Calculation method of GM-APD lidar echo energy based on improved core brdf model
A technology of lidar and calculation method, applied in radio wave measurement systems, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of not considering the daytime background light scattering model, poor guidance of daytime target detection strategies, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
[0053] The present invention provides a kind of Gm-APD lidar echo energy calculation method based on the BRDF model of improved core, comprising the following steps:
[0054] Step 1: Establish a background light model to obtain the background light. When the scattered light in the hemispherical space is mixed with the incident light intensity, a BRDF model of the background light is established;
[0055] Step 2: According to the actual reflection mechanism of the target, establish a BRDF model corresponding to the laser;
[0056] Step 3: Improve the existing BRDF model, convert the BRDF model into a time function within the lidar gating range, and use the background light equivalent intensity coefficient to establish a laser-background noise relationship function;
[0057] Step 4: Use the background equivalent intensity coefficient to establish a relationship between the laser and the background noise, so that the expression of the lidar equation is more perfect. The lidar equ...
specific Embodiment 2
[0060] 1. Theoretical model of background light
[0061] In the application of lidar, the background light is considered to be constant in theory. In fact, the background light is closely related to the sun position, background environment, target attitude, etc. There are many sources of background light in the actual scene, but it can be simplified into two parts. See formula (1):
[0062] L=L dir +L diff (1)
[0063] In the formula, L is the background light, Ldir is the sunlight directly reflected by the target, and then transmitted through the atmosphere and received by the detector, and Ldiff is the light intensity directly received by the detector after the diffuse scattered light of the atmosphere is reflected by the target .
[0064] When the diffuse scattered light in the hemispherical space is mixed in the entire incident light intensity, the BRDF model of the background light can be expressed as:
[0065]
[0066] In the formula, θ s is the zenith angle of...
specific Embodiment 3
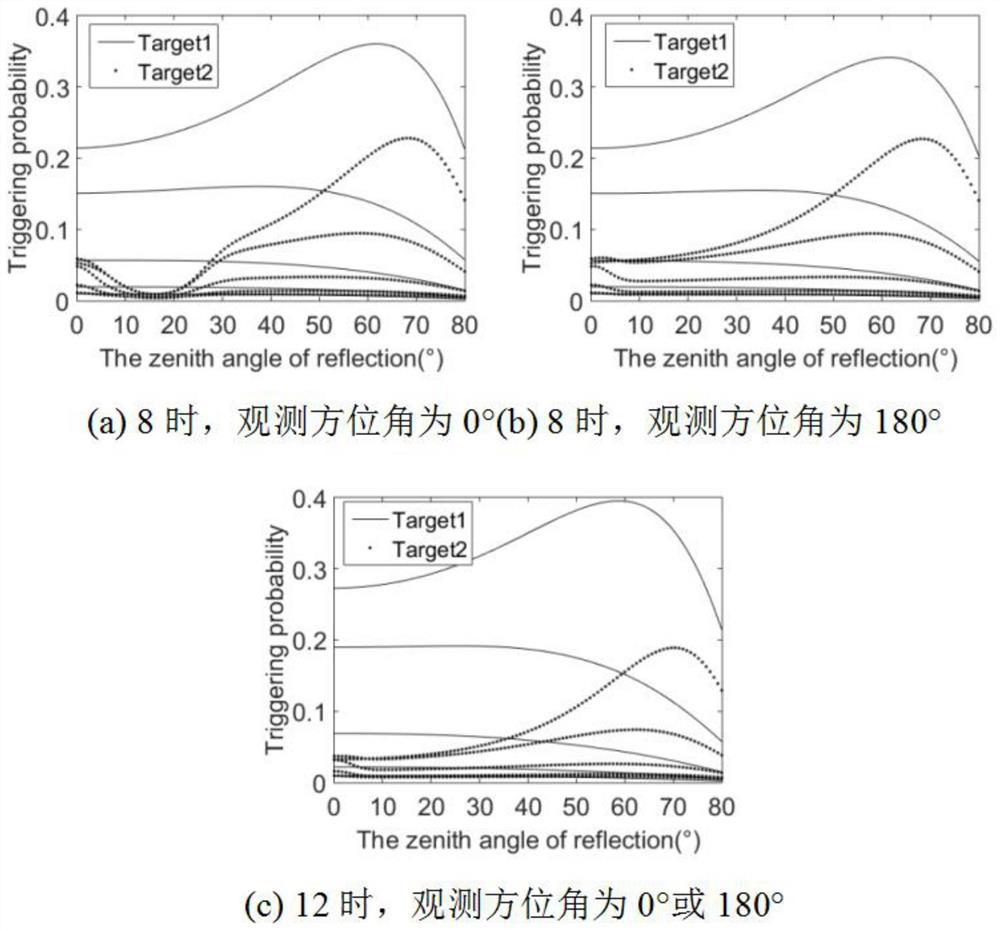
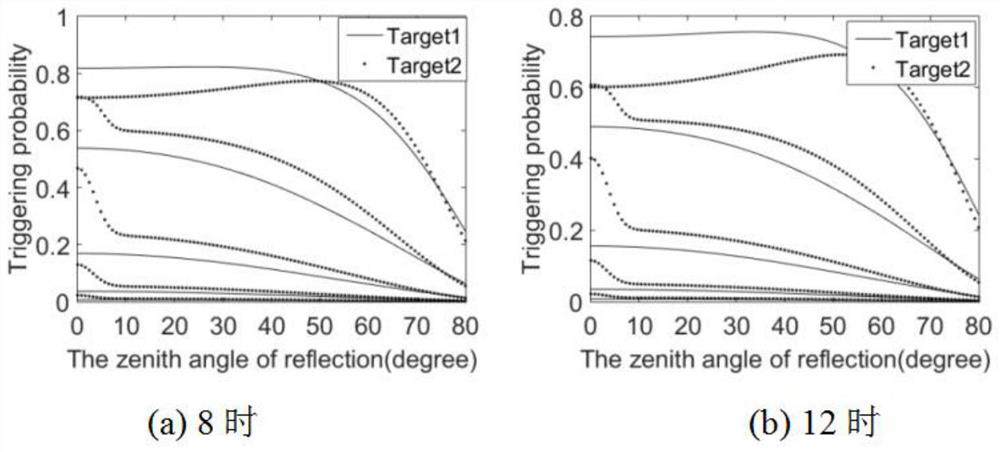
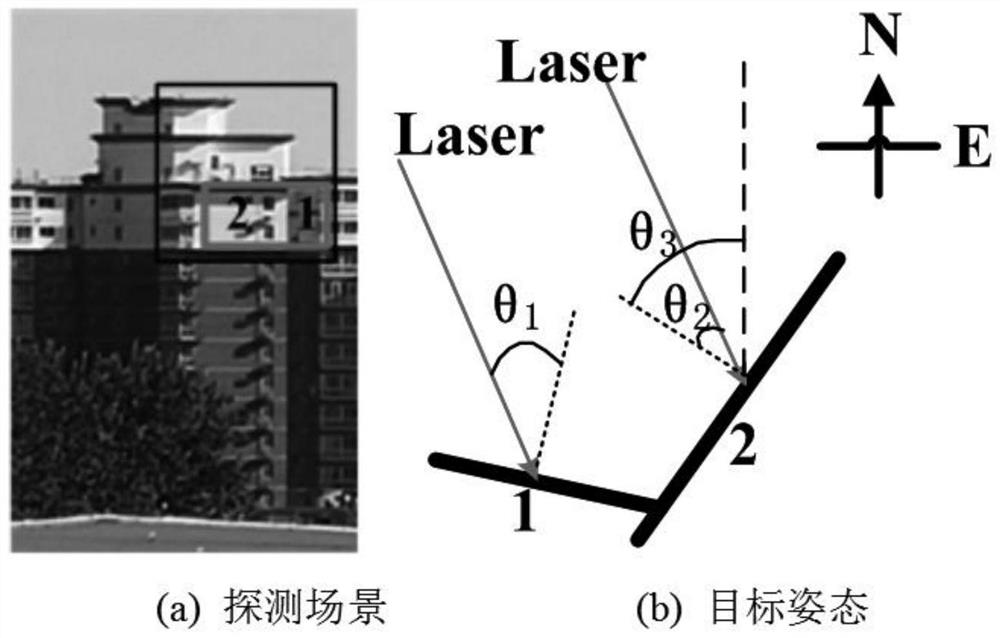
[0091] The trigger characteristics of a single pixel of area array imaging lidar are studied, assuming that the target corresponding to the pixel is a planar structure. Parameters of the lidar system: η 1 = η 2=0.9, receiving aperture D=80mm, area array Gm-APD resolution of 128×128, detector duty cycle of 0.1, laser single pulse emission energy of 1mJ, single photon detection probability of 15%, laser wavelength of 1.06μm, The laser radar filter bandwidth is 10nm, the laser emitting and receiving field of view is 2°, the atmospheric visibility is 20km, and the laser spots are evenly distributed. The length of the gate is 1 μs, the number of Δτ in the gate is 1000, and the echo pulse occupies at most one time interval, and the echo pulse is in the middle of the gate.
[0092] figure 1 It shows the change of the echo trigger probability with the detection angle when the normal direction of the target observation surface is due south and the target is at different distances at...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com