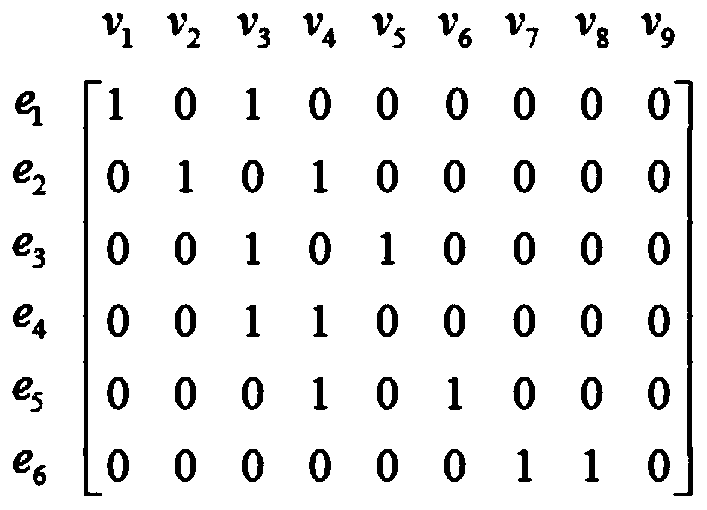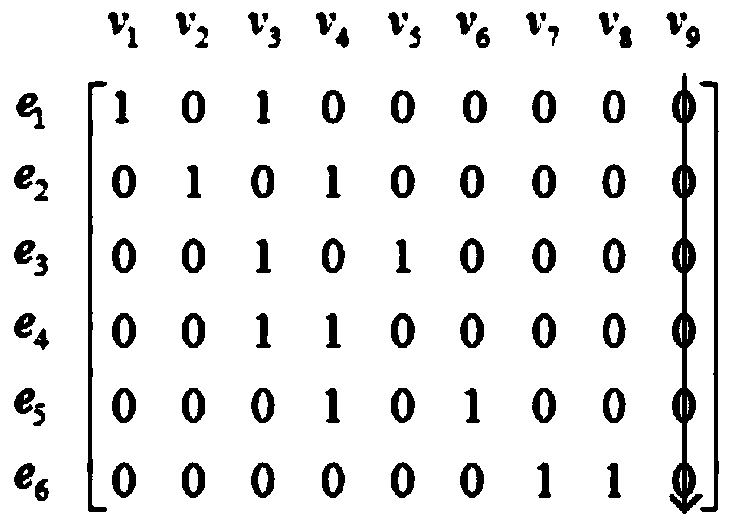Connected Slice Identification Method Based on Incidence Matrix Compression and Branch Pointer Vector Update
A technology of correlation matrix and identification method, applied in circuit devices, AC network circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of multi-redundancy calculation, matrix decomposition process and merging calculation cumbersome, to avoid logical operations, the method is efficient and reliable, Widely applicable effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
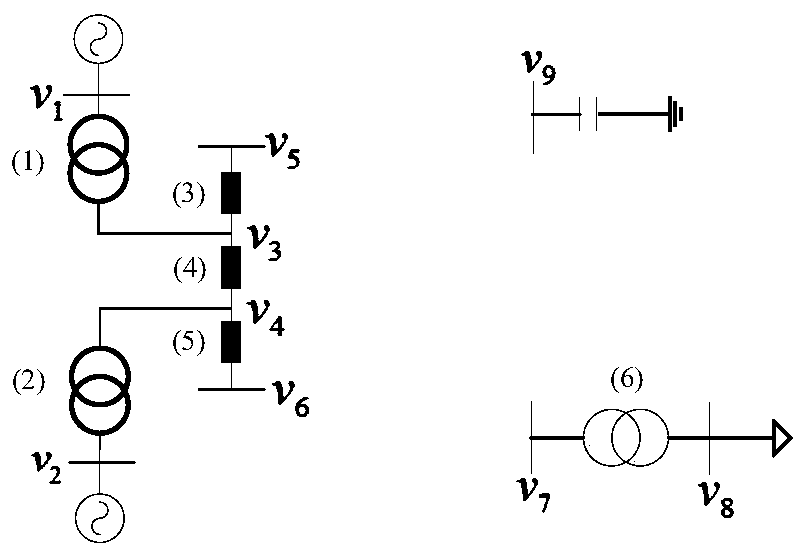
[0039] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 7 As shown, the connected slice identification method based on incidence matrix compression and branch pointer vector update includes the following steps:
[0040] Step 1: Generate the branch-node association matrix of the network according to the branch-node related information of the network;
[0041] Step 2: Search the zero column of the branch-node incidence matrix to identify isolated nodes;
[0042] Step 3: "compress" the branch-node correlation matrix by row, and only keep the column labels of non-zero elements to obtain multiple binary connected sets;
[0043] Step 4: Carry out a column scan on the branch-node correlation matrix, and update the branch pointer vector;
[0044] Step 5: According to the final branch pointer vector, the binary connected set is fused and grown to obtain the final set of connected slices;
[0045] figure 1 The shown 9-node simplified power system illustrates the method of the present invention. figure ...
Embodiment 2
[0047] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the branch-node association matrix of the network is represented by a matrix R of order m×n. When branch i is associated with node j, it is recorded as 1, otherwise it is recorded as 0. The branch-node incidence matrix for the network is a column vector r in R i Scan each element of (i=1,2,…,n), if each element is 0, that is r i = 0, it is an isolated node, named v i (i=1,2,...,n). Obtaining the binary connected set in the step 3 includes the following steps: Step 3.1: row-scanning the branch-node correlation matrix, the row vector r k (k=1,2,...,n), the non-zero elements obtained in the kth row are respectively recorded as r kp 、r kq ;Step 3.2: Take out the non-zero element r in row k kp 、r kq The column numbers p, q form a binary connected set {p, q}, and use the branch e k Representation; Step 3.3: Scan out the binary connected sets of all rows, in the form of The branch pointer vector is an m×1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com