Electrolyte heating method and device
A heating method and heating device technology, applied in the chemical industry, can solve the problems of large heat loss, unstable heating temperature, slow control speed, etc., and achieve the effects of stable electrolysis temperature, effective use of heat energy, and avoiding fluid resistance or air bubbles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
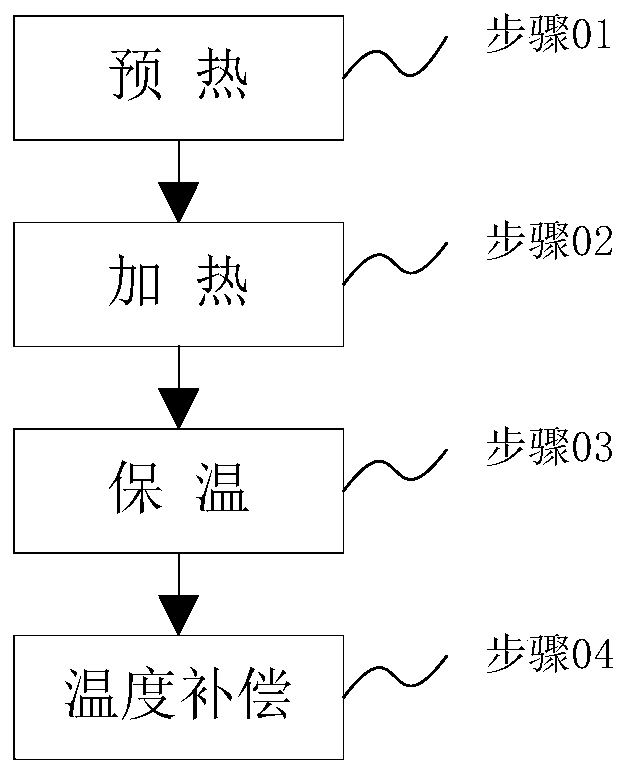
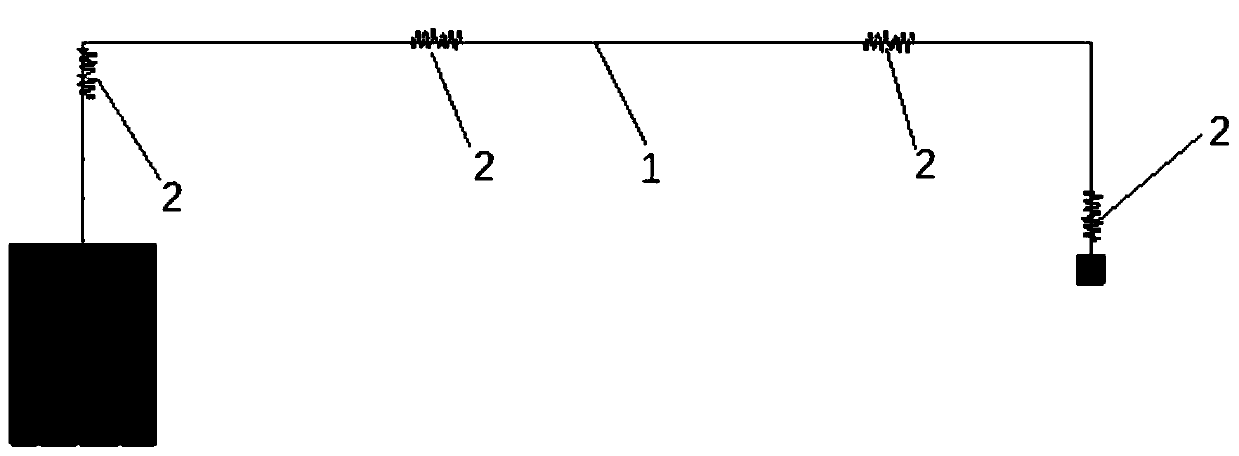
[0047] Turn on each heater in turn. Specifically, adjust the temperature to 50°C in the preheating stage, adjust the temperature to 65°C in the heating stage, adjust the temperature to 60°C in the holding stage, and adjust the temperature to 65°C in the temperature compensation stage. After the temperature is stable, turn on the electrolysis liquid transfer pump. At this time, the measured electrolyte outlet temperature was 25.3°C (that is, the electrolyte temperature when the electrolyte was output from the storage room), and the electrolyte temperature at the liquid injection port was 62.1°C. Observe that there are bubbles in the electrolyte at the liquid injection port.
example 2
[0049] Turn on each heater in turn. Specifically, adjust the temperature to 40°C in the preheating stage, adjust the temperature to 65°C in the heating stage, adjust the temperature to 60°C in the holding stage, and adjust the temperature to 65°C in the temperature compensation stage. After the temperature is stable, turn on the electrolysis liquid transfer pump. At this time, the measured electrolyte outlet temperature was 25.2°C (that is, the electrolyte temperature when the electrolyte was output from the storage room), and the electrolyte temperature at the liquid injection port was 62.4°C. It was observed that the number of bubbles in the electrolyte at the liquid injection port decreased significantly.
example 3
[0051]Turn on each heater in turn. Specifically, adjust the temperature to 35°C in the preheating stage, adjust the temperature to 60°C in the heating stage, adjust the temperature to 60°C in the holding stage, and adjust the temperature to 60°C in the temperature compensation stage. After the temperature is stable, turn on the electrolysis liquid transfer pump. At this time, the measured electrolyte outlet temperature was 25.2°C (that is, the electrolyte temperature when the electrolyte was output from the storage room), and the electrolyte temperature at the liquid injection port was 59.4°C. It was observed that the number of bubbles in the electrolyte at the liquid injection port was significantly reduced. By adjusting the difference between the overall temperature and the initial temperature, there is obviously no air bubbles at the liquid injection port.
[0052] From the above three examples, it can be seen that by adjusting the difference between the temperature in the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com