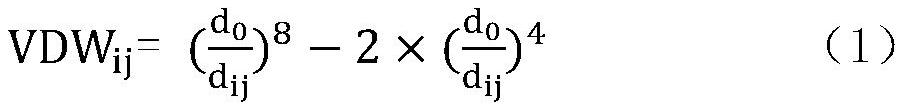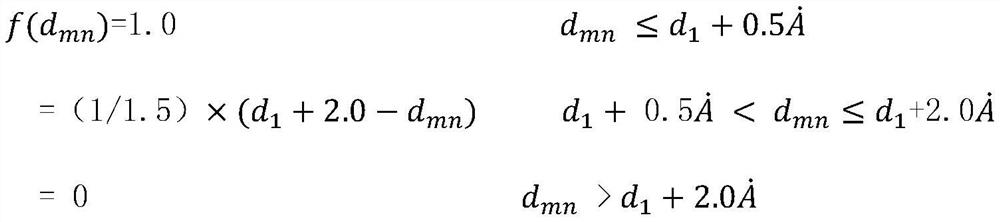Protein-ligand affinity prediction method based on interaction energy term and machine learning
A technology of interaction energy and machine learning, applied in the direction of drug reference, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient diversity, poor sensitivity of homologs, neglect of coupling effects, etc., and achieve the effect of accurate prediction results.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
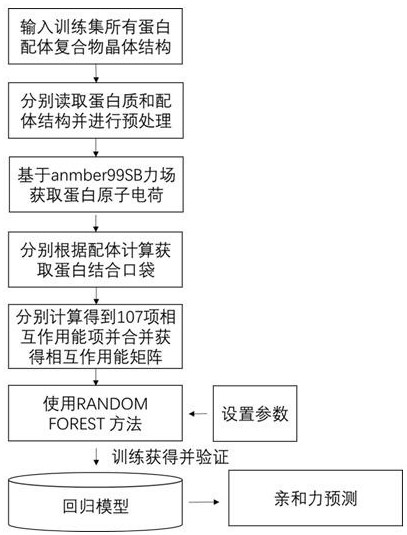
[0052]The present invention constructs 107 different interaction items for different amino acid residues by collecting 3746 protein and ligand complex crystal structures and their binding affinity experimental values in the PDBbind library, and adopts the random forest method in the machine learning method, An empirical scoring function was thus established for predicting the affinity of a given complex.
[0053] Concrete steps of the present invention:
[0054] Step 1: Collect and prepare 3746 complex structures and their affinity data from the PDBbing database. The affinity type of the ligand is Kd or Ki, and the ligand affinity values of all complexes have more than 100 distributions in picomolar, nanomolar, micromolar and millimolar levels.
[0055] Step 2: Preprocess all proteins by PDBFixer. Processing steps include filling in missing amino acid residues, filling in missing atoms, and adding hydrogen.
[0056] Step 3: Obtain protein atomic charges based on the amb...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com