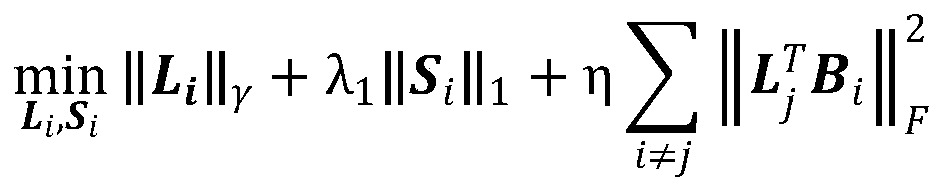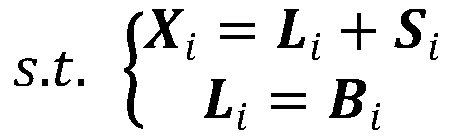Face recognition method based on discriminative non-convex low-rank decomposition and superposition linear sparse representation
A low-rank decomposition, face recognition technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, instruments, computer parts, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient training samples and incomplete dictionaries, so as to increase incoherence and remove inter-class correlation. , the effect of suppressing intra-class variation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0015] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the drawings.
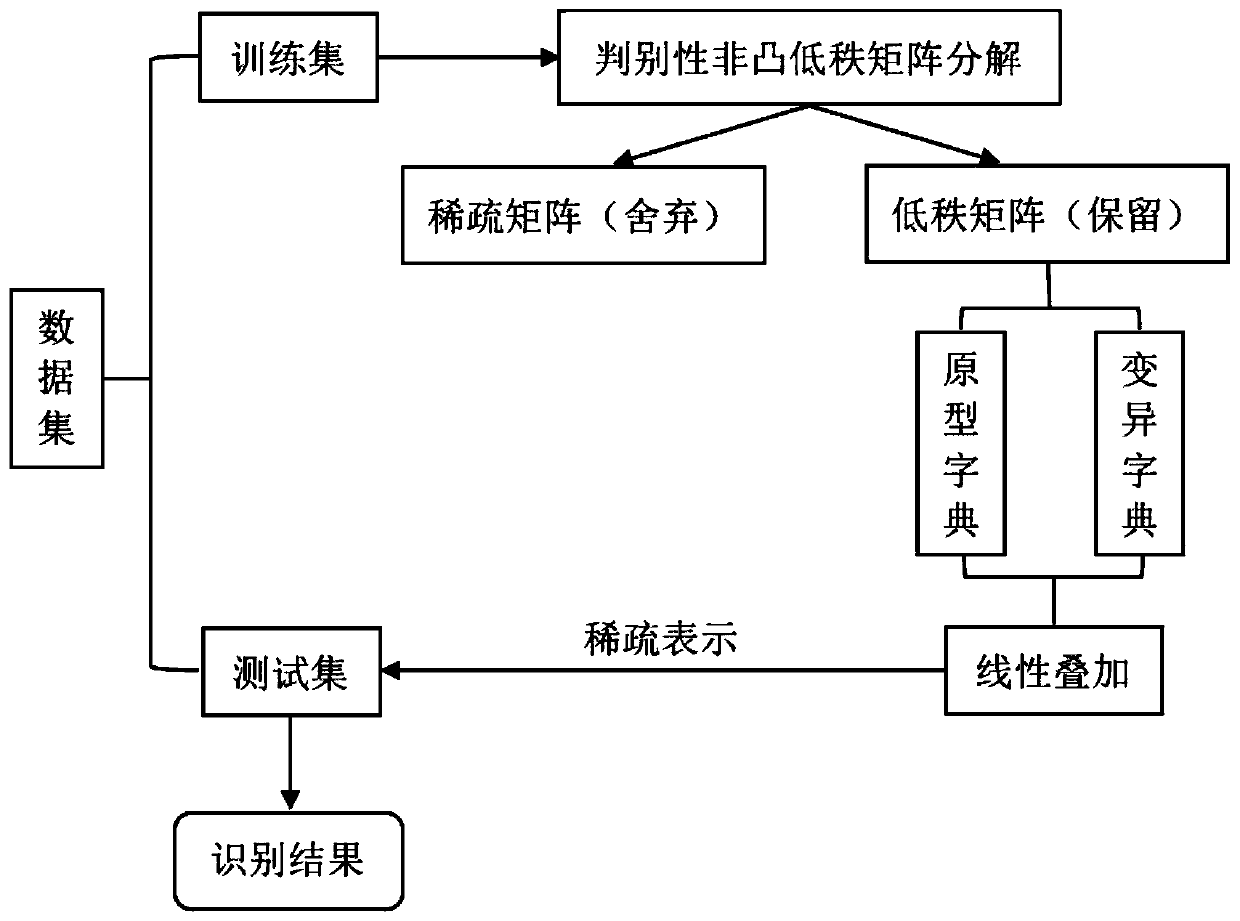
[0016] The face recognition method of superimposed linear sparse representation based on discriminative non-convex low-rank decomposition includes the following steps:
[0017] Step 1. According to the theory of low-rank matrix decomposition, replace the kernel norm with γ norm for low-rank matrix decomposition, and introduce structurally irrelevant discriminants to form discriminative non-convex low-rank decomposition;
[0018] Step 2. Use the alternating direction multiplier method to solve the discriminative non-convex low-rank decomposition, and decompose the face sample matrix into a low-rank matrix and a sparse matrix;
[0019] Step 3. The obtained low-rank matrix is decomposed into a prototype dictionary and a mutation dictionary through superposition linear representation, and then the two dictionaries are combined by linear weighting as a dictionary for testing;
[0020] Step 4. U...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com