Robust slam method for indoor robots combined with environmental semantics
An indoor robot and semantic technology, applied in the field of computer vision, can solve problems such as cumulative errors, lack of texture features, damage to the positioning accuracy of visual odometers, etc., and achieve the effect of improving robustness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] It should be noted that, in the case of no conflict, the embodiments of the present invention and the features in the embodiments can be combined with each other.
[0036] The present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and examples.
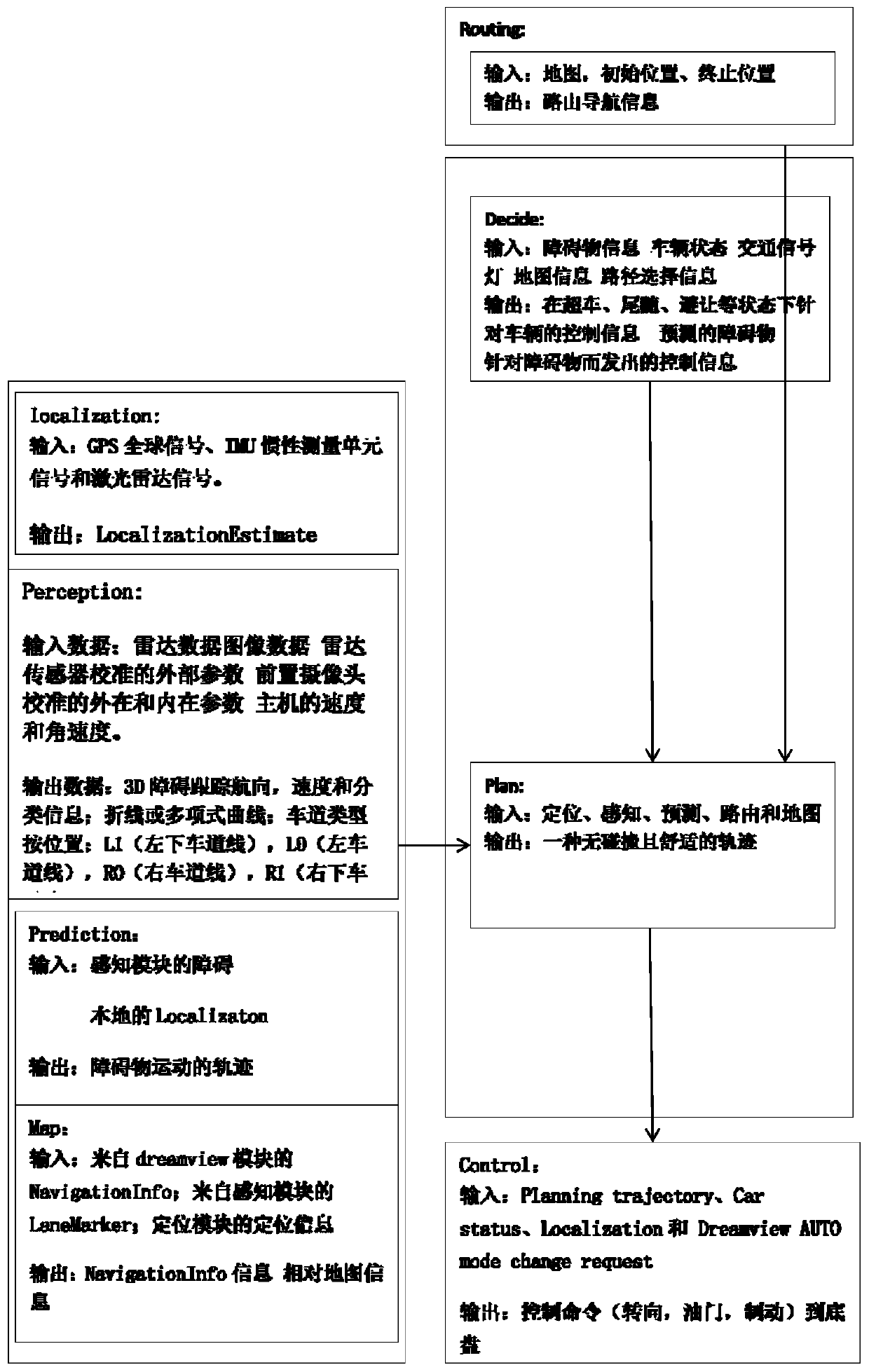
[0037] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a robust slam method for indoor robots combined with environmental semantics, comprising the following steps:
[0038] 1. Positioning of indoor robots: Use GPS global signals, IMU inertial measurement unit signals and lidar signals as original input signals, and use prior input and observation correction methods to make indoor robot positioning more accurate and robust.
[0039] In order to eliminate the positioning error caused when the robot turns at a non-right angle at the indoor corner, and this positioning error is accumulated, the error will be amplified more and more in the later road section, the indoor robot robu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com