A Momentum-Based Parameter Identification Method for Space Robotic Systems
A space robot and parameter identification technology, which is applied in manipulators, program-controlled manipulators, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems such as non-interference, fuel consumption, and affecting system motion requirements, so as to achieve the effect of saving fuel consumption and reducing requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
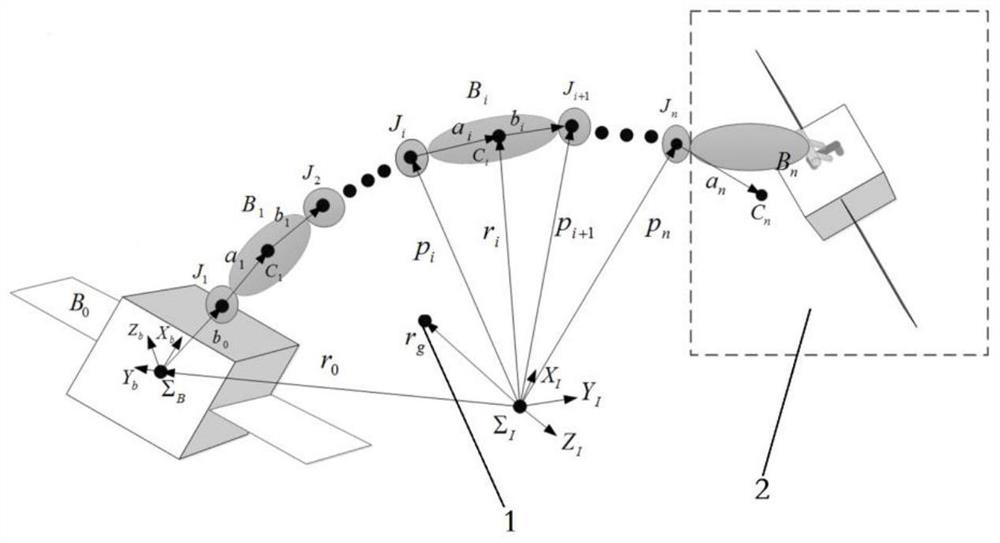
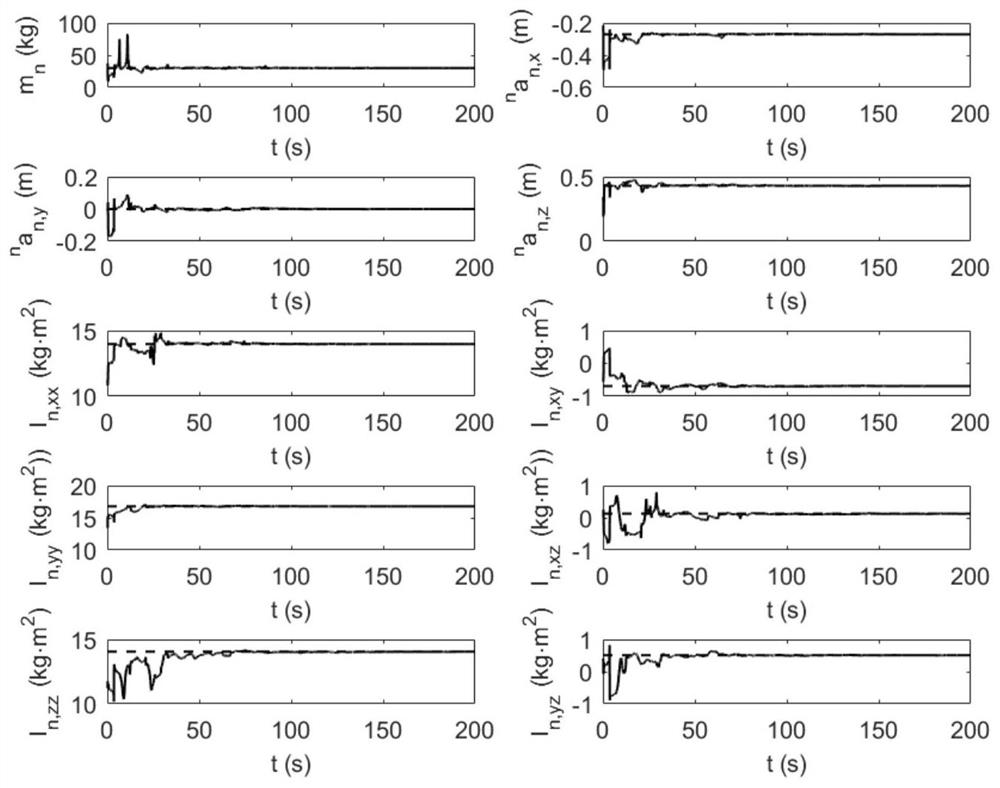
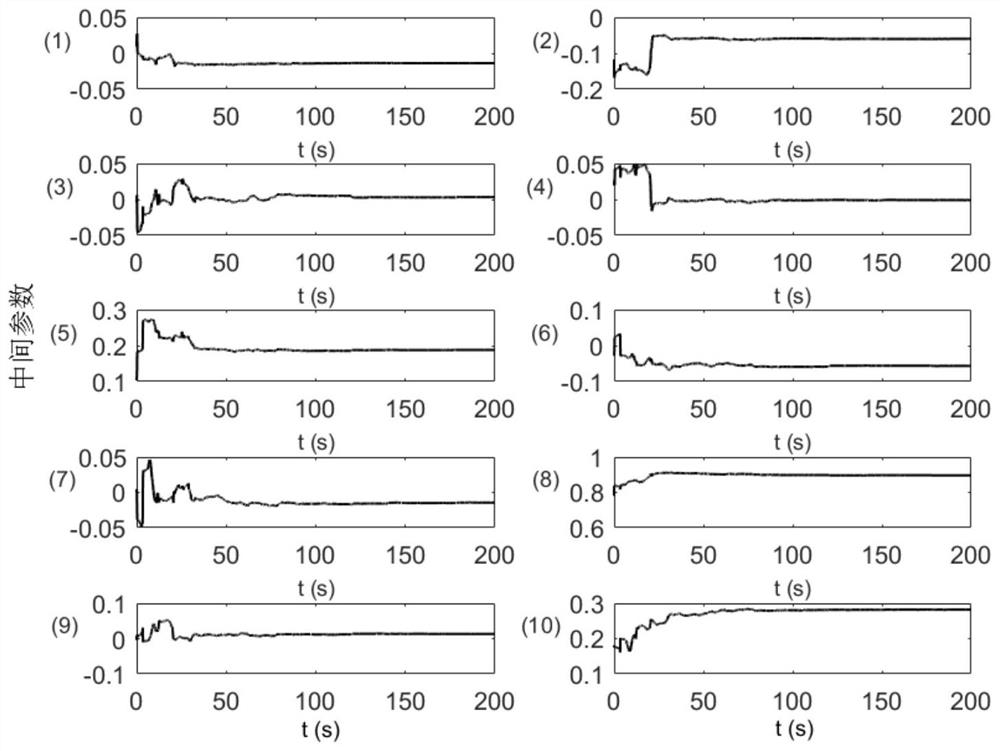
[0090] see figure 1 , a schematic diagram of the system after a space robot captures a non-cooperative target. Assume that the true values of the dynamic parameters of the last link are m respectively n =30kg, n a n =[-0.27, 0, 0.43]m, n I n,xx =13.98kg m 2 , n I n,yy =16.78kg·m 2 , n I n,zz =14.05kg m 2 , n I n,xy =-0.69kg m 2 , n I n,xz =0.13kg m 2 , n I n,yz =0.51kg m 2 . Make the motion of the system meet other task requirements, including that the motion of the arm does not interfere with the posture of the base and the angle of each joint does not exceed the limited range, but it is not required that the motion of the system meets the condition of continuous excitation. Assuming that the initial estimated value of the parameter to be identified in the system is 80% of the true value, using the parameter identification method proposed in the present invention, the estimated value curve of the unknown dynamic parameter of the system is obtained, see ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com