Variable step size perturbation observation MPPT algorithm based on dichotomy
A technology of variable step size perturbation and dichotomy, which is applied in calculation, adjustment of electrical variables, special data processing applications, etc., can solve the problems of high sensor and system hardware requirements, long training time, high tracking speed and tracking accuracy, etc. To achieve the effect of overcoming the insufficient tracking speed, good tracking efficiency and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The specific implementation of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and examples, but the implementation and protection of the present invention are not limited thereto.
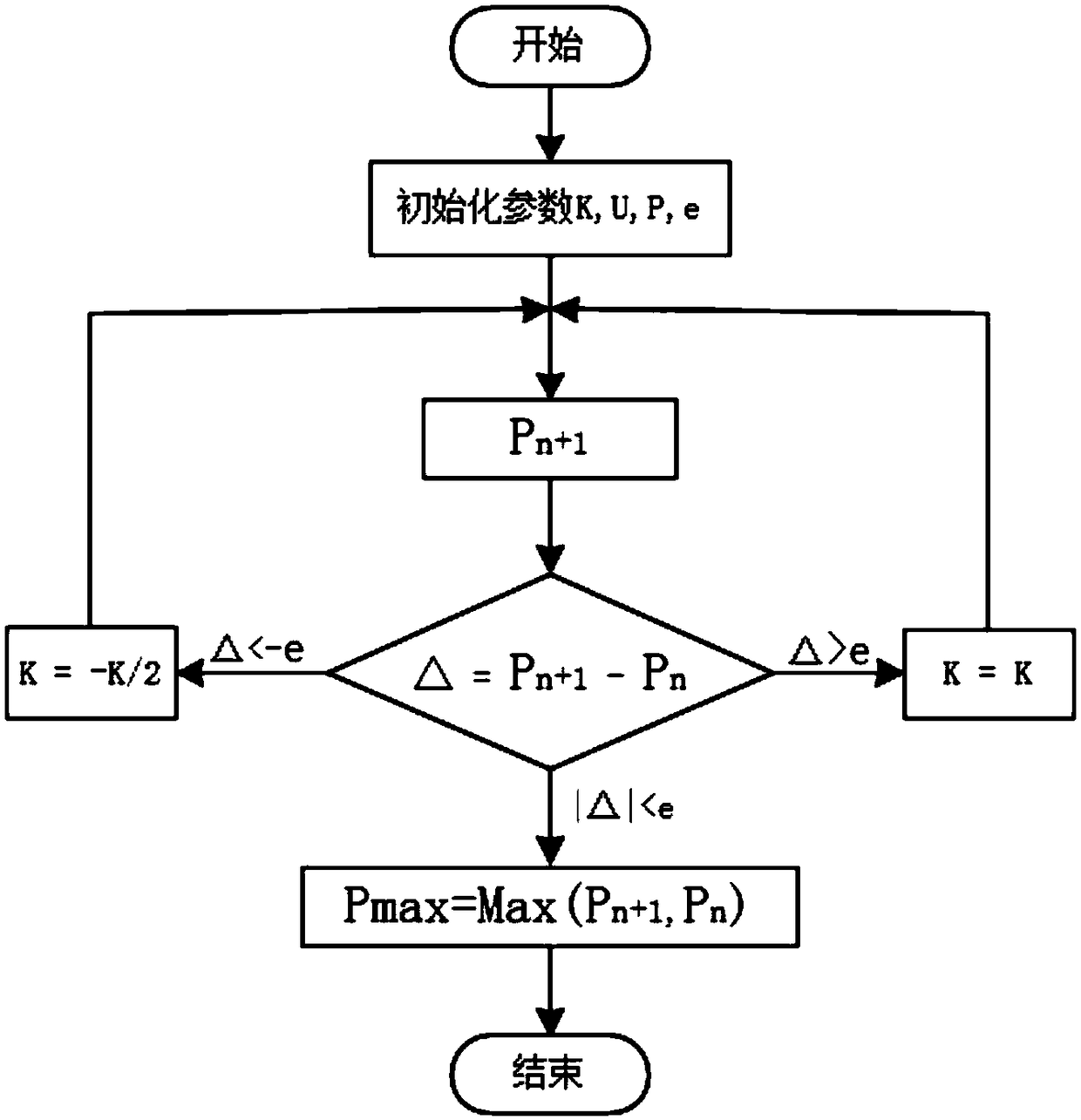
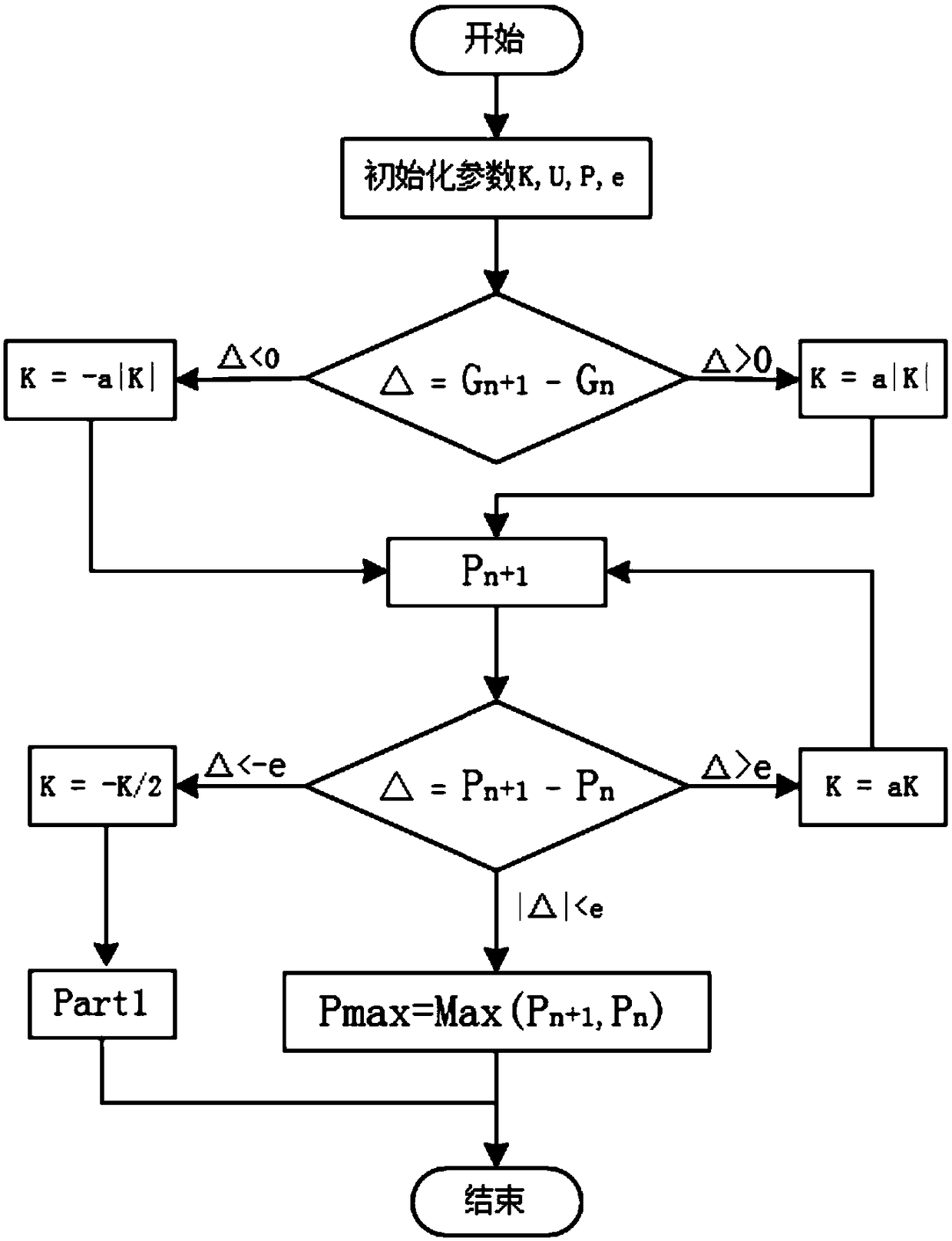
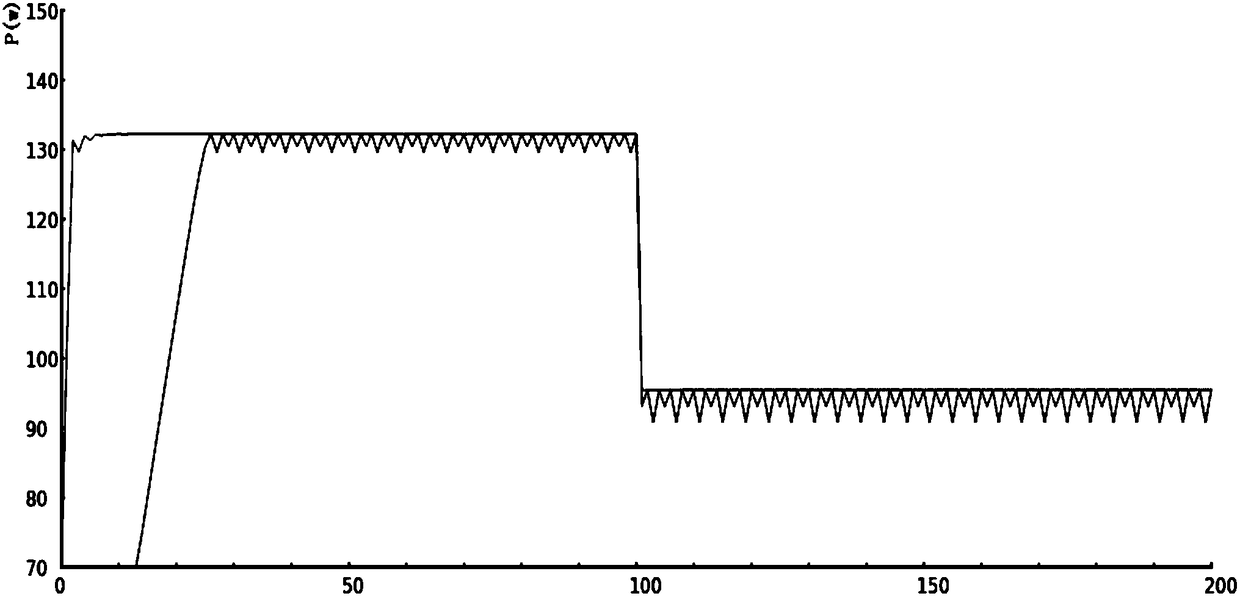
[0025] In order to improve the maximum power point tracking speed, avoid oscillation at the maximum power point, quickly adapt to environmental changes, reduce algorithm complexity and implementation cost, this algorithm uses the bisection fast convergence feature to quickly track the maximum power point at startup, and uses The comparison method updates the maximum power point of the system to avoid shocks, and uses the a-fold method and the dichotomy method to quickly track to the new maximum power point when the environment changes.
[0026] The main content of this example includes: initializing parameters, executing the dichotomy algorithm, monitoring whether the external environment changes, and executing the a times method if it chan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com