Method for quantitatively defining a non-viscous bottom sand starting critical index
A non-cohesive and bottom-sand technology, which is applied in filling planes with attributes, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of quantitatively defining the critical hydraulic index of non-cohesive sand start-up, and achieve the effect of eliminating the interference of human factors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
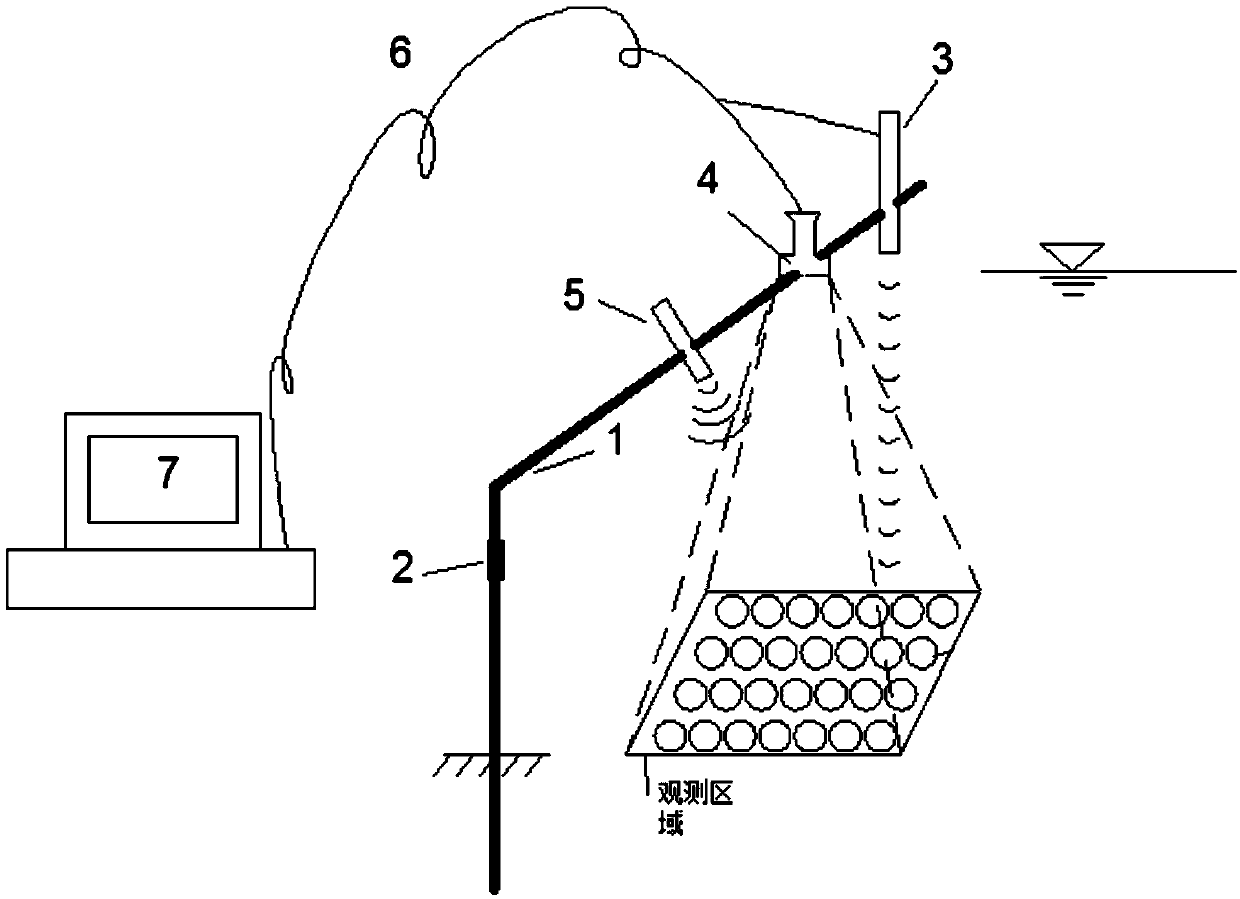
[0032] The present invention is described in further detail now in conjunction with accompanying drawing. These drawings are all simplified schematic diagrams, and only illustrate the basic structure of the present invention in a schematic manner, so they only show the configurations related to the present invention.
[0033] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention includes the following characteristic parts: 1 is a bracket, 2 is a bracket regulator, 3 is an ADCP, 4 is a camera, 5 is an LED lighting lamp, and 6 is an electric wire.
[0034] A kind of method of quantitatively defining non-sticky bottom sand starting critical index of the present invention, comprises the following steps:
[0035]Step 1: Insert the bracket vertically into the bed surface, install the LED lighting, camera and ADCP on the horizontal bracket of the bracket in sequence, and adjust the bracket adjuster so that the camera, LED lighting and ADCP are in a position that is convenient for video r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com