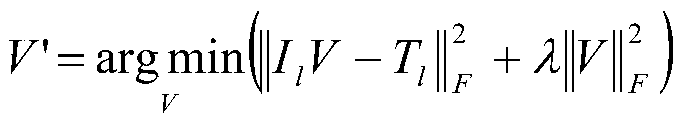Cross-modal retrieval method and system based on pseudo label learning and semantic consistency
A consistent and cross-modal technology, applied in the field of cross-modal retrieval, can solve problems such as difficult to obtain the best performance, and does not consider unlabeled data, etc., to achieve good retrieval effect, difficult to obtain, and easy cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
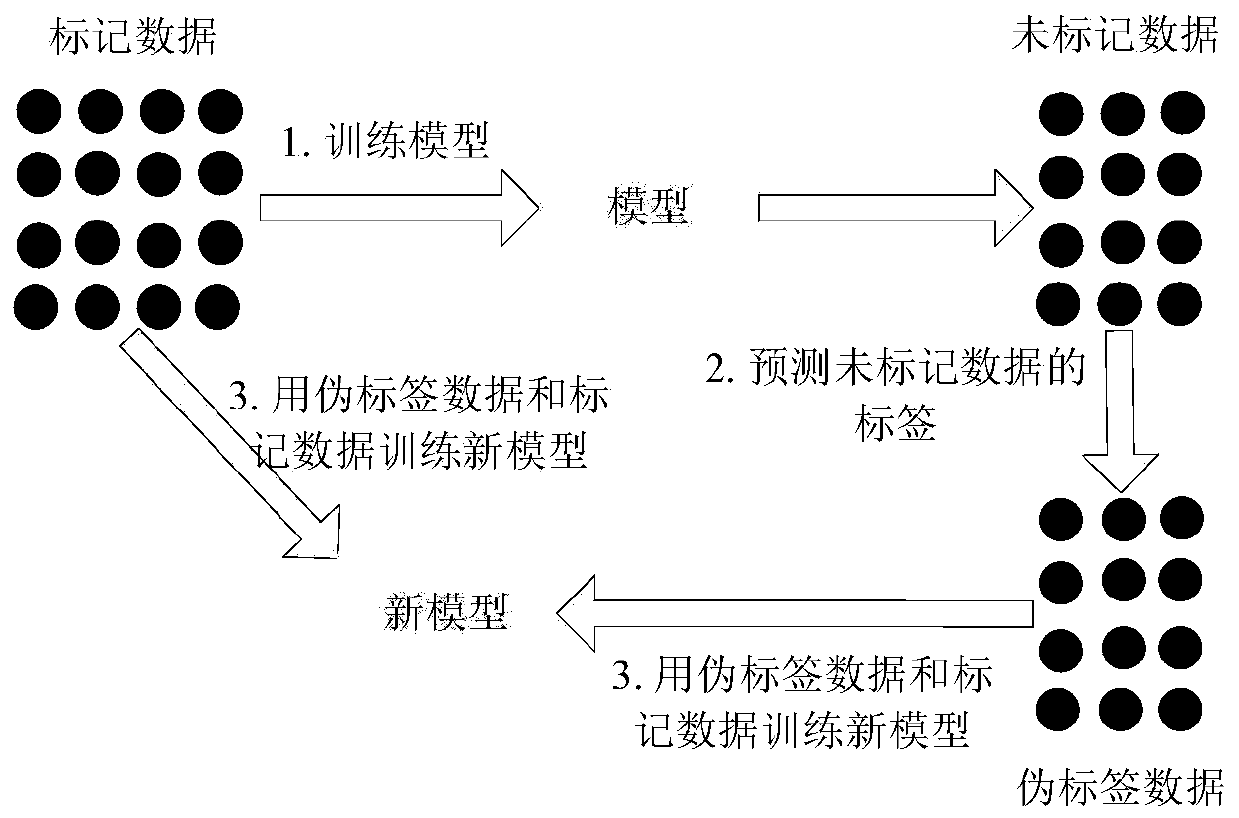
[0055] In multimodal data retrieval, the similarity between different modal data cannot be directly measured. To relate data from one modality to data from other modalities, we learn a projection matrix using both labeled and unlabeled data. This embodiment discloses a cross-modal retrieval method based on pseudo-label learning and semantic consistency, such as figure 2 shown, including the following steps:
[0056] Step 1: Receive an image dataset and a text dataset, which includes labeled image and text pairs and unlabeled image data;
[0057] Image-text pairs in the training set have special semantic information called class labels. This semantic information can be used as the third dimension of the learned subspace and used to obtain a similarity measure between semantically similar but different modality data in the shared subspace. This embodiment also utilizes class labels to obtain a better similarity measure between data points. Unlike previous methods, the dimens...
Embodiment 2
[0132] The purpose of this embodiment is to provide a computer system.
[0133] A computer system, comprising a memory, a processor, and a computer program stored on the memory and operable on the processor, when the processor executes the program, the following steps are implemented, including:
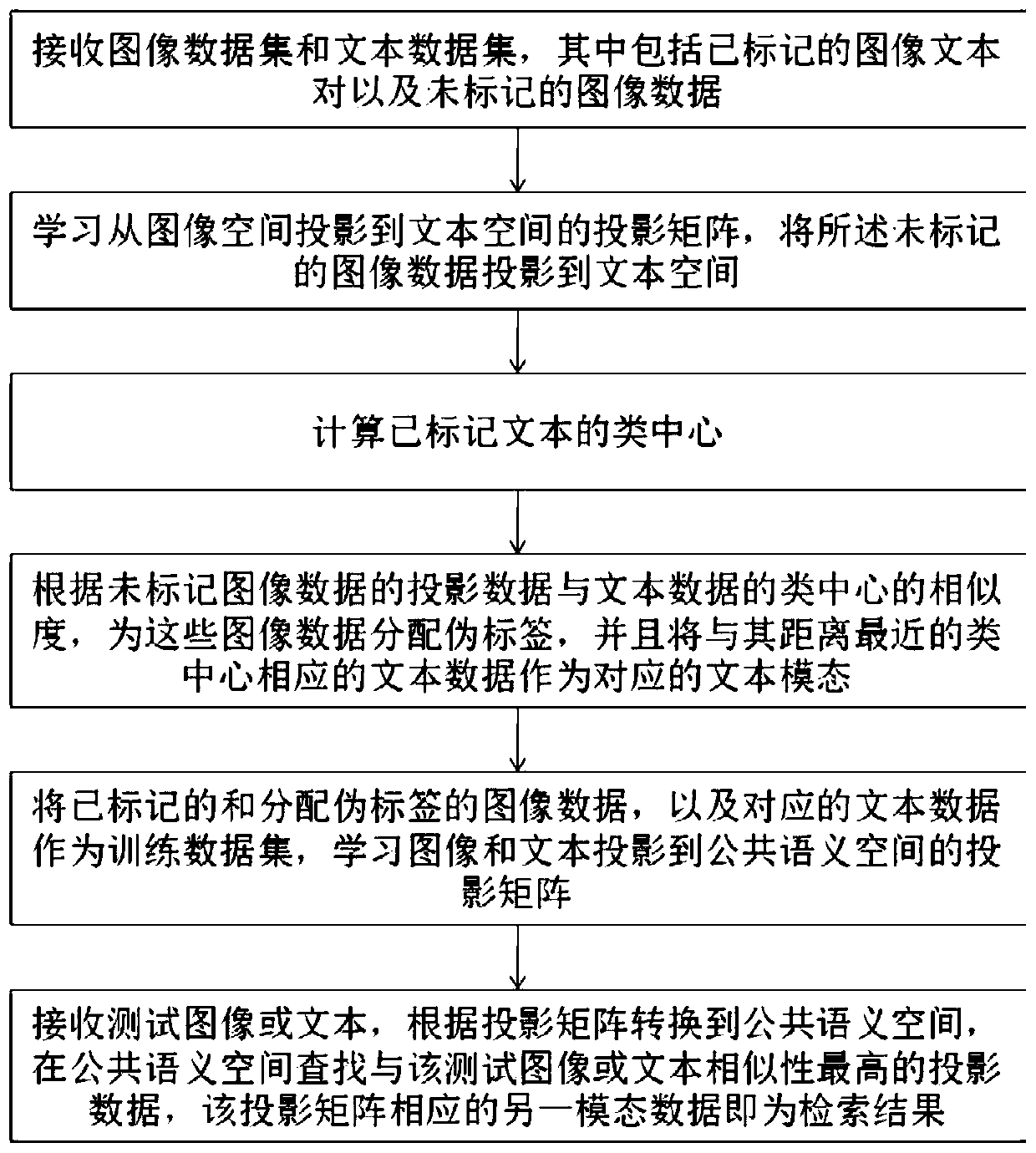
[0134] Receive an image dataset and a text dataset, which includes labeled image-text pairs as well as unlabeled image data;
[0135] learning a projection matrix from image space to text space, projecting said unlabeled image data to text space;
[0136] Calculate the class center of the labeled text;
[0137] According to the similarity between the projection data of the unlabeled image data and the class center of the text data, assign pseudo-labels to these image data, and use the text data corresponding to the class center closest to it as the corresponding text modality;
[0138] Use the labeled and assigned pseudo-labeled image data, as well as the corresponding text data as...
Embodiment 3
[0141] The purpose of this embodiment is to provide a computer-readable storage medium.
[0142] A computer-readable storage medium, on which a computer program is stored, and when the program is executed by a processor, the following steps are performed:
[0143] Receive an image dataset and a text dataset, which includes labeled image-text pairs as well as unlabeled image data;
[0144] learning a projection matrix from image space to text space, projecting said unlabeled image data to text space;
[0145] Calculate the class center of the labeled text;
[0146] According to the similarity between the projection data of the unlabeled image data and the class center of the text data, assign pseudo-labels to these image data, and use the text data corresponding to the class center closest to it as the corresponding text modality;
[0147] Use the labeled and assigned pseudo-labeled image data, as well as the corresponding text data as the training data set, and learn the pro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com