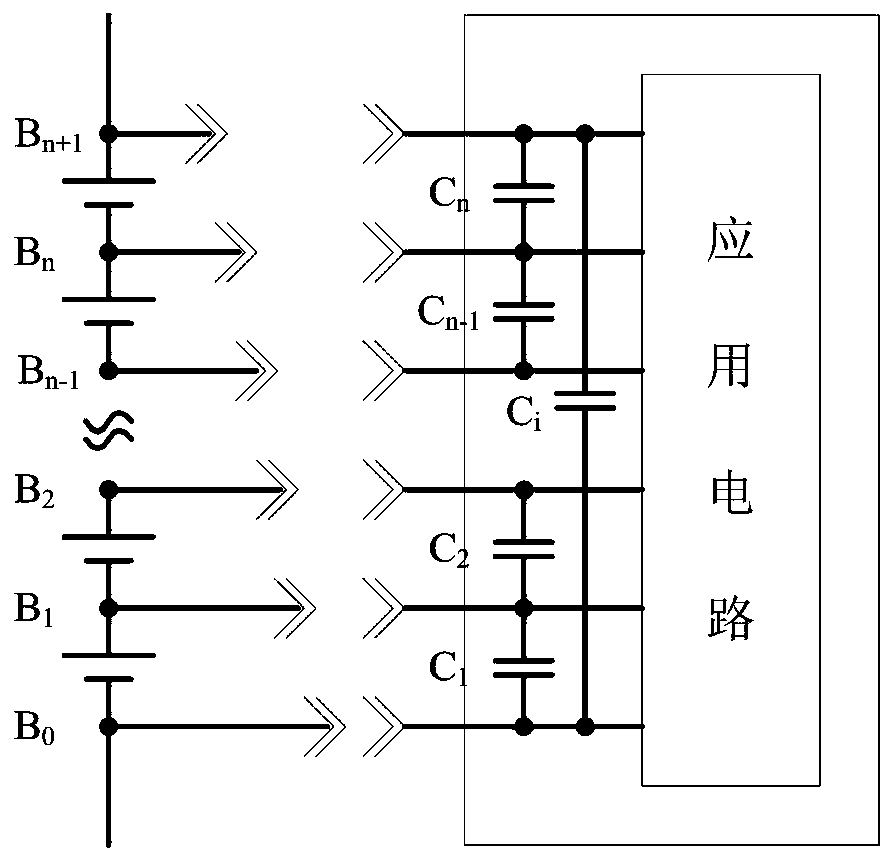
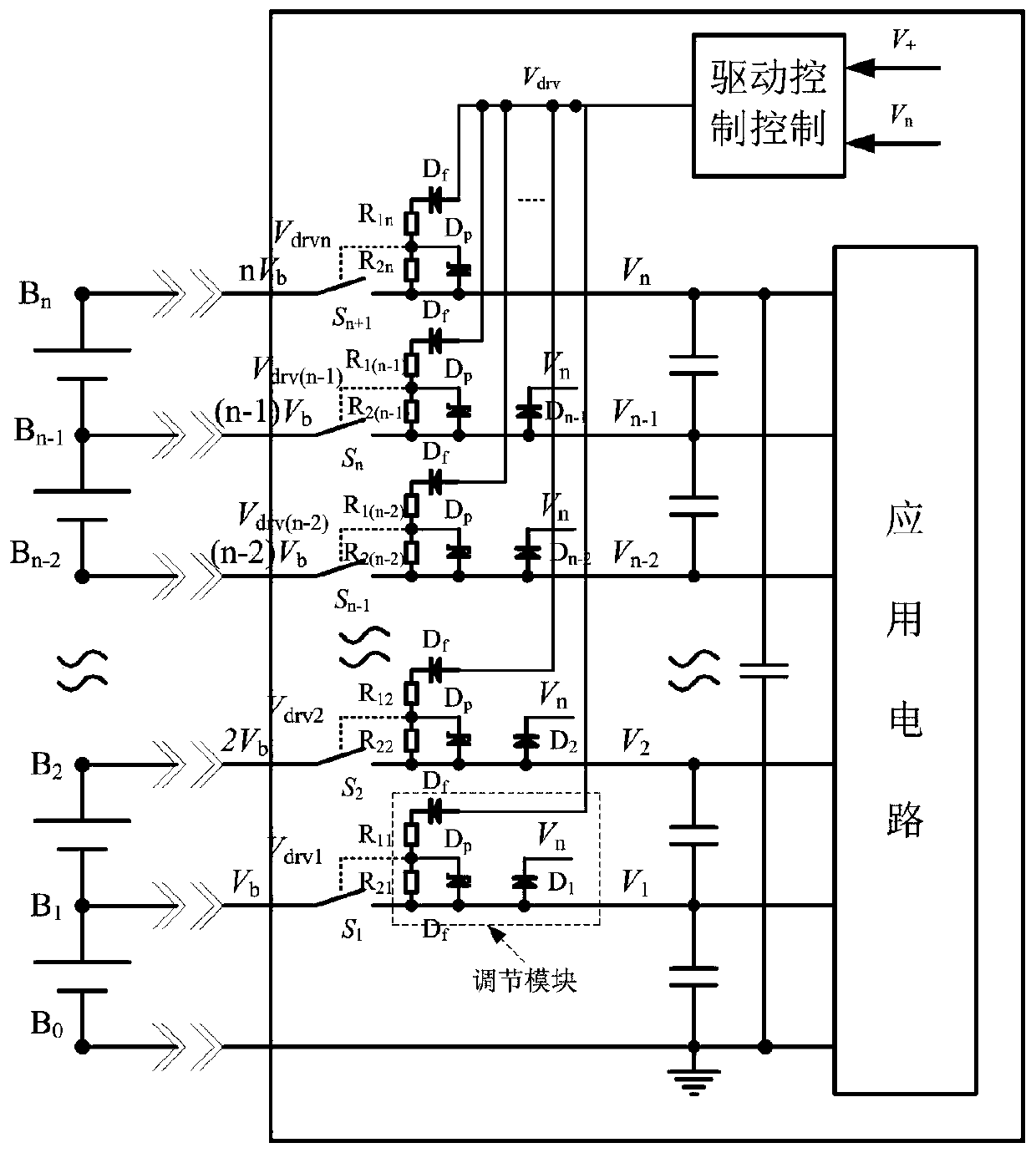
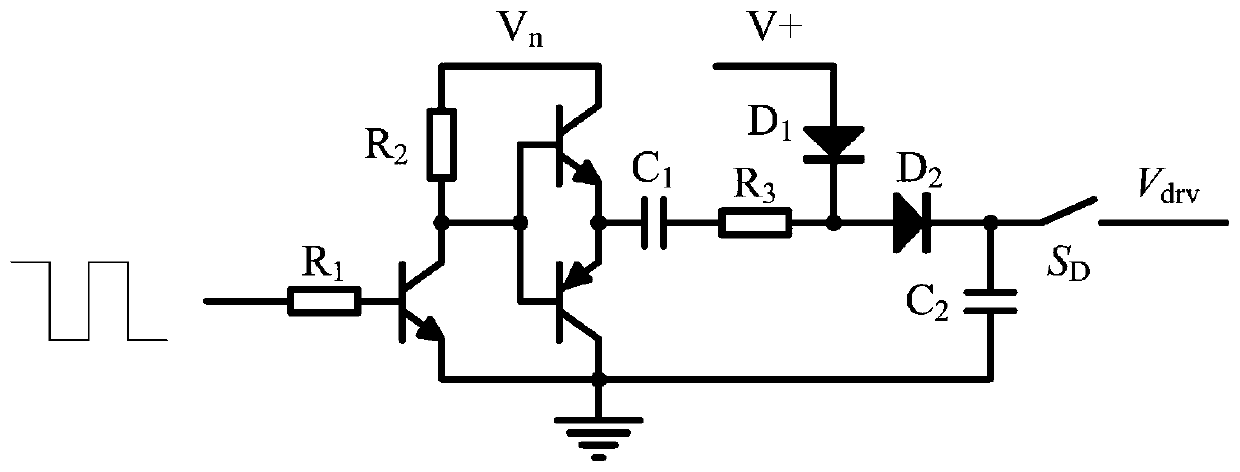
Battery pack hot plug protection circuit and method
A protection circuit, hot-swap technology, applied in the field of electronics, can solve problems such as overvoltage, overcurrent, negative pressure, etc., achieve good switching speed and power consumption, reduce system costs, and facilitate component stocking.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] Preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings, but the present invention is not limited to these embodiments. The present invention covers any alternatives, modifications, equivalent methods and schemes made within the spirit and scope of the present invention.
[0024] In order to provide the public with a thorough understanding of the present invention, specific details are set forth in the following preferred embodiments of the present invention, but those skilled in the art can fully understand the present invention without the description of these details.
[0025] In the following paragraphs the invention is described more specifically by way of example with reference to the accompanying drawings. It should be noted that all the drawings are in simplified form and use inaccurate scales, which are only used to facilitate and clearly assist the purpose of illustrating the embodiments of t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com