Soaping method for improving post-treatment effect of reactive dye dyed fiber
A reactive dye and soaping technology, which is applied in the field of fiber dyeing, can solve problems such as waste of energy, unstable color, and color fastness of staining, and achieve the effects of improving the efficiency of floating color washing, ensuring color stability, and saving process costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
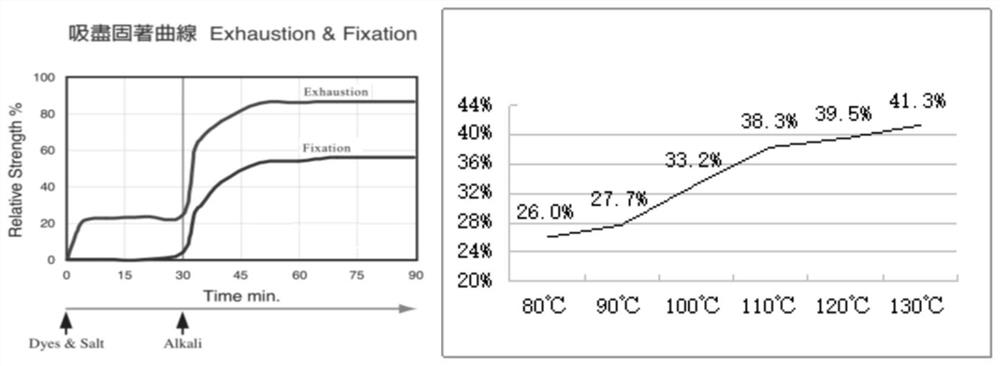
[0038] Select the CF60 / 1 pure cotton yarn of the same yarn batch, arrange the following dye formula (Table 1) to carry out pre-routine treatment and dyeing, after the dyeing is finished, it is out of the vat, split into two vats on average, and use the post-treatment process of Comparative Example 1 and the vat respectively. The post-treatment process of Example 1 of the present invention was tested and compared.
[0039]
[0040] The post-processing flow is as follows:
[0041] (1) Post-treatment process of Comparative Example 1: washing with water (50°C×5min)→acid washing (50°C×5min)→soaping (98°C×10min+soaping agent)→soaping (98°C×10min+soaping agent )→soaping (98℃×10min+soaping agent)→water washing (80℃×5min)→water washing (80℃×5min)→water washing (80℃×5min)→water washing (60℃×5min);
[0042] (2) Post-treatment process of Example 1 of the present invention: water washing (50°C×5min)→acid washing (50°C×5min)→soaping (105°C×10min+soaping agent)→soaping (105°C×10min+soapi...
Embodiment 2
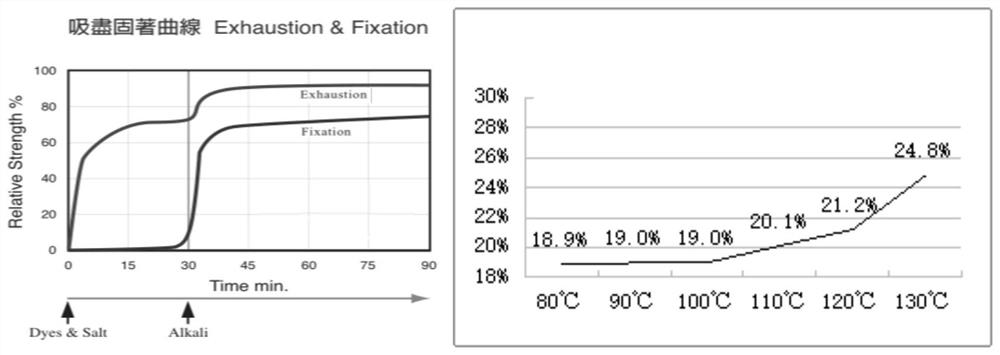
[0051] Select the CF40 / 1 pure cotton yarn of the same yarn batch, arrange the following dye formula (Table 3) to carry out conventional pretreatment and dyeing, after the dyeing is finished, it is out of the vat, split into two vats on average, and use the post-treatment process of Comparative Example 2 and the vat respectively. The post-treatment process of Example 2 of the present invention was tested and compared.
[0052]
[0053] The post-processing flow is as follows:
[0054] (1) Post-treatment process of comparative example 2: washing with water (50°C×5min)→acid washing (50°C×5min)→soaping (98°C×10min+soaping agent)→soaping (98°C×10min+soaping agent )→Soaping (98℃×10min+soaping agent)→Washing (80℃×5min)→Washing (80℃×5min)→Washing (80℃×5min)→Washing (80℃×5min)→Washing (60℃ ×5min)→Washing (60℃×5min);
[0055] (2) Post-treatment process of Example 2 of the present invention: washing (50°C×5min) → pickling (50°C×5min) → soaping (125°C×10min+soaping agent) → soaping (125...
Embodiment 3
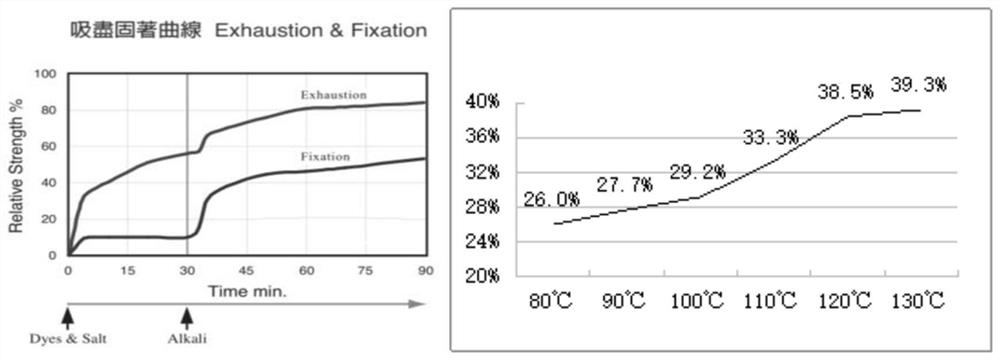
[0064] Select the CF60 / 2 pure cotton yarn of the same yarn batch, arrange the following dye formula (Table 5) to carry out conventional pretreatment and dyeing, after the dyeing is finished, it is out of the vat, split into two vats on average, and use the post-treatment process of Comparative Example 3 and the vat respectively. The post-treatment process of Example 3 of the present invention was tested and compared.
[0065]
[0066]
[0067] The post-processing flow is as follows:
[0068] (1) Post-treatment process of comparative example 3: washing with water (50°C×5min)→acid washing (50°C×5min)→soaping (98°C×10min+soaping agent)→soaping (98°C×10min+soaping agent )→Soaping (98℃×10min+soaping agent)→Washing (80℃×5min)→Washing (80℃×5min)→Washing (80℃×5min)→Washing (80℃×5min)→Washing (60℃ ×5min);
[0069] (2) Post-treatment process of Example 3 of the present invention: washing (50°C×5min) → pickling (50°C×5min) → soaping (115°C×10min+soaping agent) → soaping (115°C×10...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com