An erasing method of a single-grid non-volatile memory
A non-volatile memory technology, applied in information storage, static memory, read-only memory, etc., can solve the problems of serious over-erasing, increased cost, and complicated manufacturing process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0043] The following will clearly and completely describe the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention with reference to the accompanying drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments are only some, not all, embodiments of the present invention. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without making creative efforts belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
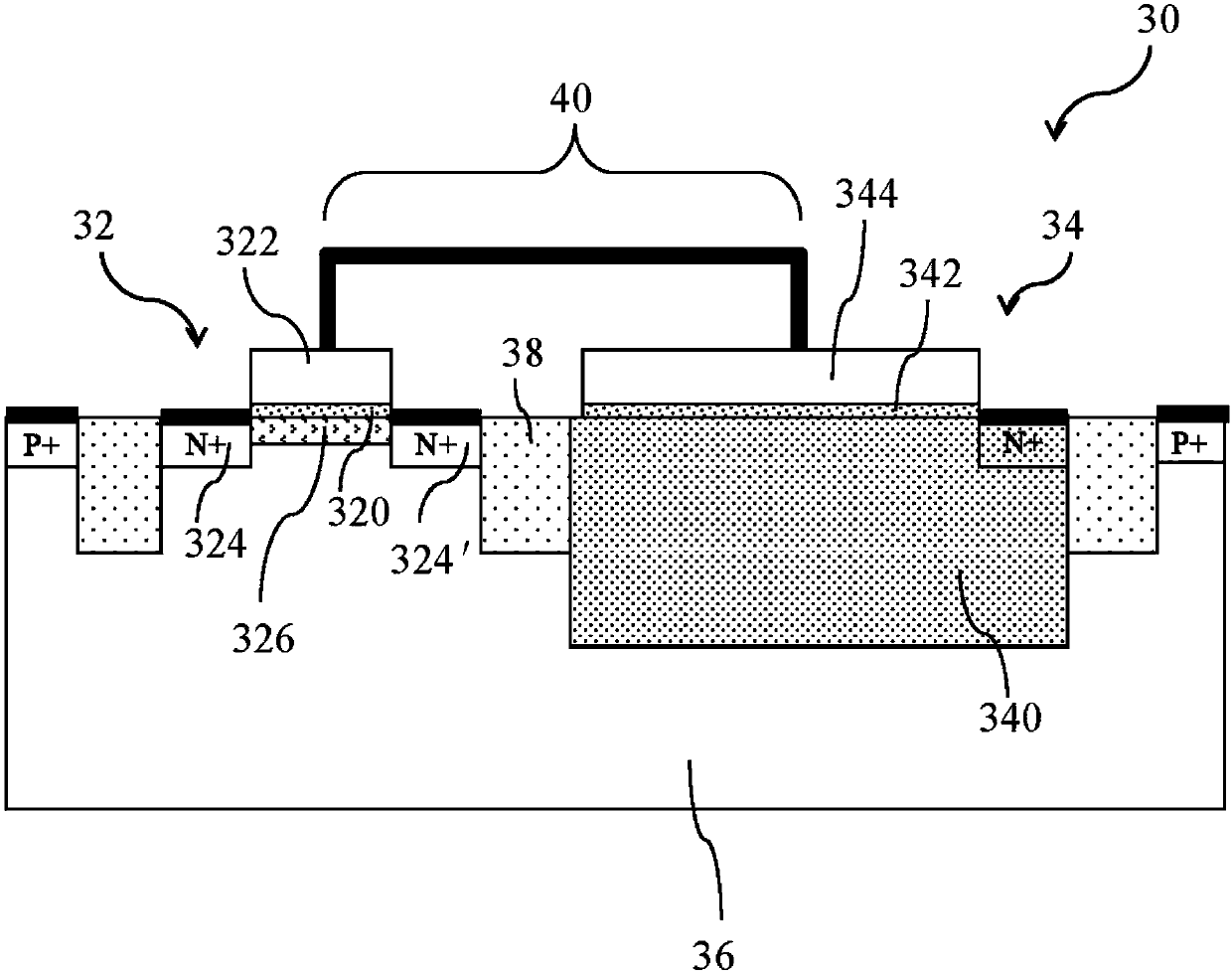
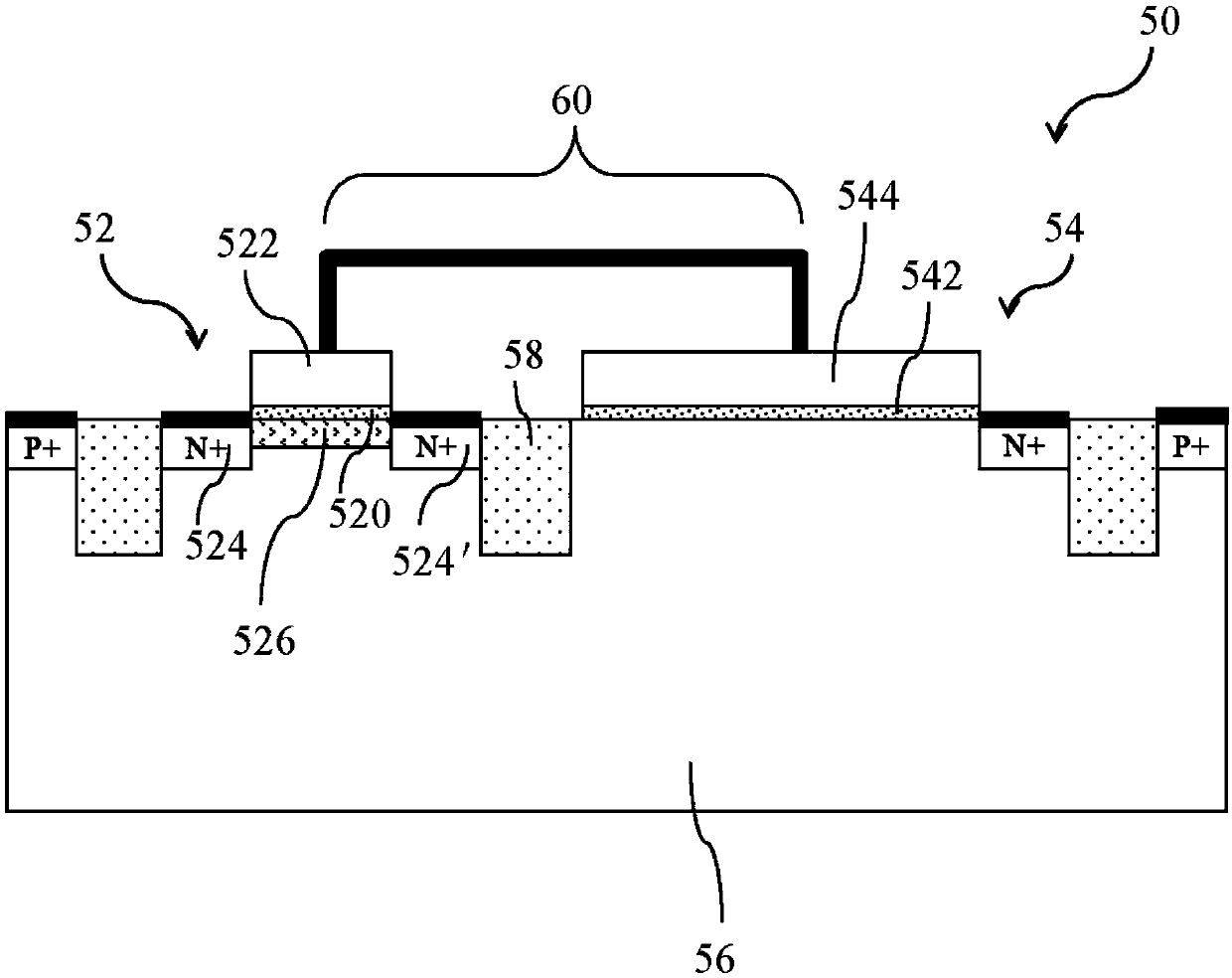
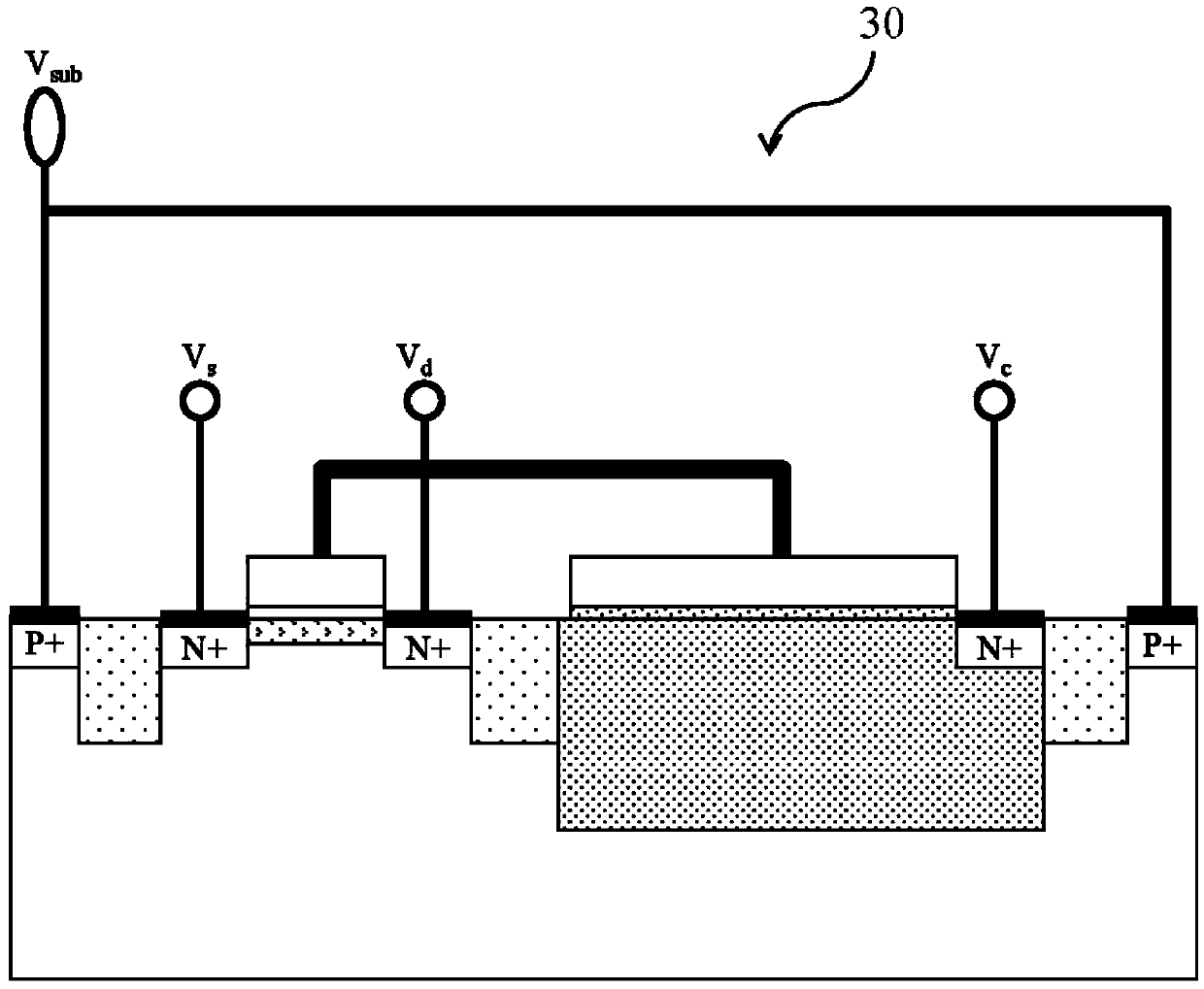
[0044] Figure 1A A cross-sectional view of the single-gate non-volatile memory structure provided by the first embodiment of the present invention, the single-gate non-volatile memory structure 30 includes an NMOS transistor (NMOSFET) 32 and an N-well (N-well) capacitor 34, In the P-type silicon substrate 36; the NMOS transistor 32 includes a first dielectric layer 320 located on the surface of the P-type silicon substrate 36, a first conductive gate 322 stack...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com