An adaptive echo cancellation method against shock interference
An echo cancellation and self-adaptive technology, used in two-way sound reinforcement telephone systems, telephone communications, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of increased steady-state error, reduced convergence speed, and huge update of tap weight vector errors. Convergence speed, fast convergence speed, low steady-state error effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
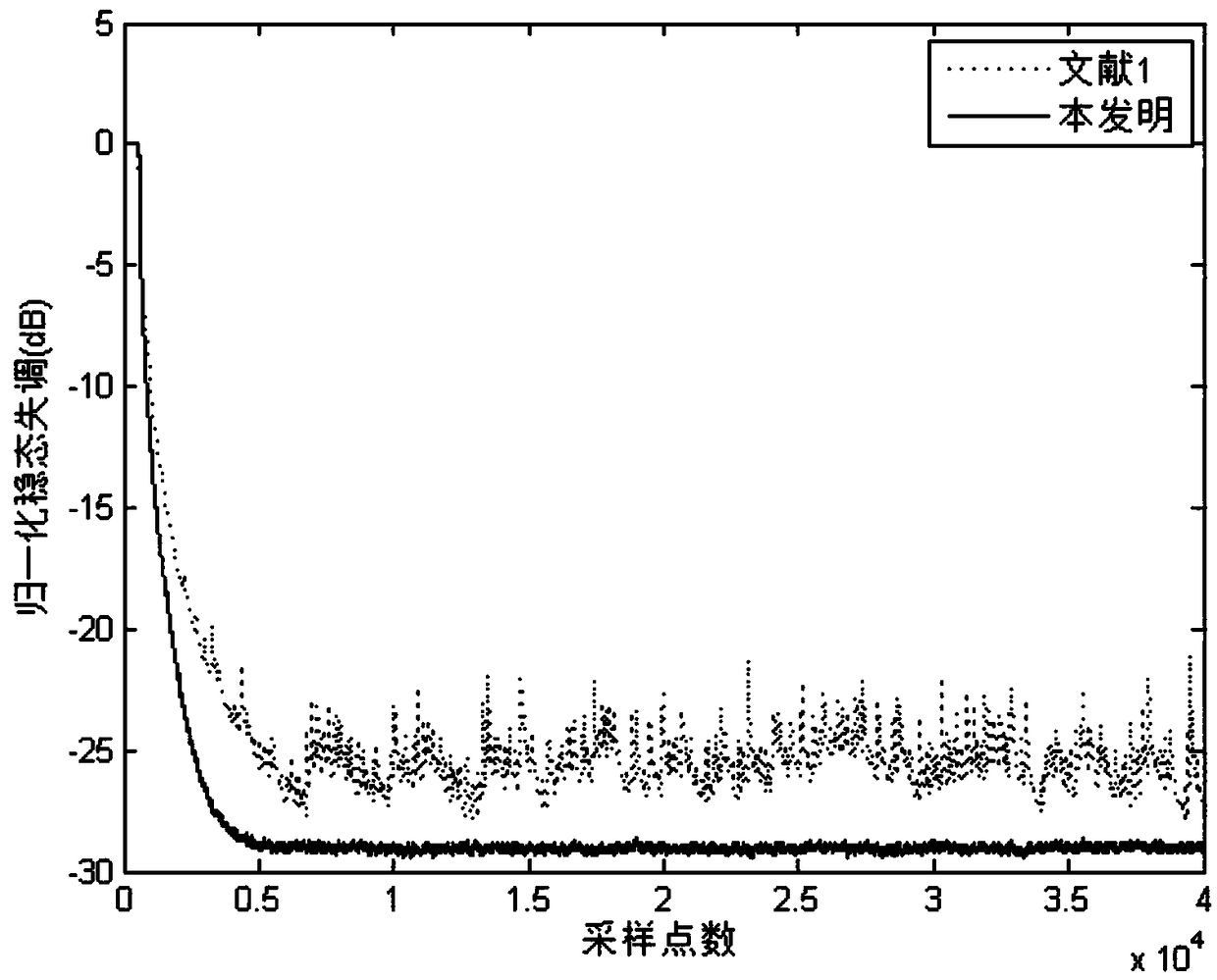
[0051] A specific embodiment of the present invention is an adaptive echo cancellation method against impact interference, the steps of which are as follows:
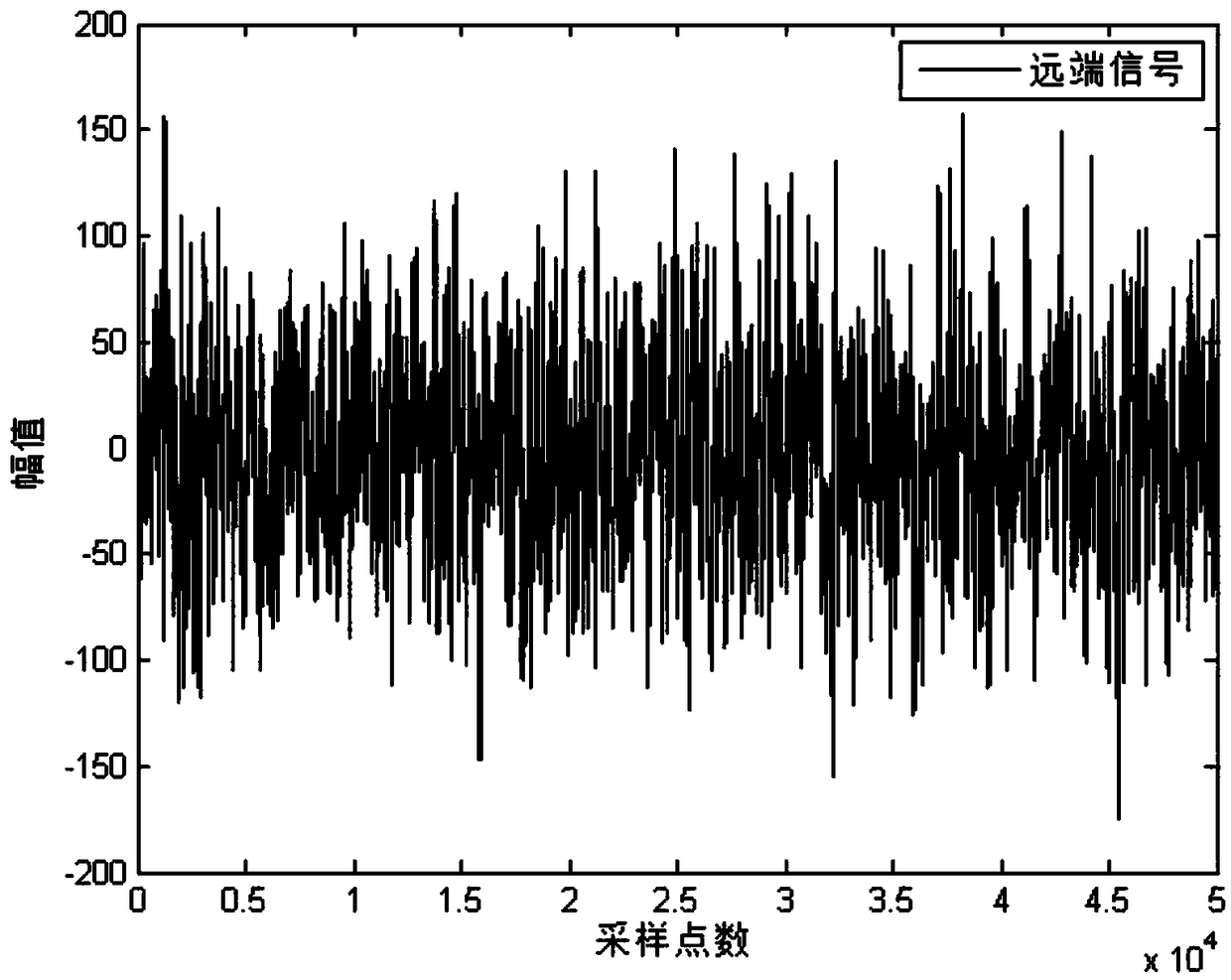
[0052] A. Remote signal acquisition
[0053] Sampling the signal from the remote end to obtain the discrete value x(n) of the remote input signal at the current time n, and the input signal x(n) and x(n- 1),...,x(n-L+1) constitute the adaptive filter input vector x(n) at the current moment n; x(n)=[x(n),x(n-1),. ..,x(n-L+1)] T , where T represents the transpose operation, and L=512 represents the number of filter taps;
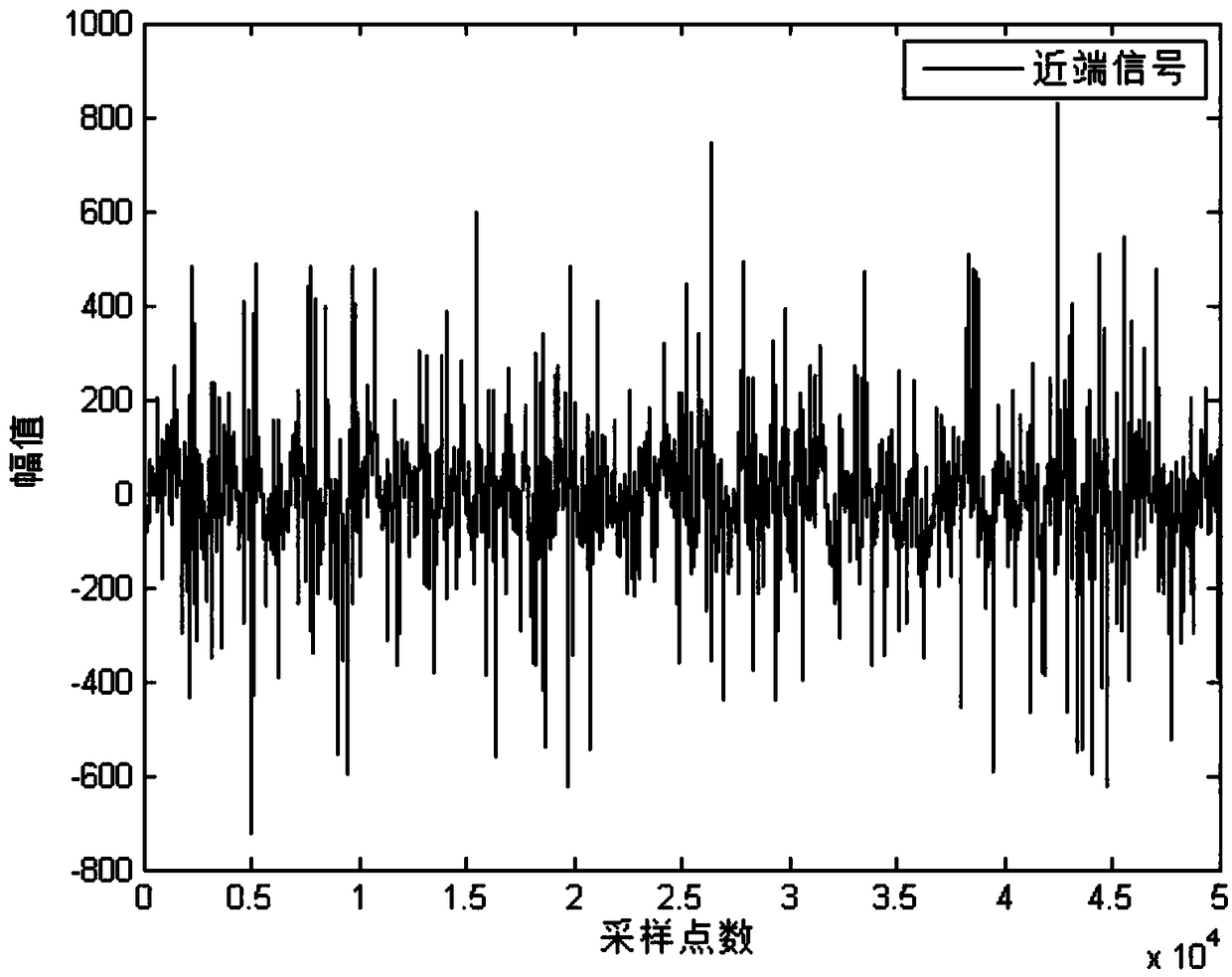
[0054] B. Echo signal estimation
[0055] Pass the input signal vector x(n) at the current moment n through the adaptive filter to obtain the output value of the adaptive filter, that is, the estimated value y(n) of the echo signal,
[0056] y(n)=x T (n)w(n)
[0057] Wherein w(n) is the weight vector of the adaptive filter tap of current moment n, w(n)=[w 1 (n),w 2 (n),...,w L-1 (n)] T , the i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com