Method for treating infectious diseases by NK (natural killer) targeted immune checkpoints
A technology for immune checkpoints and infectious diseases, applied in the direction of immunoglobulin, chemical instruments and methods, antiviral agents, etc., can solve the problems of limited treatment effect, inability to effectively protect patients from re-infection, and high price
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] Example 1. Establishment and Confirmation of HCV Mouse Model
[0076] During the course of HCV infection, acute HCV infection is characterized by a marked delay in the T cell response. In a previous study, human CD81 and OCLN liver-specific double transgenic mice (C / O-Tg mice) have been constructed on the ICR mouse background, which are able to support chronic HCV infection and mimic chronic hepatitis C. Immune tolerance, steatosis, liver fibrosis, liver cirrhosis and other disease processes (Chen J, Zhao Y, Zhang C, Chen H, Feng J, et al.2014.Persistenthepatitis C virus infections and hepatopathological manifestations in immune-competent humanized mice . Cell research 24:1050).
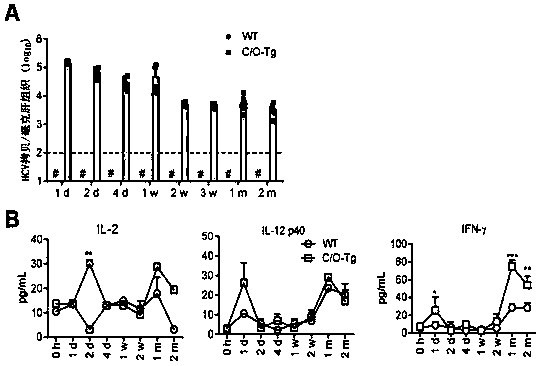
[0077] This mouse model of HCV infection was first replicated and validated. HCV (J399EM, 1mL, TCID 50 =2x10 7 ) to C / O-Tg mice and wild-type littermate control mice for tail vein infusion. Detection of HCV genome copy number in mouse liver at different time points after HCV infusion indi...
Embodiment 2
[0078] Example 2. T cell immune checkpoint blockade has no effect on HCV chronic infection
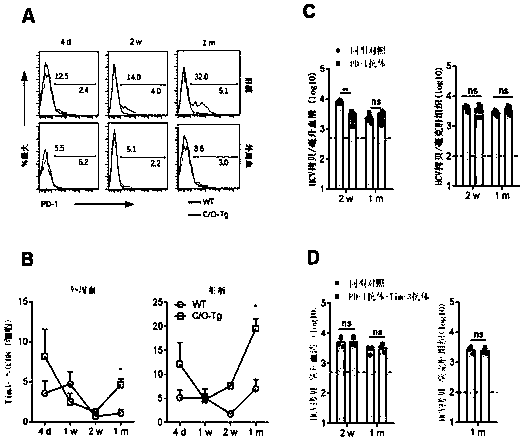
[0079] Since it is generally believed that CD8+ T cells play an important role in the process of virus infection and clearance, we first detected the expression of CD8+ T immune checkpoint molecules during HCV infection. It was found that after infection of mice with HCV, the T cell immune checkpoint molecule PD-1 ( figure 2 A) and Tim-3 ( figure 2 B) Upregulation with the establishment of chronic infection. Based on this, it was tested whether targeting T cell immune checkpoint molecules could inhibit this chronic infection process. However, if figure 2 C and figure 2 As shown in the results of D, no matter whether the PD-1 blocking antibody (clone number G4, self-produced by the hybridoma) or the combined use of PD-1 and Tim-3 blocking antibodies (clone number BE0115, purchased from BioXcell) were used alone, all Cannot effectively promote virus clearance. The above results...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Example 3. Depletion of NK cells leads to persistent infection of HCV
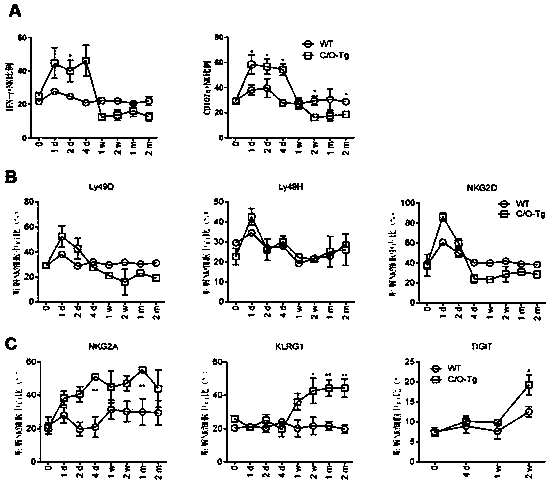
[0081] The effect of HCV infection on NK cell function was subsequently examined. Hepatic NK cell depletion during HCV infection was examined by an in vitro NK function assay. The results showed that the IFN-γ secretory ability and CD107a degranulation level of liver NK cells of HCV-infected C / O-Tg mice stimulated by target cell Yac-1 increased within 4 days after HCV infusion, which then decreased rapidly to baseline levels similar to uninfected liver NK cells ( image 3 A). Further studies showed upregulation of NK-activating receptors Ly49D, Ly49H and NKG2D within 4 days after HCV infusion ( image 3 B). These results demonstrate transient liver infiltration and activation of NK cells in response to HCV infection. However, these activated receptors decreased in hepatic NK cells 4 days after HCV infusion, whereas the expression of immune checkpoint molecules KLRG1, NKG2A, and TIGIT increased ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com