Robot distributed cooperative obstacle avoidance method based on independent virtual center point
A virtual center point, robot technology, applied in the direction of instruments, two-dimensional position/channel control, non-electric variable control, etc., can solve the problem of the robot falling into the local minimum point and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0077] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
[0078] Please refer to figure 1 , the present invention provides a robot distributed collaborative obstacle avoidance method based on an independent virtual central point, comprising the following steps:
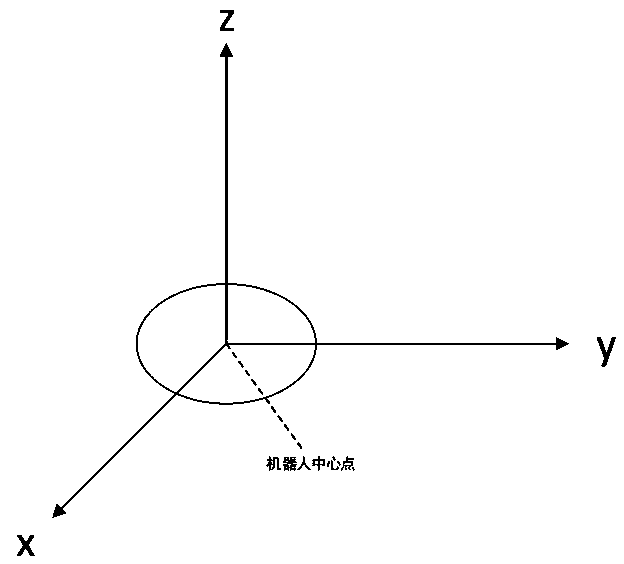
[0079] Step S1: Use the extended Kalman filter to fuse the IMU and odometer data to obtain the current pose information of several robots, where the current pose information of the i-th robot is (x i ,y i , θ i );
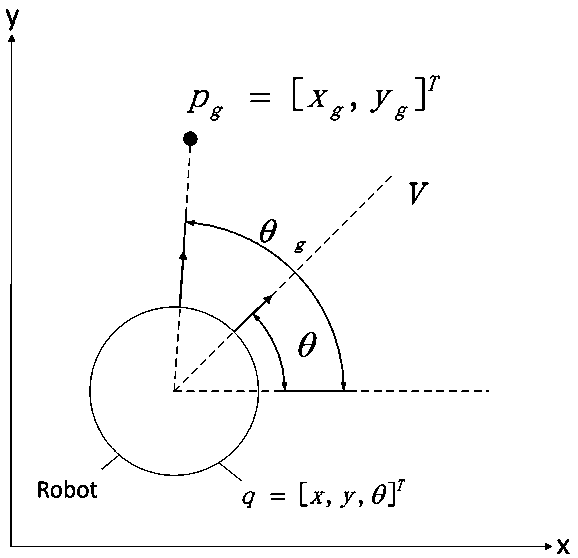
[0080] Step S2: Obtain the shared speed v and position information p between the robots through network communication, calculate the virtual center point p of the robot, and the virtual center point moves with the movement of the robot;
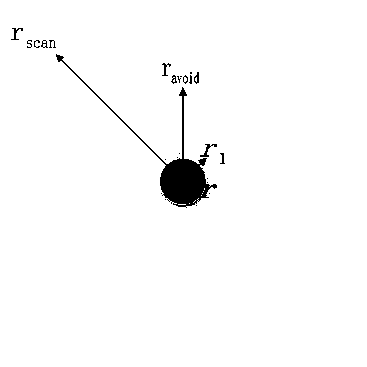
[0081] Step S3: According to the current position p of the robot i and its target point position p gi , the position p of its virtual center point, and the target vector v of the robot is obtained ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com