Interconnect substrate having cavity for stackable semiconducotr assembly as well as manufacturing method thereof
A technology for interconnecting substrates and semiconductors, used in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device components, etc. Effect of Interconnection Distance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0103] Figure 1-14 It is a diagram of a manufacturing method of an interconnect substrate in the first embodiment of the present invention. The interconnect substrate includes a core layer, a build-up circuit, a reinforcement layer, a series of metal pillars and a cavity.
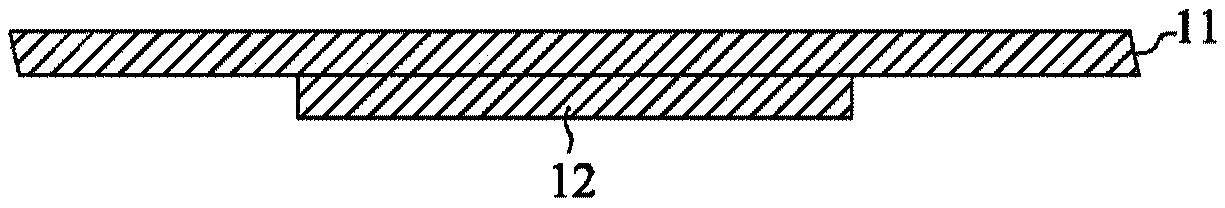
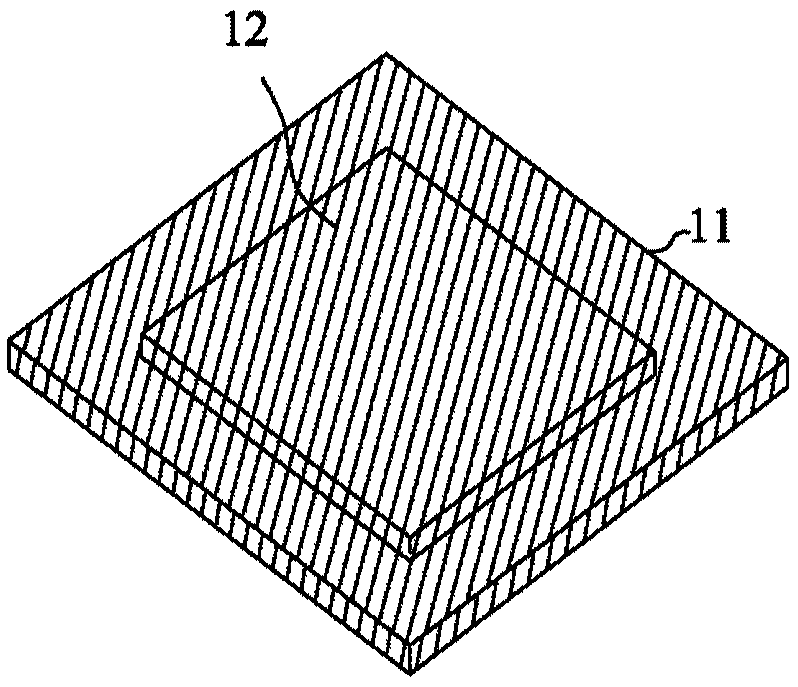
[0104] figure 1 and 2 They are respectively a cross-sectional view and a perspective view of the bottom of the metal bump layer 12 formed on the metal carrier 11 . The metal carrier 11 and the metal bump layer 12 are generally made of copper, aluminum, nickel, stainless steel, or other metals or alloys. The material of the metal bump layer 12 can be the same as or different from the metal carrier 11 . The metal carrier 11 may have a thickness of 0.05 mm to 0.5 mm (preferably 0.1 mm to 0.2 mm), and the metal bump layer 12 may have a thickness of 10 microns to 100 microns. In this embodiment, the metal carrier 11 is made of copper and has a thickness of 0.15 mm, and the metal bump layer 12 is made of cop...
Embodiment 2
[0120] Figure 20-26 It is a diagram of the manufacturing method of the interconnection substrate according to the second embodiment of the present invention, and the core layer is further provided with auxiliary metal pads.
[0121] For the purpose of brief description, any descriptions in the above-mentioned embodiment 1 that can be used for the same application are incorporated here, and it is not necessary to repeat the same descriptions.
[0122] Figure 20 It is a cross-sectional view of the metal bump layer 12 and the arrayed auxiliary metal pads 13 formed on the metal carrier 11 . The metal bump layer 12 and the auxiliary metal pad 13 extend downward from a surface of the metal carrier 11 and have the same thickness. The material of the auxiliary metal pad 13 can be the same as the material of the metal bump layer 12, and can be formed by a patterned deposition method, such as electroplating, electroless plating, evaporation, sputtering or a combination thereof, or b...
Embodiment 3
[0135] Figure 31-37 It is a diagram of the manufacturing method of the interconnect substrate according to the third embodiment of the present invention, which is provided with routing lines exposed from the cavity.
[0136] For the purpose of brief description, any descriptions in the above embodiments that can be used for the same application are incorporated here, and the same descriptions do not need to be repeated.
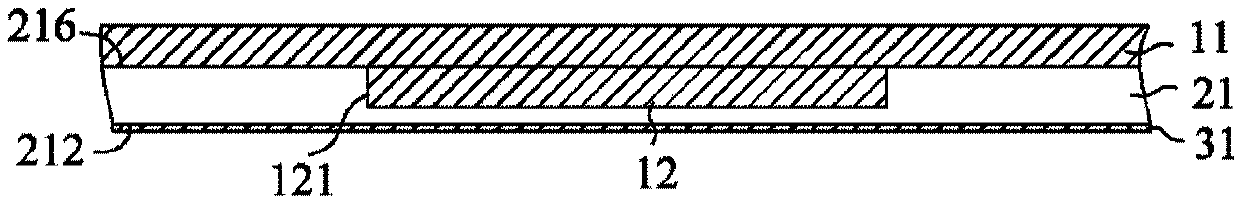
[0137] Figure 31 for Figure 20 A cross-sectional view of routing lines 311 formed on the metal bump layer 12 in FIG. The routing lines 311 are usually made of copper and can be formed by patterned deposition by various techniques, such as electroplating, electroless plating, evaporation, sputtering or a combination thereof, or by thin film deposition followed by a metal patterning step And formed.
[0138] Figure 32 It is a cross-sectional view of the core layer 21 formed on the metal carrier 11 , the metal bump layer 12 , the auxiliary metal pad 13 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com