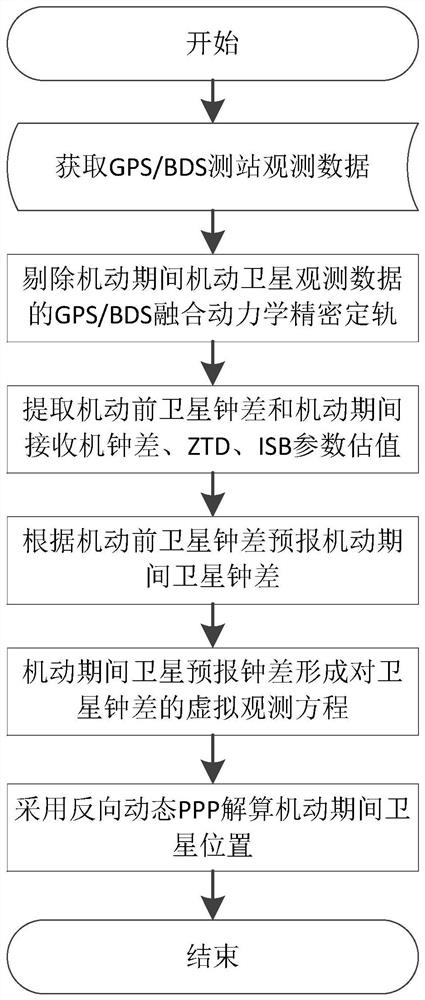
A GNSS Mobile Satellite Orbit Determination Method Constrained by Additional Clock Difference Model
A mobile satellite and mobile technology, which is applied in the field of global navigation satellite systems, can solve the problems of limited accuracy, lower orbital accuracy, and the inability of mobile satellite data to be used for positioning services, so as to improve the accuracy of orbit determination and weaken the correlation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
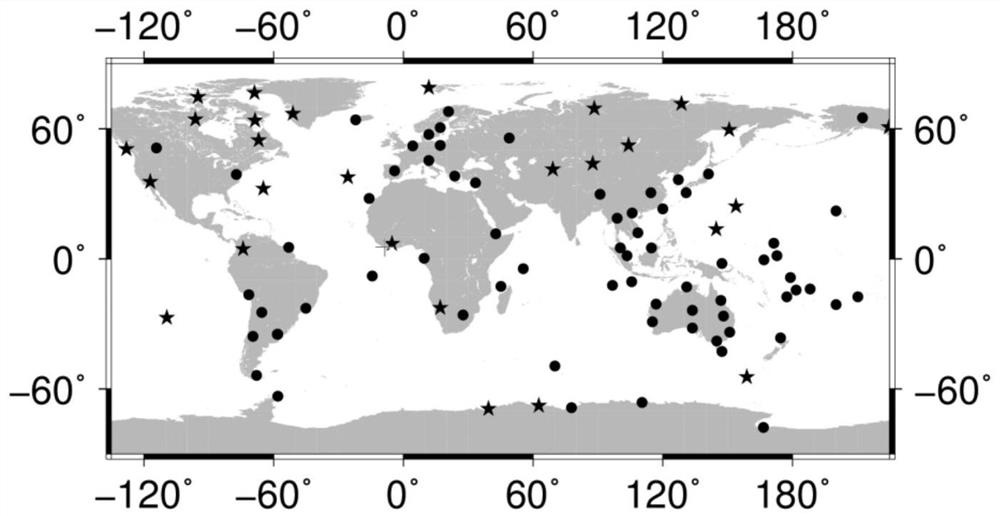
[0054] Example 1: Since the real orbit of the satellite during maneuvering cannot be obtained, in order to evaluate the orbit determination accuracy of the method of the present invention, at first the satellite under normal conditions is subjected to orbit determination using the method proposed by the present invention, and the precise orbit determined by dynamic orbit determination Comparisons were made to assess the accuracy of the method of the invention. The data of 30 days from May 1, 2017 to June 1, 2017 is processed, and the station distribution is as follows image 3 shown. The orbit determination arc section is set to 26 hours. First, the dynamic orbit determination method is used to determine the precise orbit of the satellite as a reference orbit for accuracy assessment; then, assuming that the satellite orbit maneuvers in the last 2 hours, the method of additional satellite clock difference model constraints of the present invention is adopted. Perform orbit det...
example 2
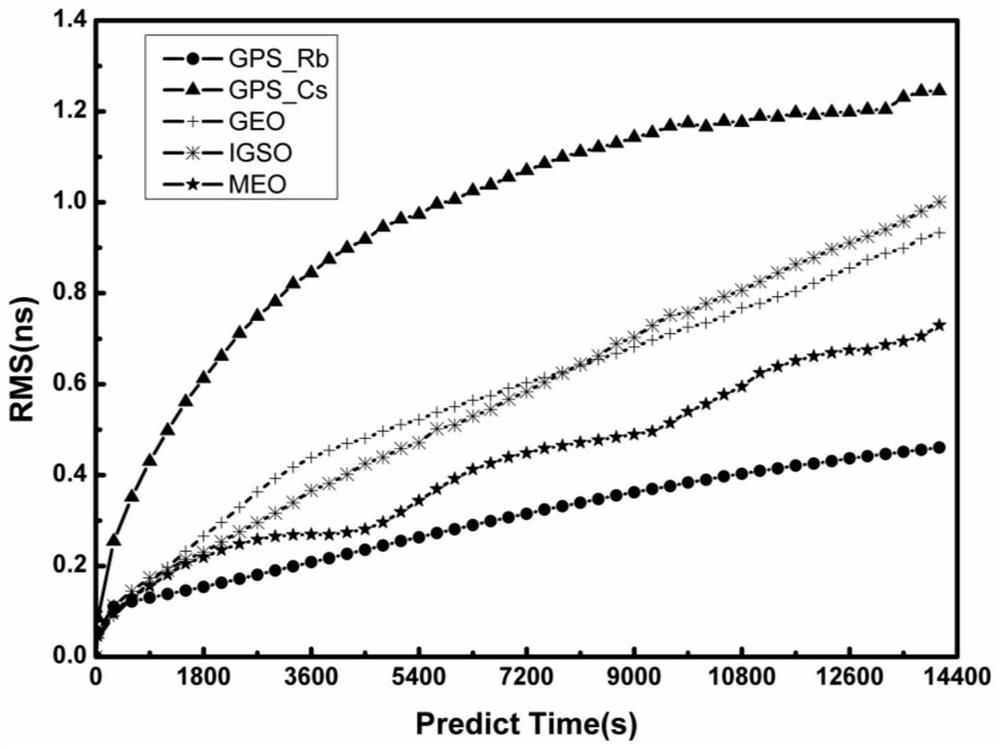
[0055] Example 2: In order to test the orbit determination effect of the method of the present invention on real mobile satellites, take four real mobile satellites in May 2017 as an example to carry out orbit determination verification during maneuvering, including two GPS satellites G22, G12 and two Beidou GEO Satellites C02 and C04, adopt the method of the present invention to carry out orbit determination calculation on the 4-hour arc section including the entire orbital maneuvering process, and compare the orbit determination results of the reverse dynamic precise single-point positioning with additional clock error model constraints with those based on the power before and after the maneuvering. Comparing the forward and backward integral orbits obtained by scientific orbit determination, the orbital differences in the radial, normal, and tangential directions are obtained, as shown in Figure 5 As shown, R_f, C_f and A_f are the differences between the satellite orbit an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com