192, sine / cosine magnetic field gradient cycle number = 5, sine / cosine magnetic field gradient maximum amplitude = 4mT / m, when the acceleration multiple When it is 2×2 times, the scan time is 45s ( Figure 11 ); when the acceleration factor is 3×3 times, the scanning time is 20s ( Figure 12 ).
[0082] Figure ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com