Method, device, equipment and storage medium for determining static state of obstacle
A static state, determination method technology, applied in the field of data processing, can solve the problems of difficult obstacles static state, wrong judgment, single sensor does not contain redundant information, etc., to improve stability, ensure independence, and solve inconsistent judgment results. stable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
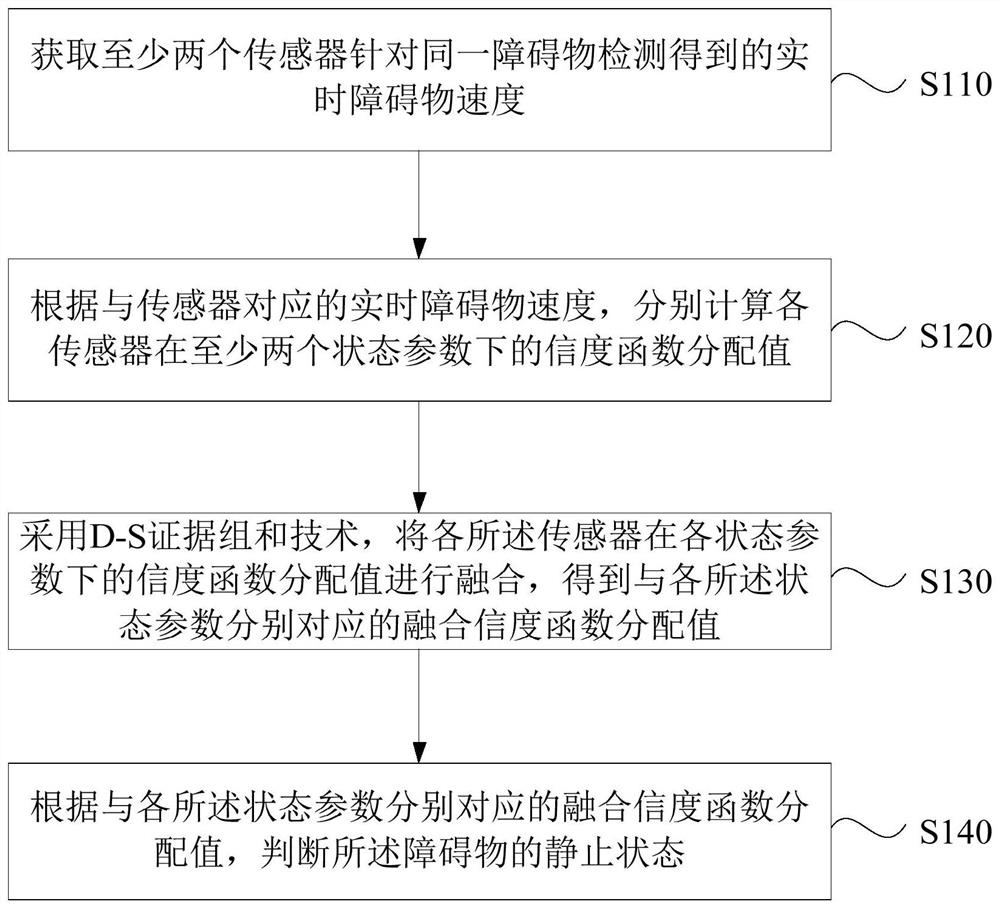
[0031] figure 1 It is a flow chart of a method for determining the static state of obstacles provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention. This embodiment is applicable to the situation where the unmanned vehicle system determines the static state of obstacles. The method can be determined by the device for determining the static state of obstacles To execute, the device can be realized by software and / or hardware, and generally can be integrated into the computer equipment configured in the vehicle. Correspondingly, such as figure 1 As shown, the method includes the following operations:
[0032] S110. Acquire real-time obstacle speeds detected by at least two sensors for the same obstacle.
[0033] Wherein, the real-time obstacle speed may be the speed of the obstacle detected by the sensor at a certain time point.
[0034] In the embodiment of the present invention, in order to accurately determine the stationary state of the obstacle, instead of using a single sens...
Embodiment 2
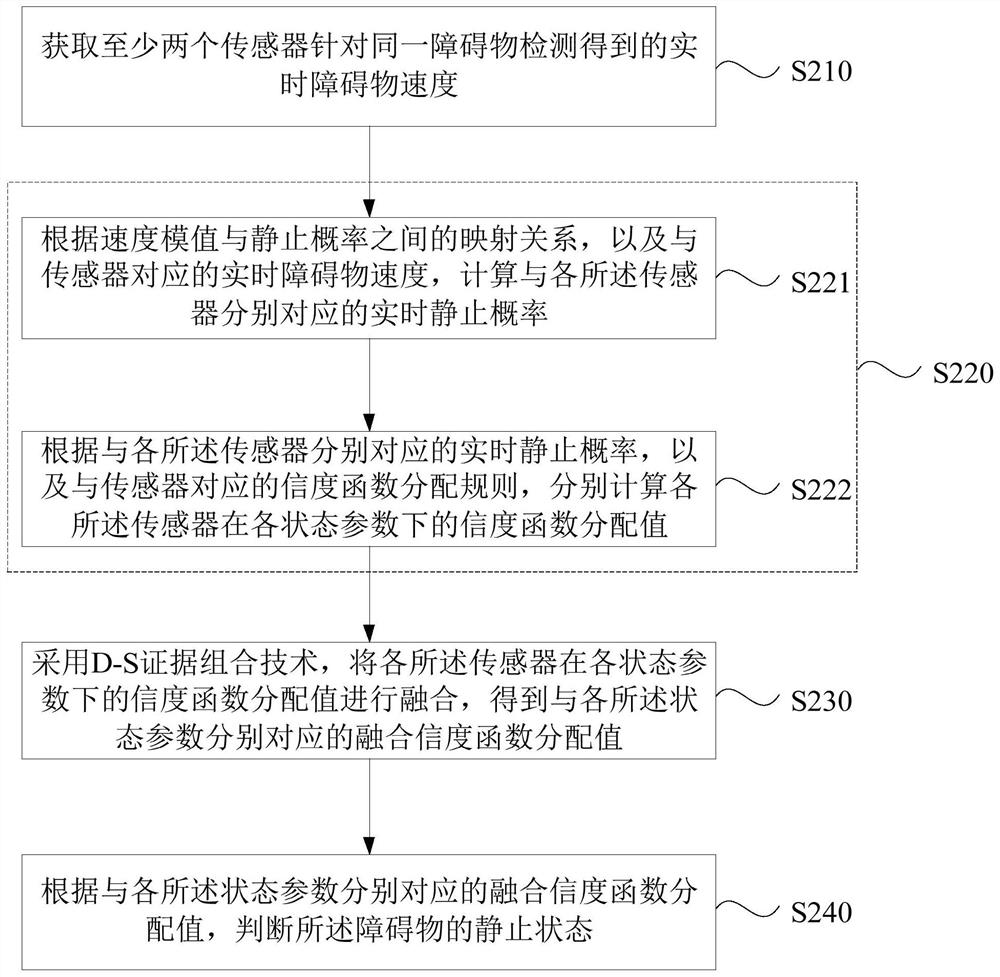
[0046] figure 2 It is a flow chart of a method for determining the static state of an obstacle provided by Embodiment 2 of the present invention. This embodiment is embodied on the basis of the above-mentioned embodiment. In this embodiment, the real-time obstacle corresponding to the sensor is given The specific implementation manner of calculating the distribution value of the reliability function of each of the sensors under each state parameter according to the speed of the object. Correspondingly, such as figure 2 As shown, the method of this embodiment may include:
[0047] S210. Acquire real-time obstacle speeds detected by at least two sensors for the same obstacle.
[0048] S220. According to the real-time obstacle speed corresponding to the sensor, respectively calculate the distribution value of the reliability function of each of the sensors under at least two state parameters.
[0049] Correspondingly, S220 may specifically include the following steps:
[00...
Embodiment 3
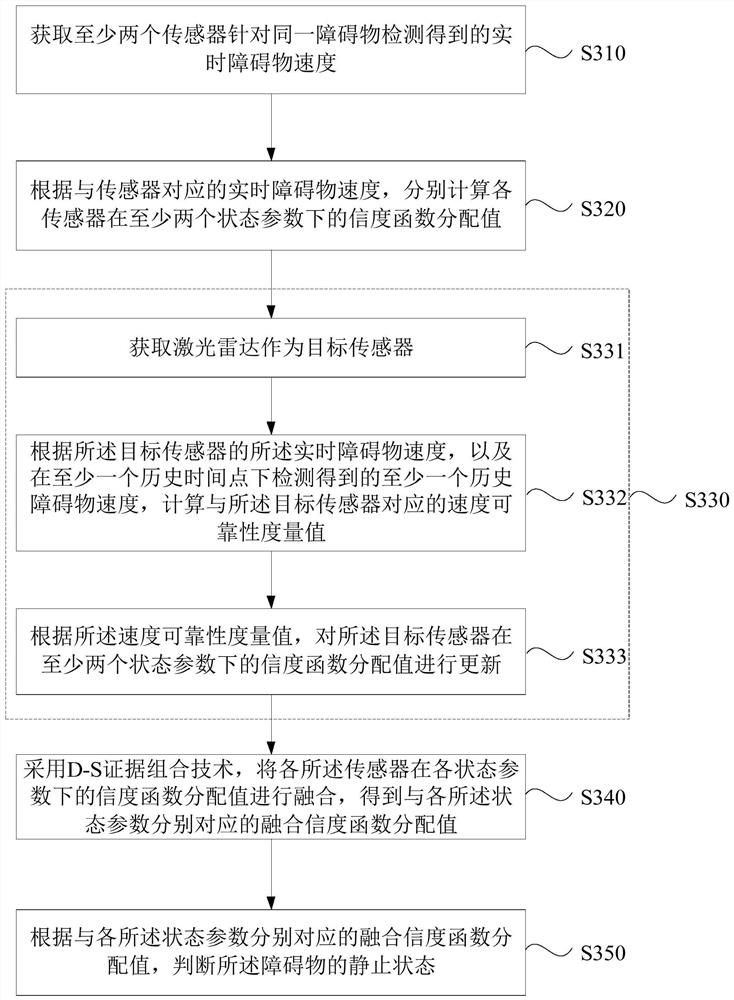
[0075] image 3 It is a flow chart of a method for determining the static state of an obstacle provided by Embodiment 3 of the present invention. This embodiment is embodied on the basis of the above-mentioned embodiments. In this embodiment, the real-time The speed of the obstacle is a specific implementation after calculating the assigned value of the reliability function of each of the sensors under at least two state parameters. Correspondingly, such as image 3 As shown, the method of this embodiment may include:
[0076] S310. Acquire real-time obstacle speeds detected by at least two sensors for the same obstacle.
[0077] S320. According to the real-time obstacle speed corresponding to the sensor, respectively calculate the distribution value of the reliability function of each of the sensors under at least two state parameters.
[0078] S330. According to the real-time obstacle speed detected by the sensor and the historical obstacle speed, update the assigned value ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com