Method and system for expanding and shrinking capacity of virtual network functions
A technology of virtual network function and capacity reduction, applied in software simulation/interpretation/simulation, program control design, instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as failure to achieve global optimality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
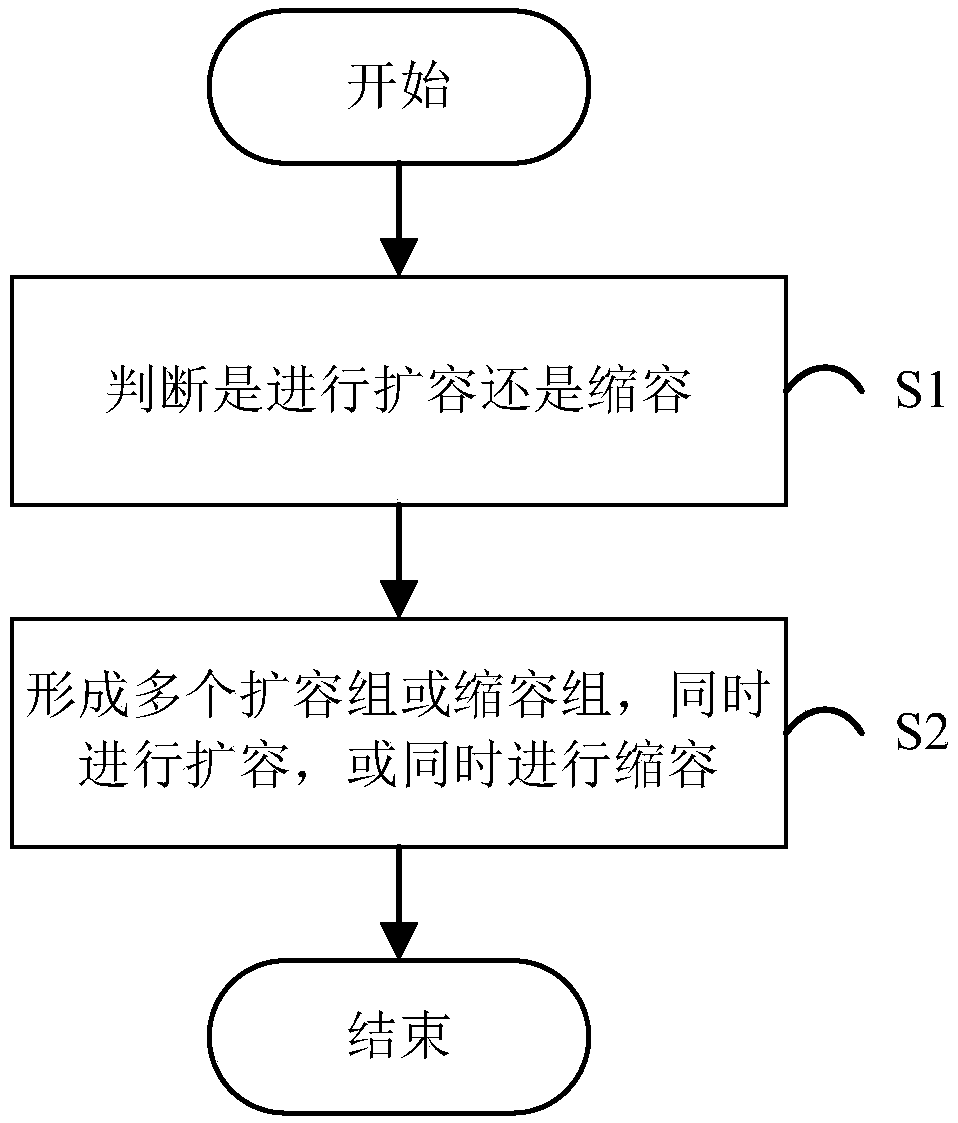
[0069] see figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides a virtual network function expansion and contraction method, the method includes the following steps:
[0070] S1. Collect and analyze historical business load data, predict the business load in the future time period, and judge whether to expand or shrink capacity according to the forecast results; and
[0071] S2. According to the high-dimensional space distance between any two virtual network function VNFs, determine the degree of correlation between VNFs, and group multiple VNFs that need to be expanded or reduced according to the degree of correlation to form multiple expansion groups or shrink Capacity group, expand the VNFs contained in each capacity expansion group at the same time, or simultaneously perform capacity reduction on the VNFs contained in each capacity reduction group.
[0072] Compared with the traditional method, it only considers the problem from the perspective of the expansion and contraction of ...
Embodiment 2
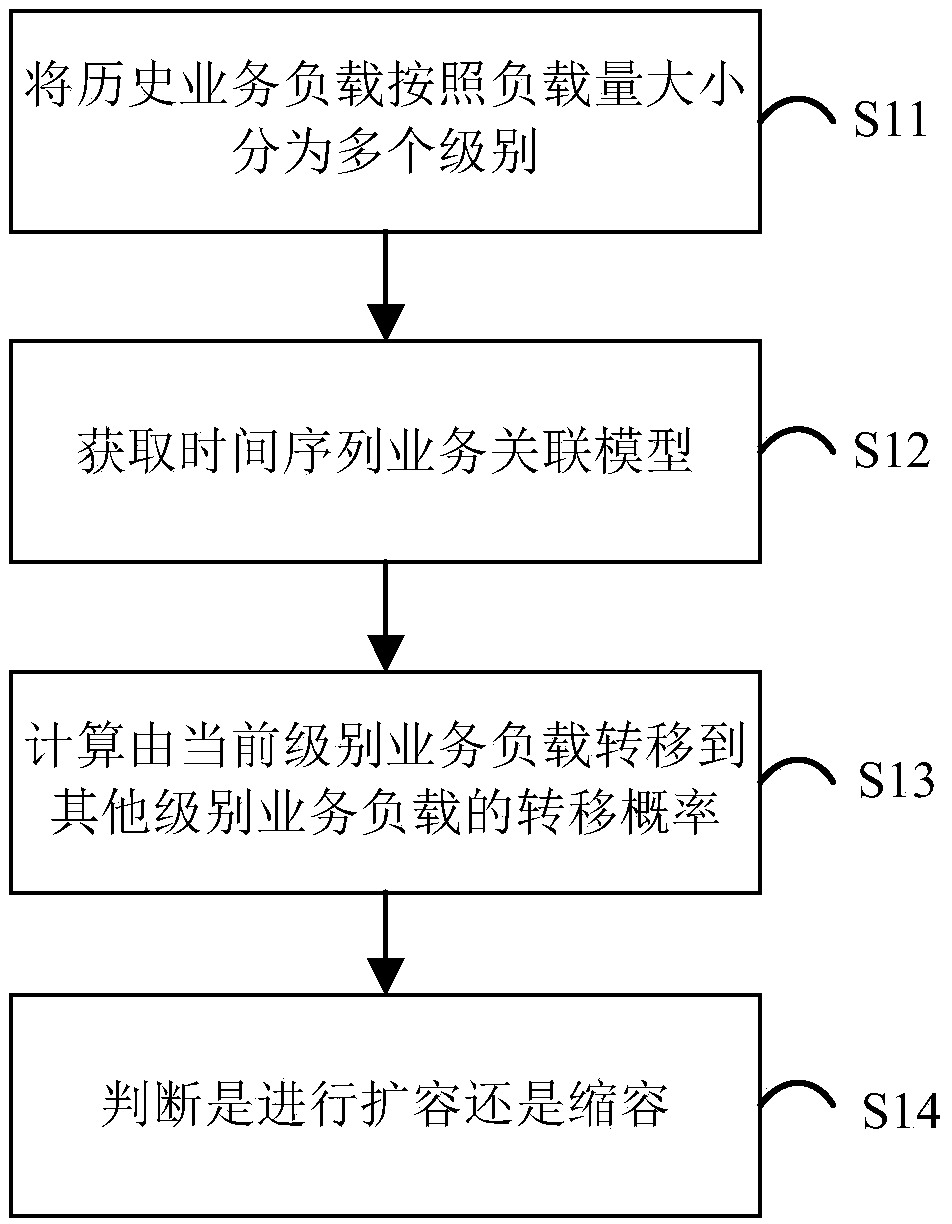
[0074] see figure 2 As shown, as a better alternative, on the basis of Embodiment 1, collect historical business data for analysis, predict the business load in the future time period, and judge whether to expand or shrink capacity according to the forecast results. The specific process for:
[0075] S11. According to the collected historical business data, the historical business load is divided into multiple levels according to the size of the load;
[0076] Preferably, in this embodiment, the service load is divided into ultra-high load UH (Ultra High Level), high load H (High Level), common load C (Common Level), low load L (Low Level), ultra-low load UL ( Ultra LowLevel) five levels. In practice, the number of classifications can be adjusted according to the number of business loads, for example, when the load variation range is large, it can be divided into seven or nine grades, and when the load variation range is small, it can be adjusted to three grades.
[0077] ...
Embodiment 3
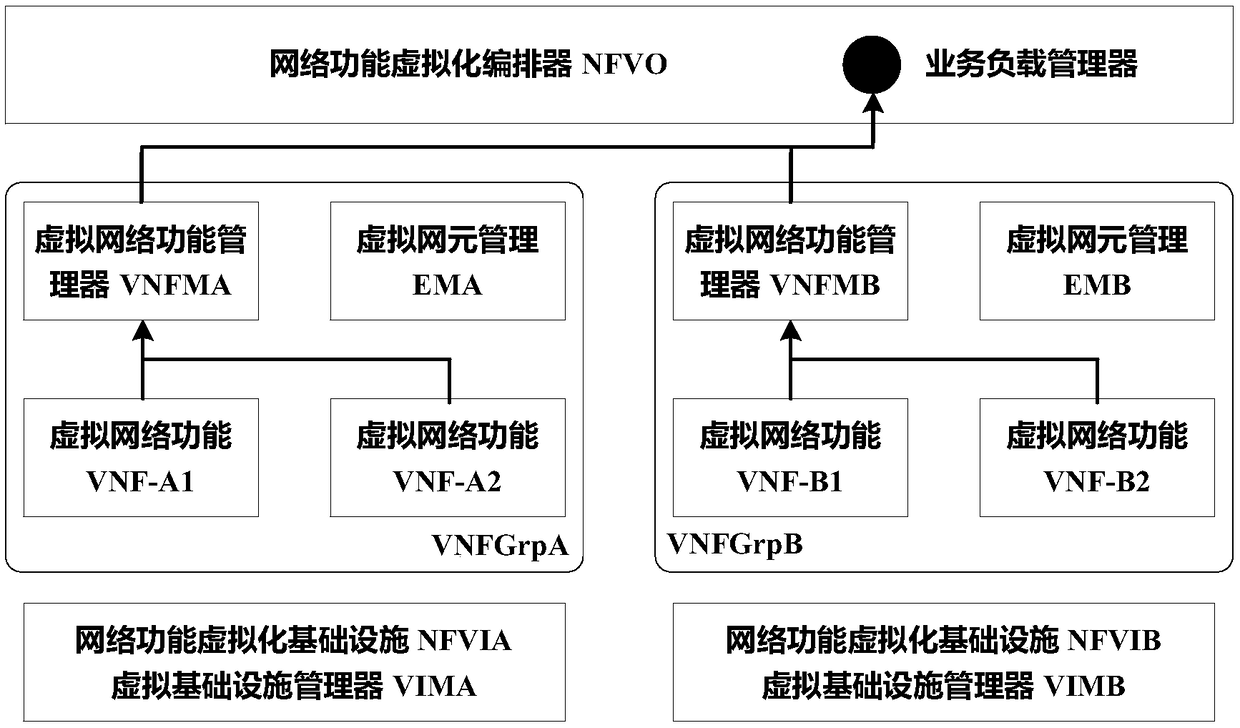
[0088] As a better alternative, on the basis of Embodiment 1, the method further includes the following step: selecting the best virtual machine from multiple data centers to run the expanded or reduced VNF. The data center refers to the cloud network data center of the operator. After the cloud transformation of the operator network, the data center built for the cloud network deploys the telecom cloud platform, virtual network function, management and orchestration platform, etc., referred to in the present invention as data center.
[0089] Further, see Figure 4 As shown, the best virtual machine is selected from multiple data centers to run the expanded or reduced VNF. The specific process is as follows:
[0090] According to the requirements of different application scenarios, select the best data center from multiple data centers. The application scenario requirements include the shortest service load transmission time, the shortest VNF path, and the highest security l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com