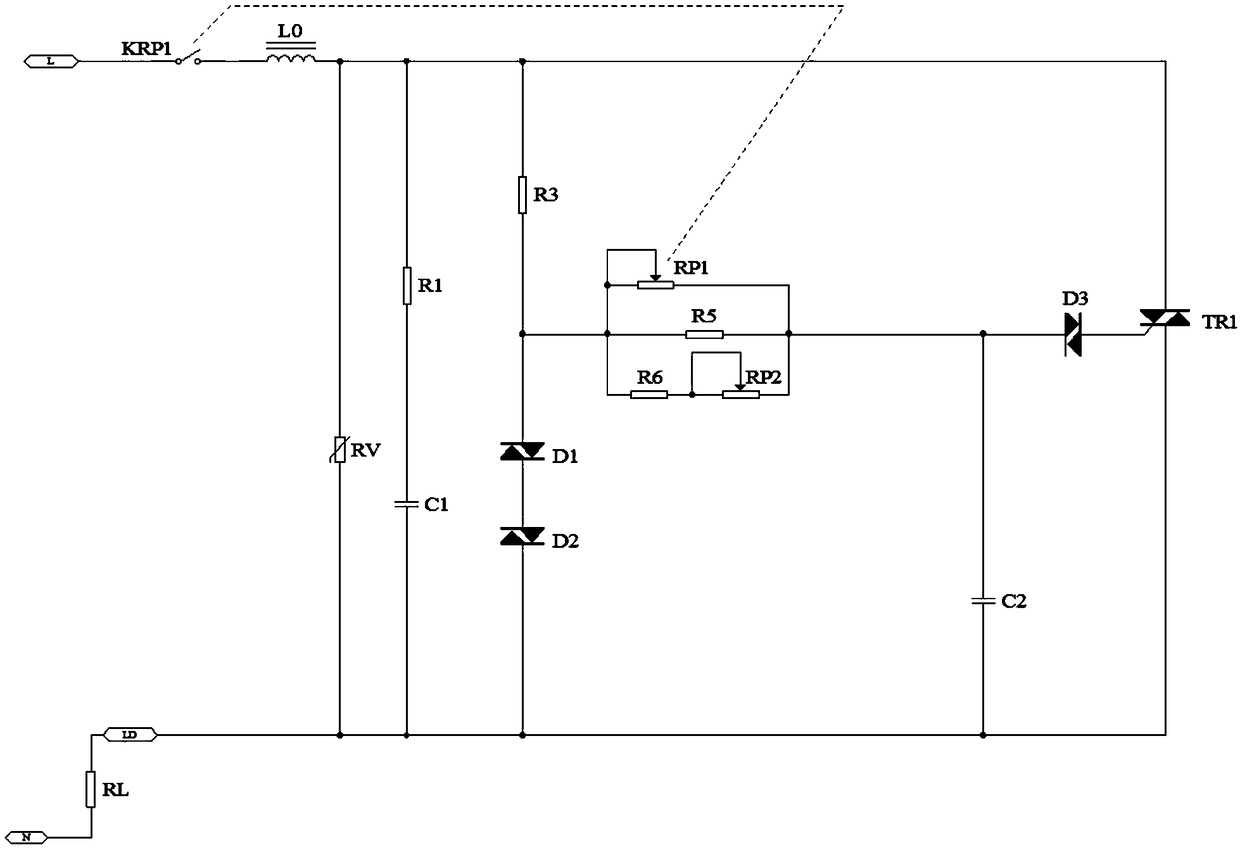
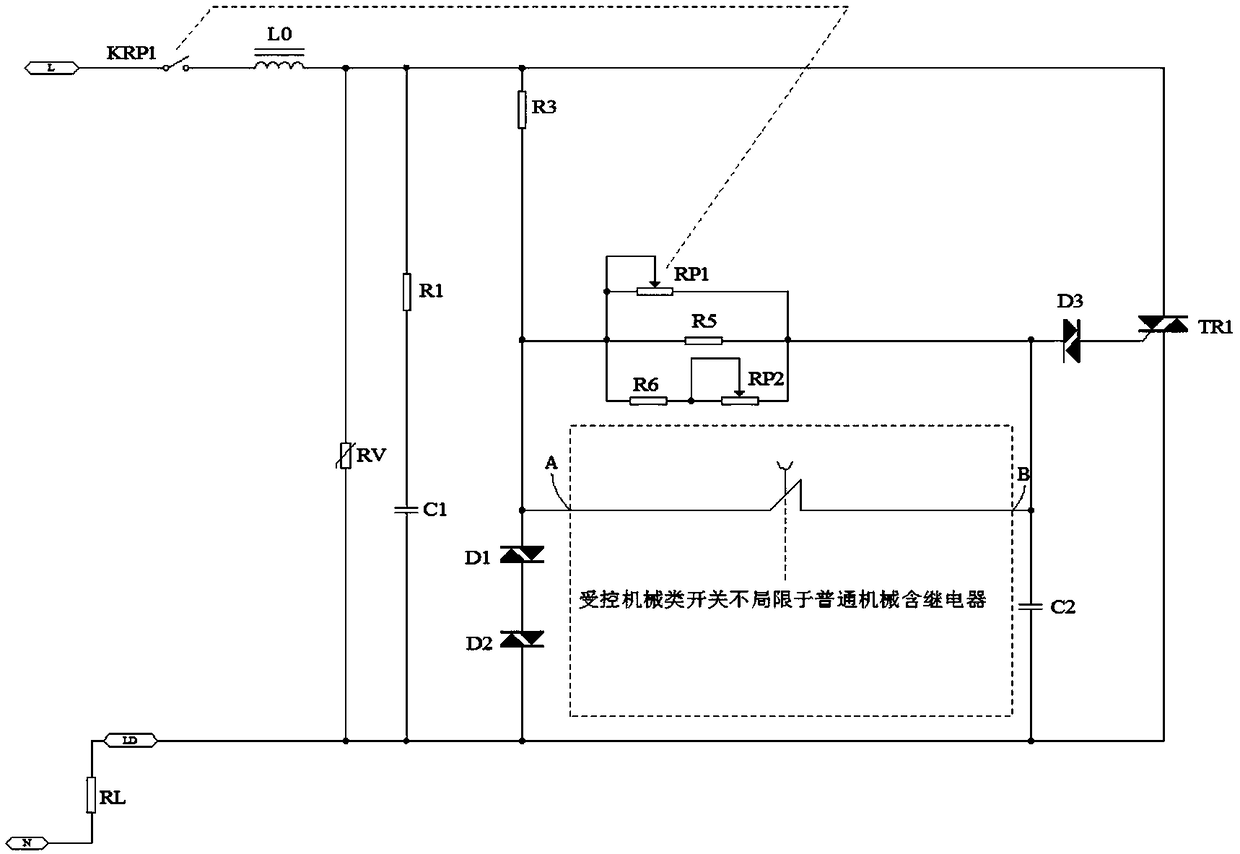
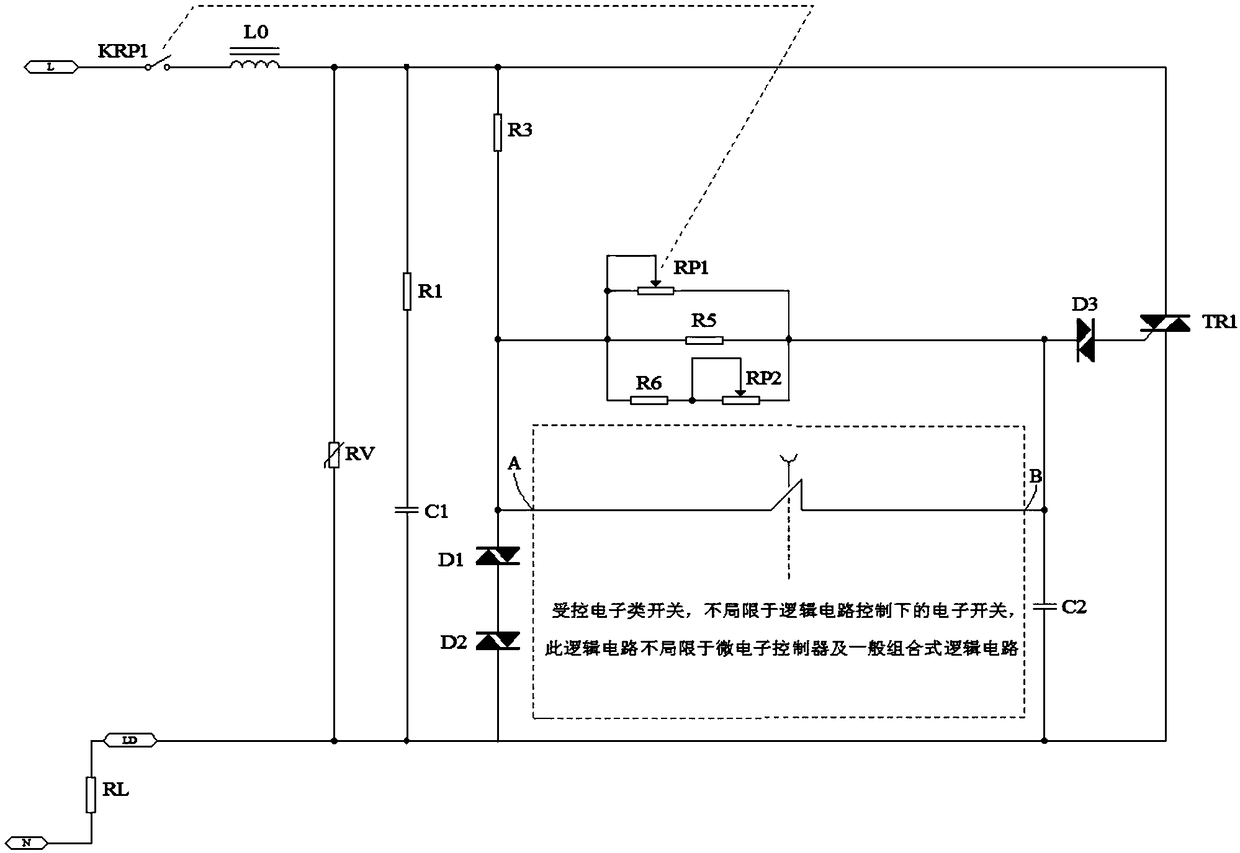
A light and speed regulating circuit
A circuit and speed regulation technology, which is applied in the direction of electric lamp circuit layout, light source, electric light source, etc., can solve the problems of dead travel, inconvenience, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] see Figure 5 As shown, in this embodiment, the ABC circuit network in the dotted line frame is composed of a relay and a corresponding controlled electronic timing off switch to realize the compensation circuit of the compensation current, specifically including: the fourth diode D4, the fifth diode D5 , the seventh resistor R7, the eighth resistor R8, the normally open relay, the sixth diode D6, the seventh diode D7, the bridge rectifier BD1, the ninth resistor R9, the voltage stabilizing module IC1, the fourth capacitor C4, the Ten resistors R10, eleventh resistors R11, and the second switch tube Q2; the cathode of the fourth diode D4, the anode of the fifth diode D5, and an AC input terminal of the rectifier bridge stack BD1 are respectively connected to the The input ends of the adjustable resistance network are connected; the anode of the fourth diode D4, the seventh resistor R7, the first contact K1 of the relay, and the cathode of the sixth diode D6 are connecte...
Embodiment 2
[0051] see Figure 6 As shown, in this embodiment, the ABC circuit network in the dotted line frame forms a compensation circuit for controlling electronic timed off switches to realize compensation current, specifically including: the fourth diode D4, the fifth diode D5, and the seventh resistor R7 , the eighth resistor R8, the sixth diode D6, the seventh diode D7, the rectifier bridge stack BD1, the third capacitor C3, the ninth resistor R9, the tenth resistor R10, the eleventh resistor R11, the twelfth resistor R12, Zener tube ZD1, first switch tube Q1, second switch tube Q2 and third switch tube Q3; the cathode of the fourth diode D4, the anode of the fifth diode D5, the rectifier bridge stack BD1 An AC input terminal is respectively connected to the input terminal of the adjustable resistor network; the anode of the fourth diode D4, the third switching tube Q3, the seventh resistor R7, and the cathode of the sixth diode D6 are connected in series in sequence connected; t...
Embodiment 3
[0057] see Figure 7 , in this embodiment, the ABC circuit network in the dotted line frame forms a compensation circuit for controlling electronic timing off switches to realize the compensation current, specifically including: the seventh diode D7, the eighth diode D8, the eighth resistor R8, the first Nine resistors R9, tenth resistor R10, twelfth resistor R12, third capacitor C3, voltage regulator tube ZD1, first switch tube Q1 and second switch tube Q2; one end of the ninth resistor R9 is connected to the adjustable The input terminals of the resistor network are connected; the other end of the ninth resistor R9 is connected to one end of the eighth resistor R8, one end of the tenth resistor R10, and one end of the eleventh resistor R11 respectively; The other end of the eighth resistor R8 is connected to the input end of the first switching tube Q1; the output end of the first switching tube Q1 is connected to the anode of the seventh diode D7; the seventh The cathode o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com