A wireless common-source wireless energy transmission method and system
A wireless energy transmission, common source technology, applied in electrical components, circuit devices, etc., can solve the problem of unsolved wireless synchronization of TR transmitting array elements, and achieve the effect of avoiding electromagnetic interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0107] Example 1: Frequency-separated wireless energy transmission based on wireless common source
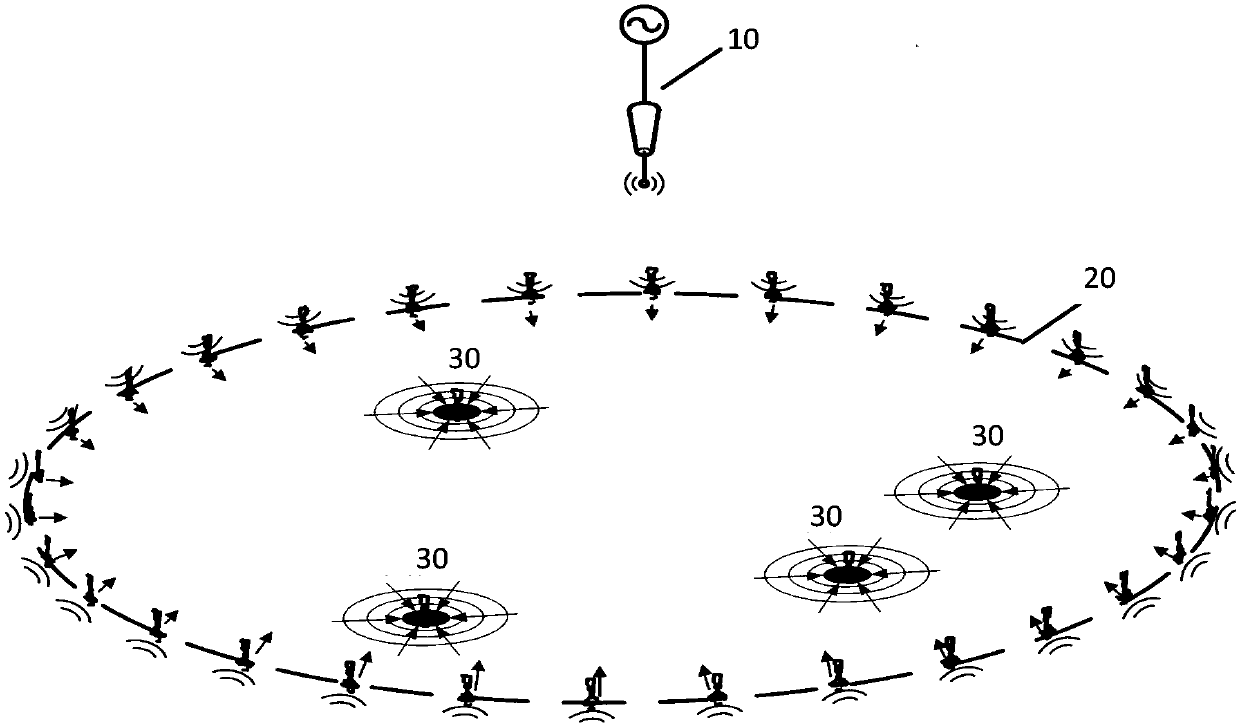
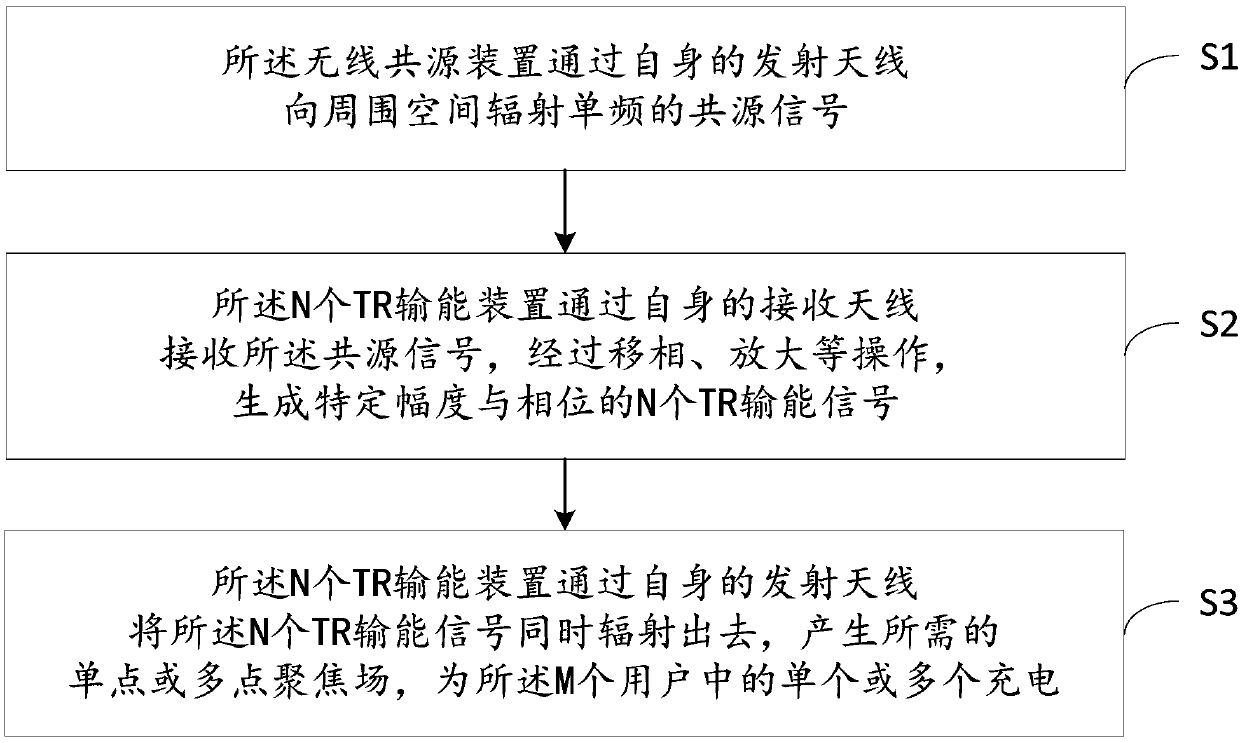
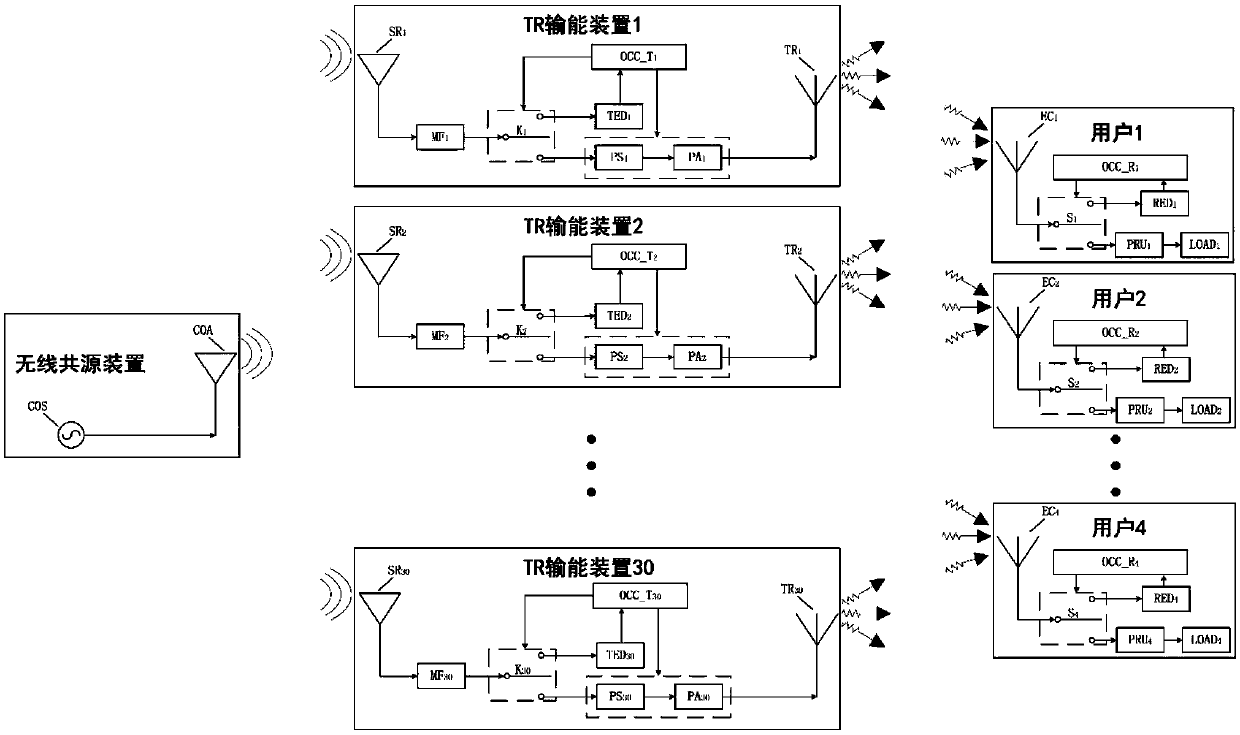
[0108] The structure diagram of this example is as follows image 3 As shown, there is 1 wireless common source device, 30 TR energy transmission devices (TR energy transmission devices 1-30) and 4 users (users 1-4). The users here can be understood as energy receiving equipment. The wireless common source device includes at least one single-frequency signal source with a frequency of 1.225 GHz and a transmitting antenna with a center frequency of 1.225 GHz. Each TR energy transmission device includes at least 1 frequency multiplier, 1 detector, 1 amplifier, 1 phase shifter, 1 receiving antenna with a center frequency of 1.225GHz and 1 transmitting antenna with a center frequency of 2.45GHz ; Each user includes at least one 2.45GHz receiving antenna, one detector, one rectifier and one load.
[0109] The structural block diagram of the wireless common source device is shown in Figu...
example 2
[0137] Example 2: Polarization separation wireless energy transmission based on wireless common source
[0138] The structure diagram of this example is as follows Figure 5 As shown, there is 1 wireless common source device, 30 TR energy transmission devices (TR energy transmission devices 1-30) and 4 users (users 1-4). The users here can be understood as energy receiving equipment. The wireless common source device includes at least one single-frequency signal source with a frequency of 2.45GHz and a vertically polarized transmitting antenna with a center frequency of 2.45GHz; each TR energy transmission device includes at least one detector, one amplifier, 1 phase shifter, 1 vertically polarized receiving antenna with a center frequency of 2.45GHz, and 1 horizontally polarized transmitting antenna with a center frequency of 2.45GHz; each user includes at least one 2.45GHz horizontally polarized receiving antenna, 1 detector, 1 rectifier and 1 load.
[0139] The structural block...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com