Built-in double-V-shaped series-parallel hybrid magnetic circuit adjustable magnetic flux permanent magnet synchronous motor
A permanent magnet synchronous motor and hybrid magnetic circuit technology, applied in synchronous motors with static armatures and rotating magnets, synchronous machine parts, magnetic circuit rotating parts, etc., to achieve small demagnetization current, increase power density, The effect of small magnetizing current
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
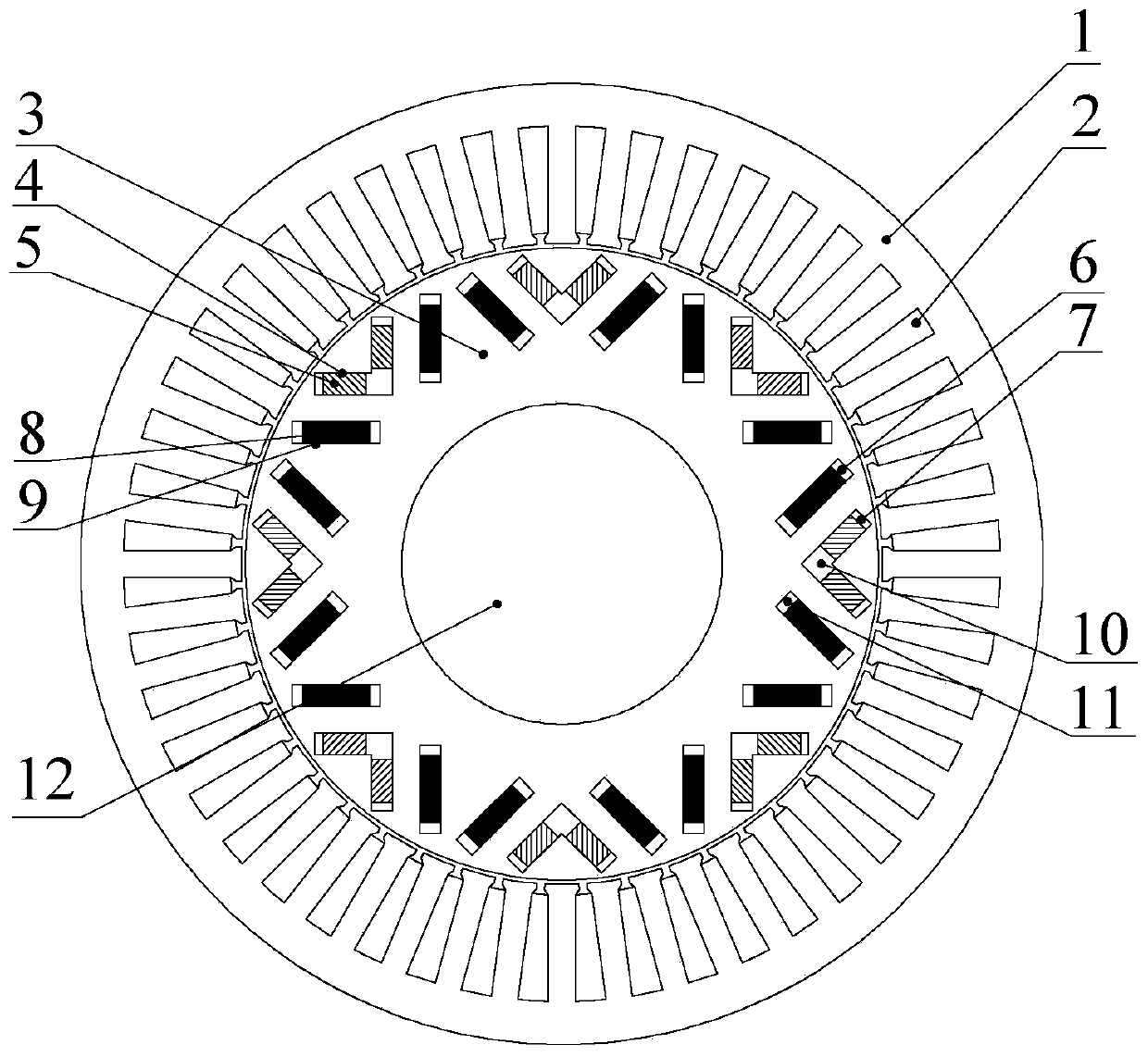
[0026] Embodiment 1: see figure 1 , the motor includes a stator core 1, an armature winding 2, a rotor core 3, a rotating shaft 12, a low-coercivity permanent magnet 5, a high-coercivity permanent magnet 8, an inner V-tip magnetic isolation groove 10, and an inner V air gap side Magnetic isolation slot 7, magnetic isolation slot 6 on the outer V air gap side, and magnetic isolation slot 11 on the outer V shaft side; the rotor core 3 is fixed on the rotating shaft 12, the armature winding 2 is located in the stator core 1, the stator core 1 and the rotor core 3 There is a radial air gap between them;
[0027] The air-gap side body of the rotor core 3 has multiple permanent magnets built in to form a P pair of magnetic poles. Each pole includes two low-coercivity permanent magnets 5 and two high-coercivity permanent magnets 8, and two low-coercivity permanent magnets. 5 Take the pole rotor direct axis as the symmetry line to form a V shape symmetrically, and the V-shaped tip is...
Embodiment 2
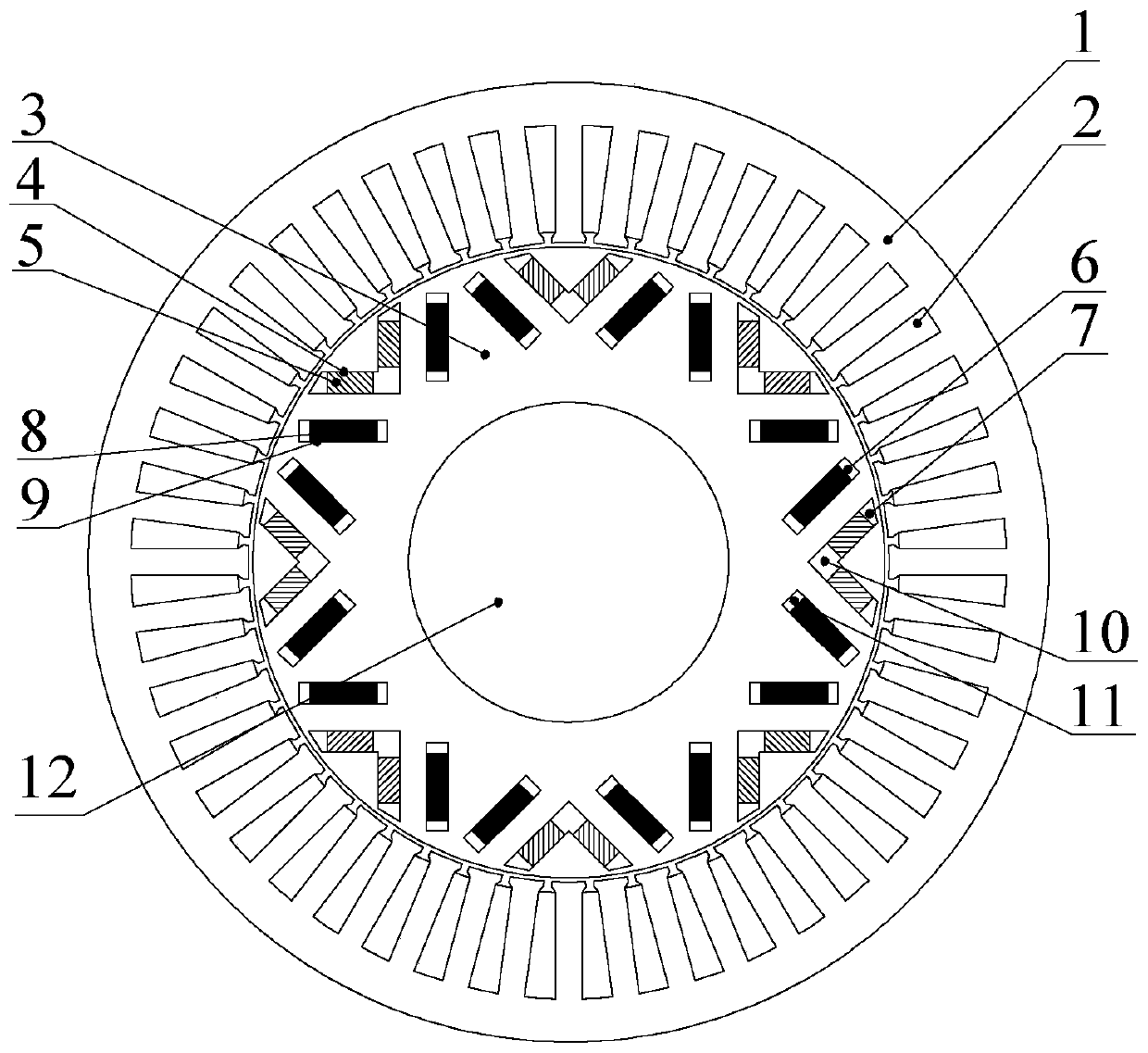
[0033] Example 2: see figure 2 , is improved on the basis of Embodiment 1, and further includes a central rib 13, which is arranged inside the inner V-tip magnetic isolation groove 10 along the direction of the rotor direct axis, and divides the trapezoidal groove into two parts.
[0034]The purpose of providing the central rib 13 in this embodiment is to improve the mechanical strength of the rotor. The width of the central rib 13 can be reasonably selected after comprehensively considering the mechanical strength and electromagnetic performance requirements of the motor.
Embodiment 3
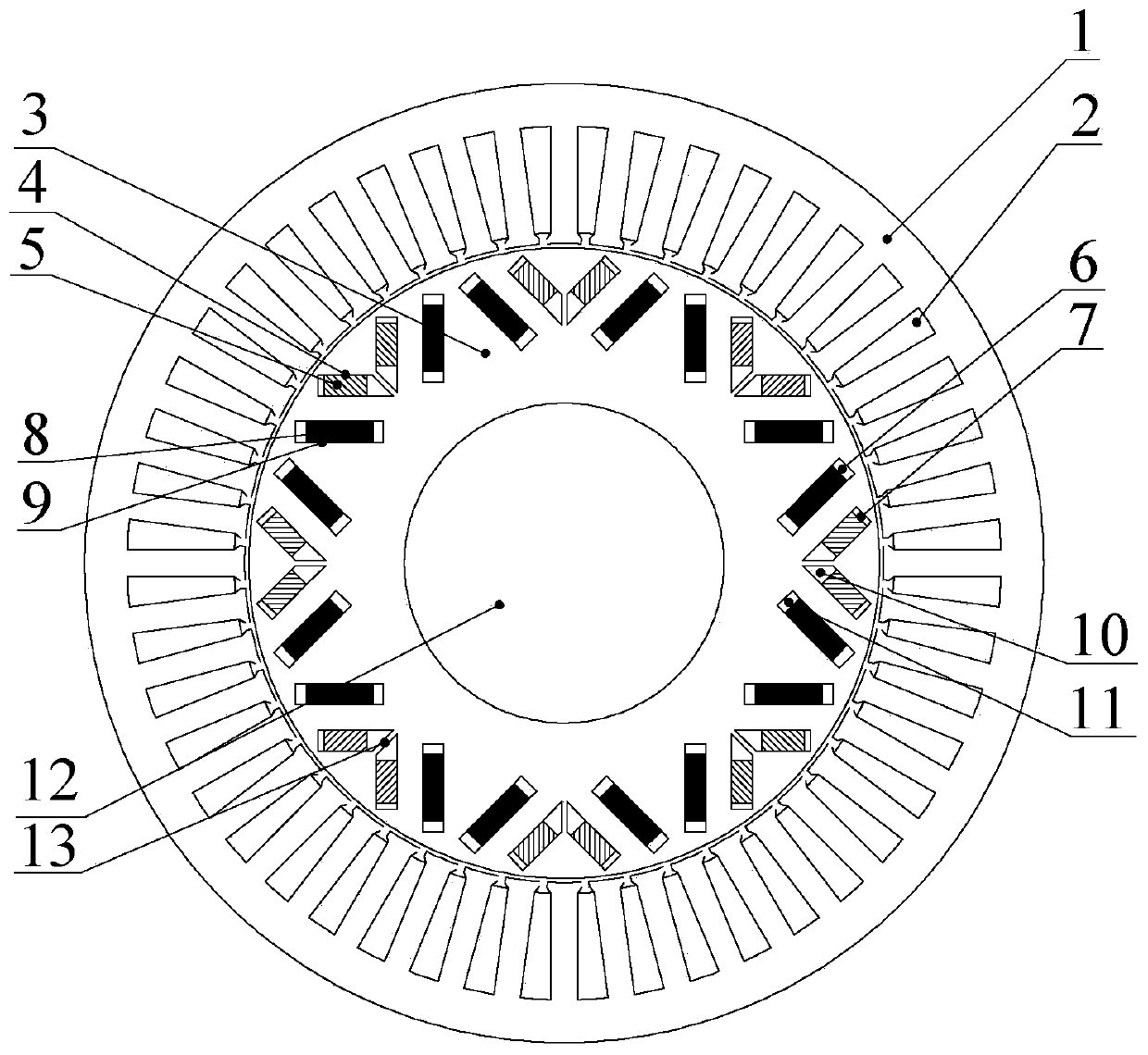
[0035] Embodiment 3: see image 3 , improved on the basis of Example 1, the inner V-tip magnetic isolation groove 10 is a trapezoidal groove, and two low-coercivity permanent magnets 5 are connected at the same time, located at the V-shaped tip formed by two low-coercivity permanent magnets 5 ; The magnetic isolation slot 6 on the outer V air gap side and the magnetic isolation slot 11 on the outer V shaft side are both rectangular slots. The magnetic isolation groove 7 on the inner V air gap side is replaced by a trapezoidal groove.
[0036] In this embodiment, the purpose of setting trapezoidal magnetic isolation grooves on the rotor air gap side is to form a magnetic bridge, limit the magnetic flux passing through the magnetic bridge, and not only reduce the magnetic flux leakage generated by the low-coercivity permanent magnet 5 due to its own short circuit, but also Reduced the influence that high-coercivity permanent magnet 8 produces on low-coercivity permanent magnet ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com