A non-structural grid nearest wall distance solving method based on a balanced KD tree
An unstructured grid, the closest distance technology, applied in the field of computational fluid dynamics and applied mathematics, can solve the problems of poor query efficiency in the far field area, large error in the nearest wall distance, unbalanced ADT tree, etc., to achieve easy implementation Parallelization, reduction of calculation amount, good practical effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
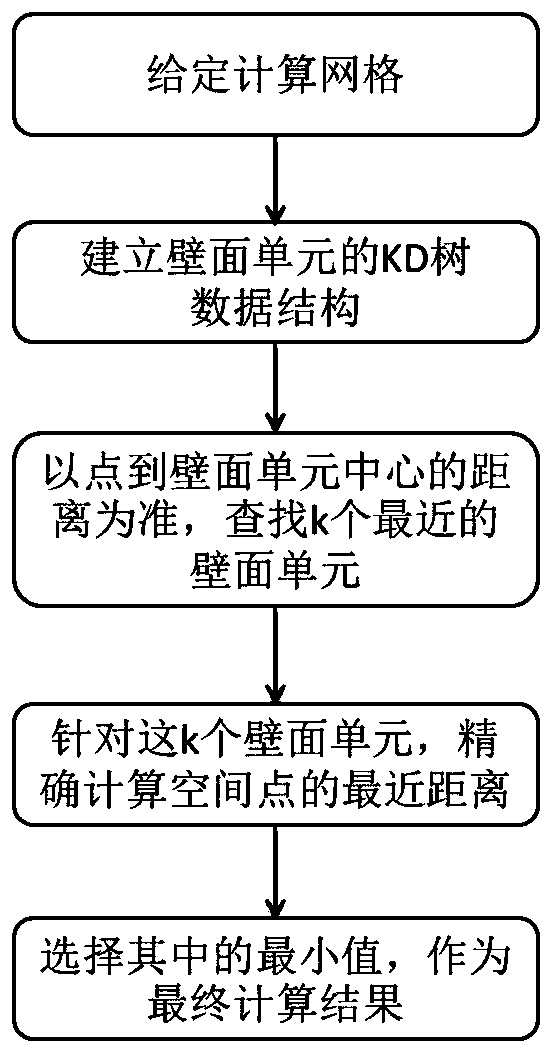
[0035] like figure 1 As shown, a method for solving the wall distance of an unstructured grid based on a balanced KD tree includes the following steps:
[0036] S1. Taking the coordinates of the center point of the wall unit as the dimension, establish a balanced KD tree data structure;
[0037] S2. For a certain target point in space, use the distance from it to the center point of the wall surface unit as the approximate shortest distance, start from the root node of the KD tree to query step by step, and select k nearest object surface units;
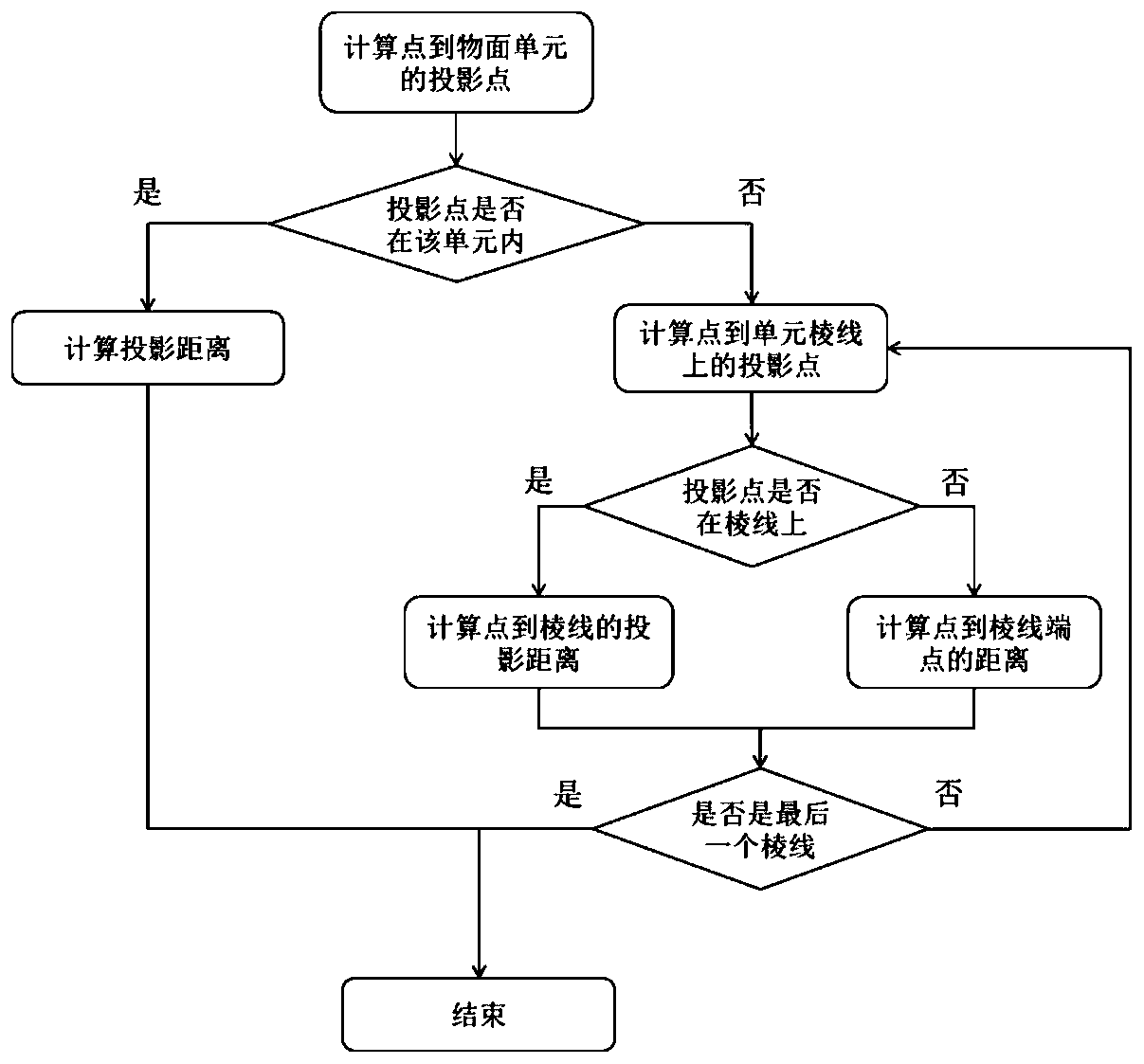
[0038] S3. After finding the k nearest object plane units based on the center point of the object plane unit, accurately calculate the shortest distance from the target point to the k object plane units, and select the minimum value among them as the final result.
Embodiment 2
[0040] This embodiment is on the basis of embodiment 1:
[0041] In step S1, taking the two-dimensional space point set {1, 2, ... N} as an example, the establishment process of the KD tree is as follows:
[0042] S11. First sort the x-coordinates of the points, and take the Floor(N / 2)th point as the root node;
[0043] S12. For the sorted subset (1~Floor(N / 2)-1), the y coordinates of the points are sorted, and the median point is taken as the left child node of the root node;
[0044] S13. For the sorted subset (Floor(N / 2)+1~N), sort the y coordinates of the points, and take the median point as the right child node of the root node;
[0045] S14. Recursively execute S11-S13, and make judgments starting from the x and y coordinates in turn until there is no point in the subset.
Embodiment 3
[0047] This embodiment is on the basis of embodiment 2:
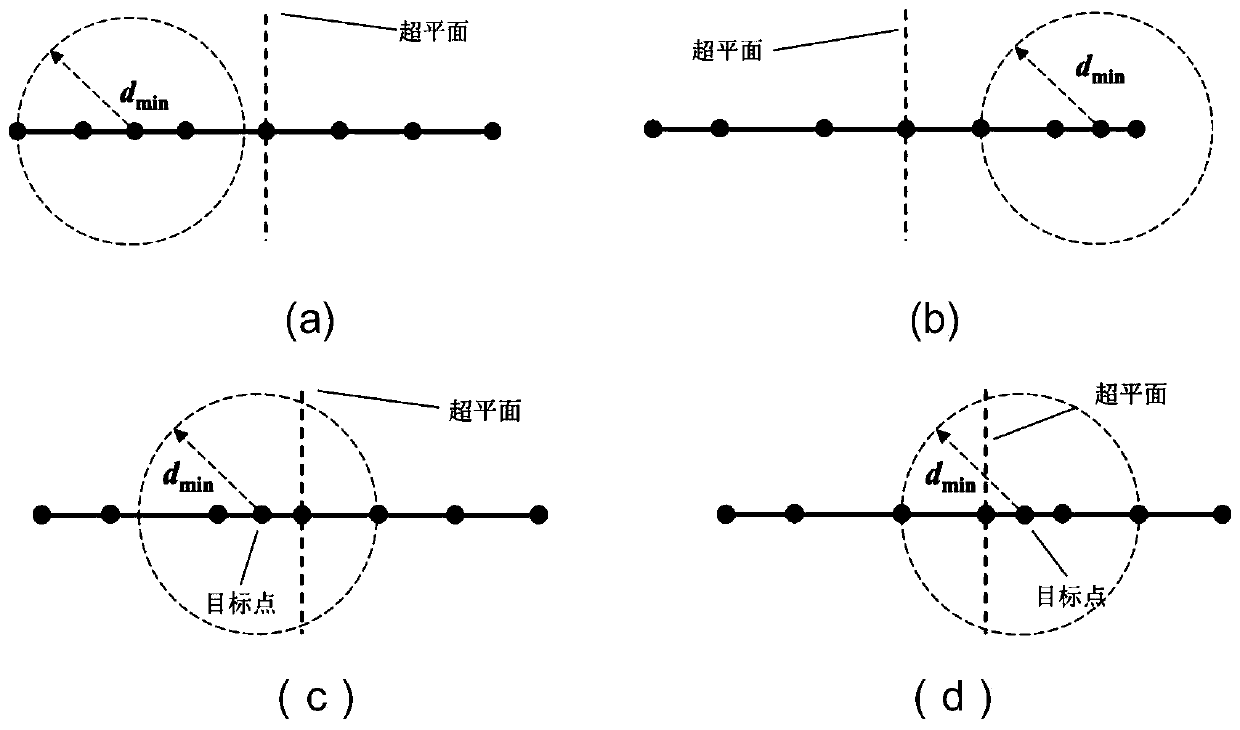
[0048] When selecting the query path, draw a circle (two-dimensional) or sphere (three-dimensional) with the target point as the center, using the currently calculated nearest wall distance as the radius, and draw a circle (or sphere), target point, hyperplane The relative position of determines the next child node to be queried. Taking the dimension x in the two-dimensional case as an example, the query method is as follows figure 2 As shown, the description is as follows:
[0049] a) If the target point is located on the left side of the current KD tree hyperplane, and its circumscribed circle does not intersect with the hyperplane, then directly enter the left subtree instead of entering the right subtree for query, wherein the circumscribed circle is the target point As the center, a sphere with the current minimum distance as the radius;
[0050] b) If the target point is located on the right side of the curren...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com