A kind of ectomycorrhizal fungus with cr(vi) tolerance and reducing ability and its application
An ectomycorrhizal and capacity technology, applied in the field of environmental pollution control, can solve the problems of secondary pollution, incomplete removal, affecting the restoration efficiency, etc., and achieve the effect of high reduction efficiency and improvement of restoration efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1 Bacterial Colony Characteristics and Physiological and Biochemical Characteristics
[0048] Strain Isolation: Pisolithus sp.T Cr -1 (CCTCC NO: M2018087) was isolated from the fruiting body collected in Sanqingshan (28.54N118.03E) in Jiangxi Province, NCBI Genbank accession number: KY075875, and the ITS sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.1. Bacteria, colony morphology and physiological and biochemical characteristics: ectomycorrhizal fungi, non-spore-forming filamentous fungi, mycelium yellowish yellow, aerobic, plant symbiotic bacteria.
Embodiment 2
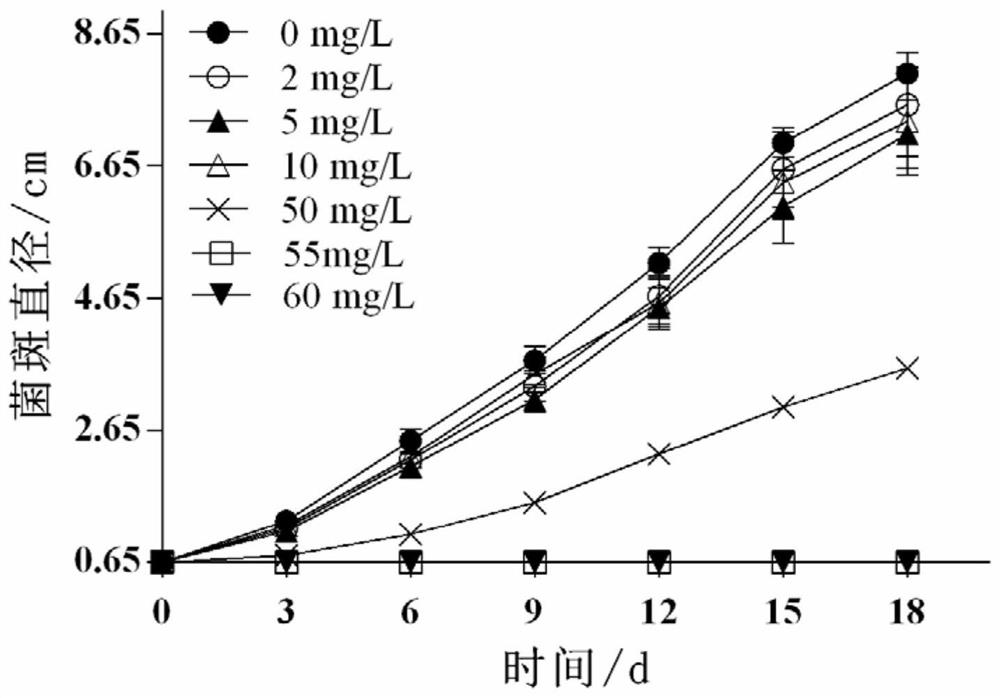
[0049] Example 2 Pisolithus sp.T Cr -1 (CCTCC NO:M2018087) Cr(VI) resistance test
[0050] Pisolithus sp.T activated in the dark at 25°C for 20 days Cr -1 (CCTCC NO: M2018087) use a 0.65cm diameter hole puncher to make a plaque along the edge and inoculate it in the center of the solid medium with a final concentration of Cr(VI) of 0, 2, 5, 10, 50, 55, 60ppm , Measure the plaque diameter every 3 days with the cross method, and finish the measurement after 18 days, and calculate its half-inhibitory concentration to Cr(VI). The experimental results can be concluded that low concentration (0-10mg / L) Cr(VI) treatment inhibits Pisolithus sp.T Cr -1 (CCTCC NO:M2018087) growth but not significantly; high concentration Cr(VI) treatment (50mg / L) significantly inhibited Pisolithussp.T Cr -1 (CCTCC NO:M2018087) growth, but still alive, 55mg / L for Cr(VI) on Pisolithus sp.T Cr -1 (CCTCC NO:M2018087) lethal final concentration, after calculation, Cr(VI) to Pisolithus sp.T Cr The half-i...
Embodiment 3
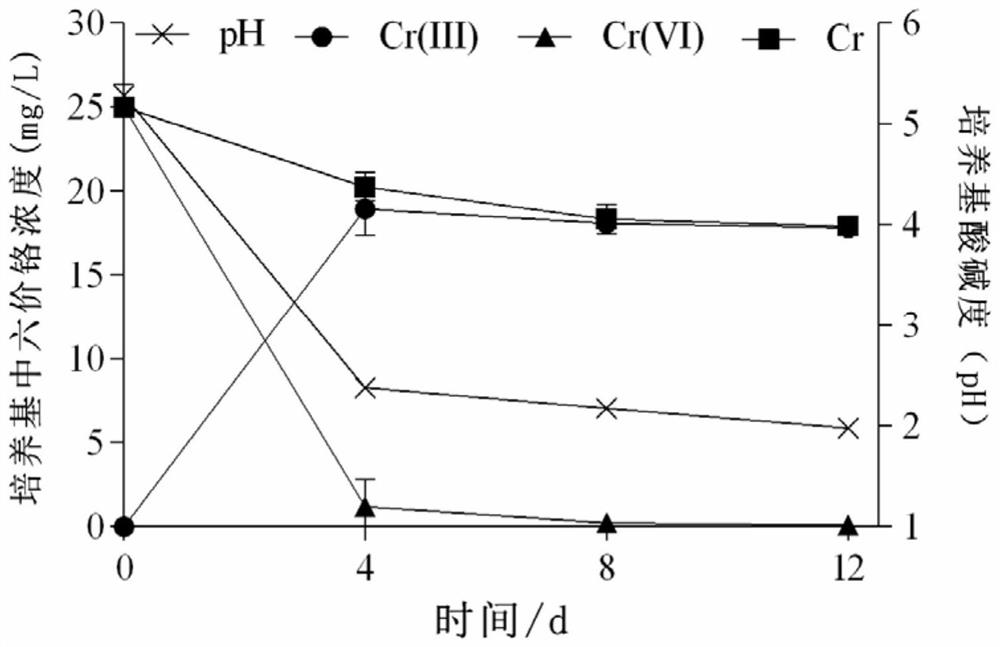
[0051] Example 3 Pisolithus sp.T Cr -1 (CCTCC NO:M2018087) Physiological Mechanism of Hexavalent Chromium Removal
[0052] The ectomycorrhizal fungus Pisolithus sp.T purely cultivated by laboratory solid Cr -1 (CCTCC NO:M2018087) to study the physiological mechanism of hexavalent chromium removal. The ectomycorrhizal fungus Pisolithus sp.T activated in the dark at 25°C for 20 days Cr -1 (CCTCC NO: M2018087) Use a hole puncher with a diameter of 0.80cm to make two plaques along the edge and inoculate it in a 150ml Erlenmeyer flask with 100ml Cr(VI) final concentration of 0,25,50ppm liquid medium, Shake at 150rpm at 25°C for 12 days in the dark, and take samples on days 0, 4, 8, and 12 to determine the contents of hexavalent chromium and total chromium in the medium. The content of hexavalent chromium was measured by diphenylcarbonyl spectrophotometry, and the removal rate of Cr(VI) in the medium was calculated, and the content of trivalent chromium was calculated by differen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com